
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Concert strobe. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
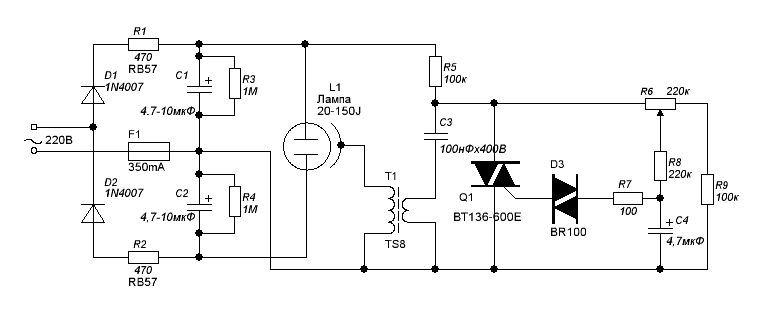
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Color and music settings The pulse transformer selected for mounting on this board allows the use of 150 J and even 250 J lamps. Description of the scheme The electrical circuit diagram of the stroboscope is shown in the figure. voltage doubler The voltage doubler makes it possible to obtain a high voltage, approximately 600.V, which is applied between the anode and cathode of the lamp. The role of the voltage doubler is performed by diodes D1 and D2. During the positive half-cycle of the mains voltage, capacitor C1 is charged to the maximum value of the mains voltage (approximately 310 V), while diode D2 is closed and prevents the supply of voltage to the capacitor C2. In the next half cycle of the mains voltage, the polarity of the voltage is reversed, and now the diode D1 is closed, while the diode D2 begins to pass current, which leads to the charge of the capacitor C2. In this case, a high voltage of approximately 1 V is applied to the flash lamp L600, which ionizes the gaseous medium of the tube without causing a glow. The glow will cause a high voltage pulse to be applied to the external trigger electrode. The brightness of the lamp flash depends on the amount of energy stored in the capacitors C1 and C2 and is a function of the voltage U at the terminals of the capacitor and its capacitance C, therefore: E = 0,5 x C x U2. The possibilities of using a flash lamp are limited by the maximum power Pmax. In this case, the maximum capacitance Cmax of capacitors C1 and C2 is determined as follows: Cmax=(1/3102)x(Pmax/Fmax) where Fmax is the maximum frequency of capacitor discharge through a flash lamp. At the time of the flash, the resistance of the lamp between the anode and cathode is very small. And if the lamp starts at the moment of the peak value of the mains voltage, the resistors R1 and R2 limit the power transmitted to the lamp. This protection facilitates the operation of the lamp and extends its life. Relaxation generator The relaxation generator sets the frequency of flashes of the lamp. Its basis is a symmetrical dinistor. Indeed, the symmetrical dinistor D3 is closed until the voltage at its terminals reaches a threshold, usually equal to 32 V. At this time, it behaves like an open switch. While the symmetrical dinistor is closed, capacitor C4 is charged through resistor R7 and potentiometer P1. Potentiometer P1 allows you to adjust the charge current of the capacitor C4 and, thus, the oscillation frequency of the relaxation oscillator. The limiting resistor R6 determines the lower frequency limit. When the voltage at the contacts of the capacitor C4 reaches the switching voltage of the symmetrical dinistor, it goes into a conducting state. The capacitor C4 is discharged before the dinistor is locked. Then the next cycle begins with a new charge of the capacitor C4. Ignition scheme So, the capacitor C4 is periodically discharged through the triac control electrode circuit, which in this case becomes conductive. When the triac is closed, the discharge current of the capacitor C3 flows through the primary winding of the pulse transformer TR1. When triac Q1 is closed, capacitor C3 is charged to approximately 310V through resistor R5 and primary winding TR1. The almost instantaneous discharge of capacitor C3 causes a current pulse to appear in the primary winding of TR1. Taking into account the transformation ratio, a very high voltage (approximately 6 kV) is applied to the starting electrode of the flash lamp. The gas contained in the lamp at this moment becomes conductive, the capacitors C1 and C2 are discharged, and the lamp emits a bright flash. The luminous flux is proportional to the capacitance of the capacitors C1 and C2 and the power of the lamp. Production In general, the fabrication is quite simple, but care must be taken during testing, since the circuit is directly related to the mains voltage. In addition, high voltages are generated on the board. So, before turning on the power with double attention, you should check the correct location of the polar radio elements, in particular - and mainly - two diodes D1 and D2, as well as two large electrolytic capacitors C1 and C2. Resistors R1 and R2 must be raised a few millimeters above the board to facilitate heat dissipation, so a secure mounting of these radio elements is necessary, as shown in the figure.
The first bend of the leads allows you to install a resistor on the printed circuit board, and the second bend along the tracks fixes the leads and increases the soldering area. The capacitance value of the two capacitors C1 and C2 depends on the desired brightness of the flash and the lamp used. A 150J lamp can produce a bright flash with 10µF/350V capacitors at a strobe frequency of 7Hz. In the case of a 40 J lamp, this capacitance can be halved. The capacitance of the capacitor C3 is determined by the parameters of the pulse transformer TR1. Given that the primary of a TS 8 type transformer can withstand a maximum energy of 4 J, a 100nF/400V capacitor is fine and this capacitance value should not be increased as the transformer primary could be damaged. The flash lamp must be handled with care. It is not recommended to directly touch the lamp with your fingers. The lamp is connected as close to the board as possible to reduce losses. It is advisable not to bend the lamp leads; if you still have to do this, then bend gently with pliers. The layout of the printed circuit board of the stroboscope and the placement of radio components on it are shown in the figure.
A light reflector will help direct maximum light to the dancers. The reflector can be made from a thin strip of aluminum or cardboard to which a sheet of aluminum foil must be glued. You can also install a strobe inside an unnecessary car headlight. If you want to change the flash frequency, it is better to turn the potentiometer knob towards the board than towards the lamp. Practical advice 1. To prolong the life of the flash lamp, do not use the strobe for too long.
Publication: radiokot.ru, cxem.net
Energy from space for Starship
08.05.2024 New method for creating powerful batteries
08.05.2024 Alcohol content of warm beer
07.05.2024
▪ Innovative lidar Velodyne VLS-128 ▪ HP EliteBook Folio Notebook PC ▪ AVerTV Mobile 510 - Android TV tuner that works without internet
▪ site section Power supply. Article selection ▪ article There is no stupidity bitterness, like stupidity! Popular expression ▪ article What is glue made of? Detailed answer ▪ article Charger. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: