 Free technical library
Free technical library
Medical transistor thermometer. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Electronics in medicine
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
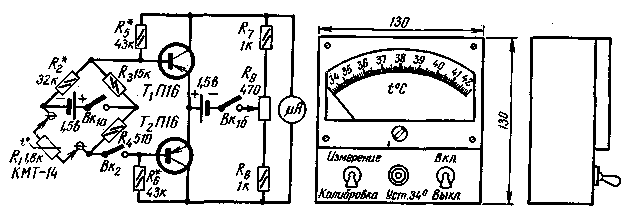
This device allows you to measure the patient's temperature in no more than 5 seconds with an error of ± 0,05 ° C. The measurement limits are from 34 to 42 ° C. The device is powered by two FMC-type elements, consuming a current of not more than 1 mA.
The device (see diagram) is a bridge, one of the arms of which includes a sensor - the KMT-14 thermistor with a DC amplifier based on two transistors T1 and T2 of the P13-P16 type. The indicator is a measuring device of the M-24 type for a current of 200 μA, the scale of which is calibrated in degrees Celsius.
(click to enlarge)
When in contact with the human body, the resistance of the thermistor changes, the balance of the bridge is disturbed, and the current flowing along the diagonal of the bridge is amplified by transistors 20-50 times and deflects the arrow of the device. The shift in the range of the measured temperature is achieved by selecting the resistor R2, and expanding or narrowing this range - by selecting the resistors R5 and R6.
Switches Vk 1a and Vk 1b (tumbler) are used to simultaneously turn on both batteries. Calibration of the device to the beginning of the scale (at 34 ° C) is carried out by the potentiometer R9 with the contacts of the switch Vk2 open, and the patient's temperature is measured with the contacts Vk2 closed.
All parts and batteries of the device are placed in a duralumin case with dimensions of 130x130x35 mm.
The thermistor sensor is connected to the device using a two-wire cord.
The instrument is calibrated as follows: the thermistor is placed in a thermostat with water stirred by an impeller. The temperature of the water is controlled by a laboratory thermometer, and the resistance of the thermistor in the desired temperature range is fixed by a DC bridge of the MO-62 type. Then, instead of a thermistor, the same bridge is included in the bridge arm (as a resistance box) and resistors R2, R5 and R6, set the desired range of measured temperatures.
Author: A. Manzyuk; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Electronics in medicine.
See other articles Section Electronics in medicine.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Communication with sensors through the wall
27.04.2011
A system has been created for communicating with sensors inside a closed vessel without any wires. It is not easy to look out of a submarine - you need to drill a hole in the hull and lead a wire through it to a sensor located outside. This solution is unsuccessful, because the hole must then be sealed, and it weakens the structure.
A system created by Renssellaer Polytechnic University student Tristan Lauri, who received a student award of 30 US dollars for his work, allows you to refuse communication by wire. It uses ultrasound to communicate with an external sensor, as well as to power it with energy. The basis of the system is piezoelectric elements capable of converting an audio signal into electricity and vice versa. With their help, Lauri transmits up to 6 watts of power and 50 MB of data per second through a 12,4 cm thick steel wall.
This invention will help not only the military. In this way, it is possible to communicate with sensors (and, apparently, give commands to manipulators) in any hermetically sealed vessel or, conversely, from inside the vessel. Such a "vessel" can be a nuclear power plant reactor, a chemical reactor, a pipeline, a tank, a spaceship.
Because it is powered externally, the sensor does not need any batteries and can operate for many years without human intervention.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Companion on a string
▪ Safe transportation of Martian soil
▪ 32Gbps transceiver from Altera
▪ Intel Haswell processors with DirectX 11.1 support
▪ Mobileye EyeQ4 single-chip system for semi-autonomous vehicles
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Clocks, timers, relays, load switches. Article selection
▪ Article Fellow travelers. Popular expression
▪ article What is the healthiest fat? Detailed answer
▪ article Transportation of students by road
▪ article Milling machine. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article High frequency VOX. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: