
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Water purifier. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
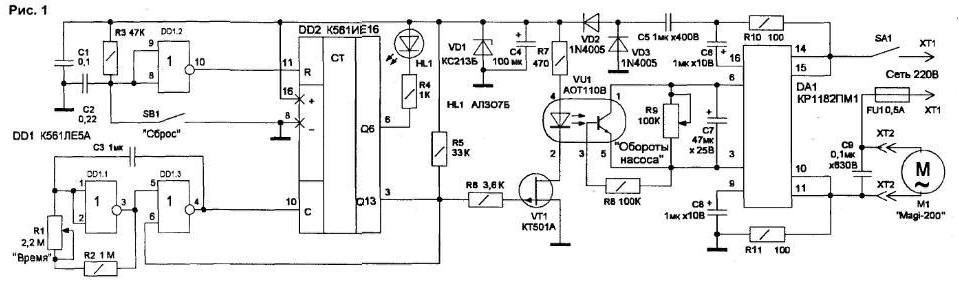
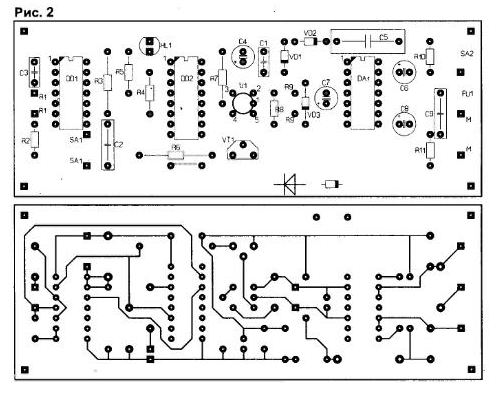
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Home, household, hobby When using fresh water for cooking or drinking, it is desirable to purify it of any impurities. Mechanical impurities include suspensions (sand, clay, rust, etc.). On the surface of water basins, there may be an oil film or paraffin from the operation of river transport or the exit from cracks in the earth's crust. Impurities of animal origin occur as waste from underwater life. High-quality water comes from artesian wells or wells. In addition to a small amount of mechanical impurities, it usually does not contain other inclusions. Artesian water for household use is taken from a depth of up to 10m. for drinking and cooking - from a depth of up to 100 m. The difference in the quality and taste of water depends on the distance of the aquifer from the surface of the earth. Tap water for purification from pathogenic bacteria is most often chlorinated, mechanical impurities are filtered. But even after preliminary industrial treatment, impurities remain in the water that reduce its taste properties. Various additional filters are used to improve the quality of water. A simple water purification device can be made from a plastic bottle with a cut bottom. The bottle is fastened with a bracket in a convenient place with the neck down, a bag of coal is placed inside the bottle, and medical cotton wool or cellulose is stuffed on top. Below is a container for collecting clean water. Water is gradually poured from above into the bottle, and it is cleaned in layers of coal and cotton wool from all types of precipitation. Filters are changed as they work out. Such a device requires constant tedious pouring of water. A water purification device has been developed in the laboratory "Automation and Telemechanics" of the Irkutsk DTT Center. It consists of a mains-powered electronic cleaning device and a converter for driving from the vehicle battery in camping mode. To increase productivity, an industrial cleaning unit "MAGIC-JET FILTER" with a pump "Magi-200" with a power of 5 W, a capacity of 200 l / h and a head of 60 cm is used. The unit includes a mains-powered pump and a system of carbon and cellulose filters . The electrical part of the unit is protected from moisture and can even be installed on the bottom of a tank with unfiltered water. During cleaning, water is supplied to the receiving tank through a hose with a diameter of 6 mm. For an hour of work, a barrel of water of 200 liters is cleared, while there is no overheating of the pump motor. The developed automation scheme (Fig. 1) improves the service capabilities of the device and provides: automatic shutdown (by the time the tank is filled), signaling the need to change filters, manual and automatic adjustment of the filtered water supply rate, setting the pump operation time depending on the volume of the receiving tank. To automatically turn off the pump when the tank is full, taking into account its mains supply, for safety reasons, not level sensors are used, but control of the operating time (pump capacity is approximately 3 l / min). The time relay on two microcircuits DD1 and DD2 allows you to work out time intervals - from 15 minutes to 2 hours. For galvanic isolation of the mains voltage from the electronic circuit of the device, the command to turn off the pump passes through the VU1 optocoupler. As a key, an amplifier on a field-effect transistor VT1 is used. The rectangular pulse generator is made on two elements 2OR-NOT chip DD1 (DD1.1 and DD1.3). The frequency of the generator is determined by the approximate formula: f=0.44/RC; where f is the frequency (in kilohertz); R is the total resistance of the resistors R1 + R2 (in kiloohms); C - capacitor capacitance C3 (in microfarads). The minimum generator frequency is 0,2 Hz, the maximum is 4,4 Hz (with zero resistance R1). The generator frequency does not depend on temperature and supply voltage (in the range from 4 to 15 V). The duty cycle of the pulses is equal to two. Element DD1.2 is used to reset the DD2 counter in automatic mode. When the power is turned on, the capacitor C2 is discharged, at the inputs 8. 9 D1.2 a low level is obtained, respectively, at the output 10 DD1.2 - high, which resets the counter DD2 at the input R After charging the capacitor C2 through the resistor R3, a high level appears at the inputs DD1.2, the element switches, and a low level at its output allows the counter DD2 to work. Chip DD2 contains a 14-bit asynchronous counter. The counter is incremented on every negative clock edge. The output signal is taken from output 013 (pin 3 of DD2), although any output from Q9 to 013 can be used by making changes to the operation of the generator. With a pulse frequency of 1,066 Hz, "1" appears at pin 6 of DD2 one minute after reset. The multivibrator on DD1.1 and DD1.3 stops after a high level appears at the output of Q13. The score can be reset at any time by pressing the SB1 button. Account control indication is made on the HL1 LED. Every 8 pulses the LED is lit, and the next 8 pulses are off. The duration of the multivibrator pulses is set by a variable resistor R1. The speed controller of the pump motor is the DA1 chip - a phase power controller. It consists of two thyristors, a control unit and a thermal protection device. The microcircuit in case of overload and overheating limits the power in the load. The pump speed is quite smoothly regulated when the voltage on the electric motor is from 80 to 240 V. A low level from output 3 of DD2 during the count shunts the voltage of the divider R5-R6, so the field effect transistor VT1 is closed. There is no current in the drain circuit of the transistor, the optocoupler LED VU1 is off, so the collector-emitter circuit of the internal optocoupler transistor has a high resistance and does not shunt resistor R9. The DA1 phase regulator is open and the pump motor is running at full capacity. At the end of the count, a high level occurs at pin 3 of DD2, which opens transistor VT5 through resistor R1. The optocoupler LED turns on and opens the internal transistor, which shunts pins 3 and 6 of the DA1 chip. The DA1 regulator is turned off, and the load is smoothly de-energized for a time depending on the capacitance of the capacitor C7. Turning on the pump after pressing the SB1 button also occurs smoothly, which protects the mechanics from premature failure. The pump speed is controlled by a variable resistor R9. There are practically no adjustments in the scheme. When the voltage is turned on, the device does not work (the pump does not rotate, the HL1 LED is off). Work begins by pressing the SB1 "Reset" button. After a short press of SB1, the LED lights up and the pump motor starts to rotate. A running multivibrator should output 4 DD1.3 pulses with a duration of 1 s at the output. The device is powered from the mains according to a transformerless circuit with a quenching capacitor C5 through a rectifier based on VD2 diodes. VD3 and parametric stabilizer on the zener diode VD1. Current consumption - no more than 2 mA. The supply voltage of microcircuits should not exceed 15 V. The circuit is assembled on a circuit board with dimensions of 115x45 mm (Fig. 2).
The housing is only slightly larger than the circuit board. LED HL1. button SB1, speed controller R9 and mains switch SA1 with fuse FU1 are installed on the front panel of the device. To connect the pump, a special socket is provided, which is located in any convenient place. When setting up, it is desirable to power the circuit from a laboratory source or a separate adapter (12 V / 0,1 A) in order to comply with safety measures. Literature
Authors: V.Konovalov, A.Vanteev, Irkutsk.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Men spread negative information less often than women ▪ Turbine from the other side of the world ▪ Found an effective way to cheer up ▪ Tracking satellites and space debris ▪ A new way to obtain alternative fuel
▪ site section Parameters of radio components. Article selection ▪ Article by Sextus Propertius. Famous aphorisms ▪ article Who and how first showed that air has weight? Detailed answer ▪ article Work in diesel. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ article Copper. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: