
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Features of trinistor regulators. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
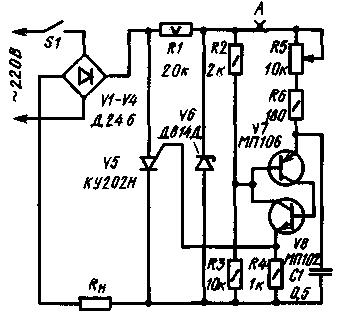
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Regulators of current, voltage, power Many radio amateurs, while operating home-made or store-bought trinistor regulators, have found that sometimes these regulators do not work clearly, and low-voltage lighting devices used in conjunction with them quickly fail. This article tells about the features of the operation of a trinistor AC power controller, leading to such phenomena, and some possible ways to improve the reliability of devices with such controllers. The magazine "Radio" pays much attention to trinistor AC power regulators (see, for example, a selection of articles "Thyristor voltage regulators" .- "Radio", 1975, No. 10, pp. 47-49). These devices, which have become very popular in recent years, allow you to change the effective value of the voltage at the load from a few volts to almost the mains voltage. It would seem that. with the help of such a regulator, a wide variety of low-voltage devices can be powered from the network. Is it so? To answer this question, let us briefly consider the operation of a full-wave trinistor power controller, one of the most typical circuits of which is shown in Fig. 1 (it is borrowed with minor changes from the above source). The voltage at the load of such a regulator is a truncated sinusoid in shape. For example. at angles of inclusion of the trinistor V5 exceeding 90 °, this voltage has the form conventionally shown in fig. 2 with a solid line. The maximum switching angle of the trinistor in the controller under consideration is 172°. Voltmeter of the magnetoelectric system connected to the load R11 (Fig. 1). shows a voltage of 6 V.
The amplitude value of the voltage at the load Un.vf[ at this switching angle is easy to determine: Un.max=Umax*sin (180°- 172°)=220*1.41* 0,139=43V. where Umax is the peak value of the mains voltage. Measuring the voltage Un.max with an electronic oscilloscope gives the same result. Probably. not every load, calculated nor the nominal voltage of 6 V, can withstand such significant, albeit short-term, for a long time. periodic surges. For example, the filament of an ordinary MN-38 incandescent lamp (for a voltage of 6,3 V, the current consumption is 0,22 A), when supplied with a voltage of this form, often burns out after a few seconds. The considered fact is not the only reason that limits the possibility of using a trinistor regulator to power a low-voltage load. The second reason is that at any angle of switching on the trinistor set by the resistor R5 (see diagram), the voltage at the load can become equal to the full rated voltage of the mains for a short time. This phenomenon was detected using an electronic oscilloscope at the moments when the regulator was disconnected from the mains. The switch was an ordinary plug. This phenomenon can be explained as follows. Due to irregularities on the surface of the plug pins, the disconnection of the regulator from the mains does not happen instantly in most cases, but is accompanied by alternating openings and closings of the supply circuit (as in the case of "contact bounce"). At the first opening of the circuit, the voltage at the base of the transistor V7 becomes zero and the analog of the unijunction transistor V7V8 opens. Capacitor C1 is discharged and an opening current pulse flows through the control junction of the trinistor V'5. If now the supply circuit is again closed, then the full voltage of the network through the opened trinstore will be applied to the load until the end of the half-cycle. During experiments with the incandescent lamp regulator in question. for example, those rated for a nominal voltage of 36 V. usually burned out already at the first or second turn off of the regulator, despite the fact that the resistor R5 set the maximum switching angle of the trinistor and in the steady state the lamps glowed for an arbitrarily long time. Observations using an oscilloscope over the process of opening contacts in switches T1, T2, TP2-1 and others showed that this opening occurs in them practically without "bounce". When such switches were used in the regulator, incandescent lamps did not burn out under the same conditions even when the on-off cycle was repeated many times. This confirms the correctness of the assumption about the causes of the observed phenomenon. Is there any way to eliminate the possibility of excessive voltage on the low voltage load even if there is a "bounce" of the contacts of the switch S1? It is likely that a number of such methods can be found. One of them, for example, is to use an additional switch installed at point A (see diagram). First, turn on the SI switch. and then close the circuit at point A. You need to turn off the regulator in the reverse order. This method has been tested in practice and showed good results. Its effectiveness is also a confirmation of the correctness of the assumption about the causes of the considered phenomenon.
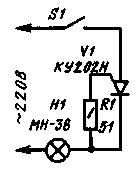
It should be noted, however, that even the use of additional switches in regulators does not completely eliminate the disadvantage described above. Indeed, the cause of the "bounce" can also be insufficiently tight contact of the plug in the socket and short-term power outages in the mains. In addition, it must be added that the indicated phenomenon was reproduced on the regulator, the circuit of which is shown in Fig. 1. Other regulators may have other features, but, probably, in all cases, the described phenomenon will be associated with the operation of the control unit of the key element, Sometimes one hears the opinion that the described cases of failure of low-voltage incandescent lamps powered by a trinistor regulator. due to the spontaneous switching on of the trinistor due to the high rate of rise of the anode voltage dU/dt when the regulator is connected to the mains, if, for example, this happens at a time when the mains voltage is close to the maximum. One cannot agree with such a statement. For the KU201 and KU202 series trinistors most common in amateur radio practice, the anode voltage rise rate is not standardized. This means that the said trinistors allow almost any rate of rise of the anode voltage, unless its amplitude value exceeds the allowable maximum forward voltage on the closed trinistor (Upr.scr.max). And, therefore, a serviceable trinistor, KU202N, for example, in the absence of current in the control electrode circuit, should not open when it is connected to an alternating current network with a voltage of 220 V, no matter at what point in the period such a connection occurs. This is easy to check, e.g. having assembled a simple device according to the scheme shown in Fig. 3. The low-voltage incandescent lamp H1 will not glow and remain intact after any number of switching on by the SI switch (if the trinistor V1 is good, of course).
All of the above allows us to draw some conclusions. First, the shape of the output voltage of AC-powered SCR regulators is a factor that limits the ability of such regulators to power low-voltage loads. Secondly, in trinistor controllers, the possibility of the appearance of voltage pulses on the load, corresponding to small switching angles of trinistors, is not ruled out, even if the elements of the time setting value set the switching on angle of the trinistor to the maximum. The conclusions drawn lead to the conclusion that reliable operation of a device with a trinistor power controller can only be guaranteed if the supply voltage does not exceed the rated load supply voltage, i.e. when the trinistor controller is used only to reduce the load voltage. Author: V. Cherny, Moscow; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ The smartphone will replace all remote controls ▪ Sleep protects against colds ▪ The warmer it gets in cities, the less carbon dioxide the trees absorb.
▪ Modeling section of the site. Selection of articles ▪ article A plot worthy of Aivazovsky's brush. Popular expression ▪ article Why did the rebellious Parisians take the Bastille in 1789? Detailed answer ▪ Polyspasta article. Travel Tips
Comments on the article: Dumov I read it with great pleasure. [up] It would be interesting to know your opinion about the triac controller for inductive load.
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: