Voltage converter for powering the varicap. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The use of varicaps in low-voltage transistor equipment is often limited due to the need to use sources of increased stabilized voltage (about 40 V) to power them. A simple voltage stabilizer for a varicap (see figure) provides an output regulated stabilized voltage of 0..39 V. The device consumes a current of about 60 mA, the maximum load current is 12 mA.
On the logic elements D1.1-D1.3 of the D1 chip, a rectangular pulse generator with a repetition rate of about 90 kHz is assembled. A buffer cascade is made on element D1.4. Transistor V1 operates in key mode on an inductive load L1. At the moment the key is closed, self-induction EMF pulses appear on the collector of the transistor, which are rectified by the V2 diode and smoothed out by the capacitor C2.
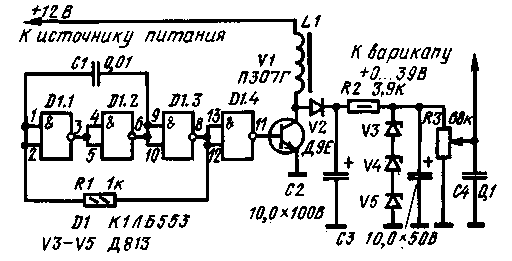
The DC voltage is stabilized by the parametric stabilizer R2V3V4V5 and is supplied to the varicap through a voltage divider on a variable resistor R3. Capacitor C4 protects the varicap from the penetration of high frequency voltage into its power supply circuit.
Coil L1 is wound on two K10X6X3 rings of 600NN ferrite folded together. The winding consists of 200 turns of PEV-2 0,1 wire. The microcircuit is powered directly from a 12 V voltage source through a 270 Ohm limiting resistor (not shown in the diagram).
The converter must be carefully shielded and decoupled from the supply circuits, as it is a source of interference in a wide frequency range (up to several megahertz).
Editorial note. To protect the transistor and the microcircuit from possible overloads, a current-limiting resistor with a resistance of about 1 kOhm and a power of 0,25 W should be included in the base circuit of the transistor.
Author: S. Rotar, Chisinau; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters.
See other articles Section Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Stress changes the brain
20.05.2023
Working with mice, the researchers found that a single stressful event triggered rapid and lasting changes in brain cells that cleared the brain of debris.
Research by Si-Kwong Jun Liu, MD, professor of cell biology and anatomy at the Center for Health Sciences at Louisiana State University New Orleans, has shown how stress changes brain structure.
It is noted that based on the results, a potential therapeutic target for prevention and treatment can be identified.
Working with mice, Liu and her research team found that a single stressful event triggered rapid and lasting changes in astrocytes, the cells in the brain that clear away debris. The stressful episode caused the tips of astrocytes to move away from synapses, through which information is transmitted from one cell to another.
The team also uncovered a mechanism leading to communication disruption. They found that during a stressful event, the hormone norepinephrine inhibits the molecular pathway that normally produces the GluA1 protein, without which nerve cells and astrocytes cannot communicate with each other.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ US military learn to rescue wounded soldiers
▪ GIS is useful for politicians
▪ Thyroid in jelly
▪ Cases with a fingerprint sensor for Android devices
▪ Potato bacterium antibiotic
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Electricity for beginners. Article selection
▪ article by Julian Tuwim. Famous aphorisms
▪ article What were boomerangs used for? Detailed answer
▪ article Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for working conditions
▪ article Knots of amateur radio equipment. Generators, heterodynes. Directory
▪ article AM FM path on the SHA1238 chip. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: