 Free technical library
Free technical library
Microphone with a narrow polar pattern. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Audio equipment
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
A narrow-beam microphone can be used when recording and amplifying speech in conditions of high noise, as well as recording sounds from distant sources, such as birdsong. The directivity of the microphone significantly increases the signal-to-noise ratio at the input of the bass amplifier.
Schematically, the device of such a microphone is shown in Fig.1. Its main detail is an electromagnetic primer (3) placed in a cylindrical case (1). The capsule is filled with epoxy resin on both sides. The side of the capsule facing the open opening of the case has a small "sensing window" that provides sound vibrations with access to the membrane. With the help of three stretch marks, the capsule is suspended on a wire ring (4), which is located in the back of the case. To reduce reflection from the walls, the inside of the case is covered with a layer of felt or felt (2) about 12 mm thick.
The microphone is connected to the input of the preamplifier, one of the possible circuits of which is shown in fig. 2. Reducing the inherent noise of the first stage is achieved by choosing a low-noise transistor T1 and using it at low collector current. The second stage, assembled on a transistor T2 according to a common collector circuit, allows you to match the output of the device with a power amplifier.
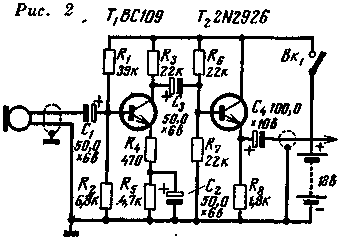
Preamp circuit
A DEMSH capsule can be used as a microphone capsule. For the first stage, you can take the transistor MP111A, for the second - MP38A.
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Audio equipment.
See other articles Section Audio equipment.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Poplars will learn to decompose poisons
08.01.2018
Sharon Doty, a plant microbiologist at the University of Washington, USA, and her colleagues were able to isolate a very effective strain of detoxifying bacteria from a particular poplar (Populus nigra) and introduce it to other trees. This enhanced the poplars' natural ability to degrade the carcinogen trichlorethylene (TCE), an industrial solvent that seeps into groundwater near landfills. Thus, modified trees can be planted in areas with heavily polluted groundwater, where they will serve as an effective and inexpensive means of treating these waters.
One of Doughty's students collected Enterobacter strain PDN3 microbes from Wisconsin poplar shavings. The researchers soaked their hybrid seedlings with a suspension of these bacteria and planted them next to untreated seedlings at three Superfund sites near San Francisco, heavily contaminated with trichlorethylene and selected for cleaning by the US government.
Three years later, the positive effect became apparent. The soil around the "grafted" poplars contained 50% more chloride ions, harmless residues of the decomposition of TCE molecules, than the soil around the untreated poplars. In addition, treated trees had 30% thicker trunks than untreated trees, suggesting healthier growth. In general, the concentration of TCE at the landing site fell below the maximum limit for drinking water set by the Environmental Protection Agency.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ ferromagnetic semiconductor
▪ Smartphones charge faster and understand voice
▪ Circadian cycle gene influences lifespan
▪ Miniature internal combustion engine
▪ Windows 8 preview
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the website Experiments in Physics. Selection of articles
▪ Article All or Nothing. Popular expression
▪ article How did a Jewish girl win an Aryan children photo contest? Detailed answer
▪ Article Anamyrta cocculus. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Timer for spot welding machine. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Crawler coil. physical experiment
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: