
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Incubator motor control device. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
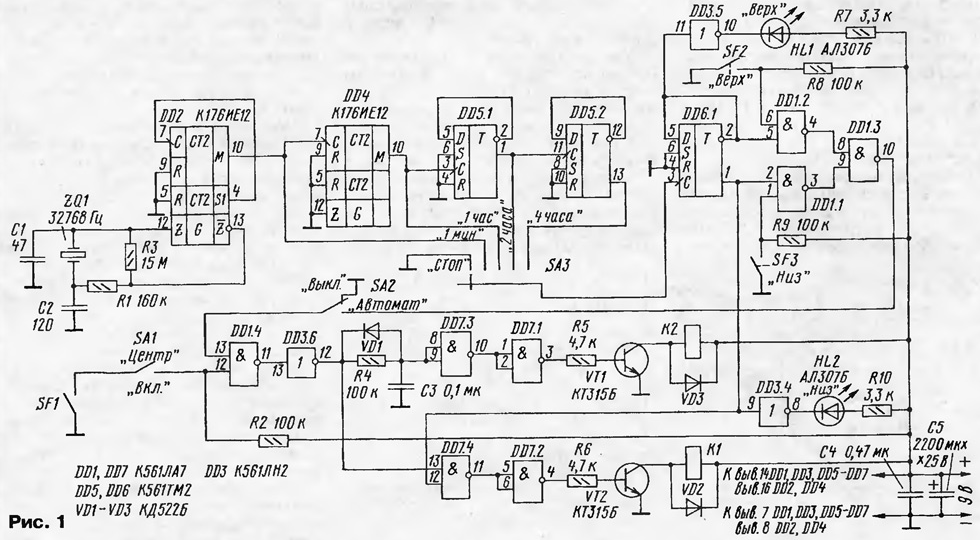
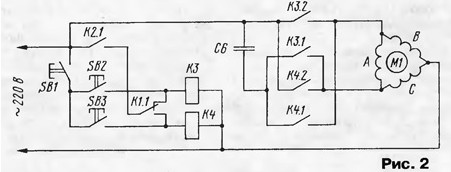
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers In the motor control devices for turning the incubator trays [1, 2], single-phase motors without reverse are used. These devices are applicable in small incubators designed for laying 30...50 eggs. The proposed article describes a control device for a three-phase motor of any power included in a single-phase network. It can be used in incubators of farms with laying eggs from 500 pcs. (incubator from the refrigerator) up to 50 thousand pieces. (industrial incubators like "Universal"). This device has been operating in an incubator made from a refrigerator for 11 years. The design contains control and power blocks. The control unit (Fig. 1) includes a generator and frequency dividers on DD2, DD4, DD5 microcircuits, a driver for turning on the engine on elements DD6.1, DD1.1-DD1.4, DD3.6, an integrating circuit R4C3, switches on transistors VT1, VT2, relay K1, K2. The generator and frequency divider to minute pulses are assembled according to the standard scheme on the DD2 chip (K176IE12). For division up to 1 hour, a divider by 60 is used (chip DD4). Triggers DD5.1 and DD5.2 divide up to 2 and 4 hours. Switch SA3 to select the required time after which the trays will rotate. The duration of the pulses at the outputs of the trigger DD6.1 corresponds to the selected period of time. The fronts of these pulses through the elements DD1.1-DD1.3 turn on the motor for turning the trays. On the front of the pulse from the direct output of the trigger DD6.1, passing through the elements DD7.4, DD7.2, in addition, the engine is reversed. Elements DD1.4, DD3.6 are required to switch the operating modes "Manual" - "Automatic" and install the trays in the horizontal position "Center". An integrating circuit R4C3 is used to delay the engine on after the reverse. With the ratings indicated in the diagram, this time is about 10 ms. Control pulses through transistor switches VT1, VT2 turn on the engine start relay K2 and the reverse relay K1. When the supply voltage is turned on, a high potential will be set at one of the outputs of the trigger DD6.1, for example, this is output 1. If the limit switch SF3 is not closed, then the output of element DD1.3 will be high and relays K1, K2 will work. The next time trigger DD6.1 is switched, the reverse relay K1 does not turn on, since a low level will be applied to the input of element DD7.4. Relays K1 and K2 turn on for a short time, only for the time of turning the trays, since when the limit switches SF2 or SF3 are triggered, a low level will be set at the output of element DD1.3. Indication of the state of the trays (top, bottom) is carried out by LEDs HL1, HL2. The inscriptions "Top", "Bottom" show the position of the front edge of the tray and are conditional, since the direction of rotation of the motor can be easily changed by connecting the motor windings accordingly. The power block diagram is shown in fig. 2.
Relays K3 and K4 (turn on alternately) switch the motor windings and, therefore, control the direction of rotation of the rotor. Since relay K1 (if necessary) is activated earlier than relay K2, then the engine will be switched on by contacts K2.1 after the corresponding position is selected by contacts K1.1. Buttons SB 1 -SB3 duplicate contacts K2.1, K1.1 and are designed to manually set the position of the trays. The SB1 button is structurally installed between the SB2 and SB3 buttons for the convenience of simultaneously pressing two buttons. It is desirable to make the inscription "Top" under the top button. The movement of trays in manual mode must be done in the switch position SA2 "Off". The capacitance of the phase-shifting capacitor C6 depends on the motor switching circuit (star, delta) and its power [3]. For a motor switched on according to the "star" scheme, C=2800l/U, for switching on according to the "triangle" scheme C=4800l/U, where I=P/(1,73-Uη-cosφ); P - nameplate power of the engine in watts; cosφ - power factor; η - efficiency; U - network voltage in volts; C is the capacitance of the capacitor in microfarads. The device is assembled on a printed circuit board (Fig. 3). Short circuit relay, K4 and capacitor C6 are located in close proximity to the engine.
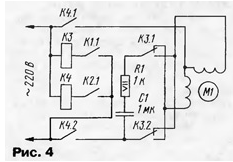
The device uses switches SA1, SA2 - P2K, SA3 - PG2-9-6P2N. Limit switches SF1 - SF3 - MP1105. Relays K1 and K2 - RES49, passport RF4.569.426. Relays KZ and K4 can be used of any type for an alternating voltage of 220 V with the corresponding maximum current through the contacts. A three-phase M1 motor with a gearbox can be used with any one with enough power on the shaft to turn the trays. For calculation, it is necessary to take the weight of one chicken egg approximately equal to 60 g, duck and turkey - 80 g, goose - 190 g [4]. In the author's version, an FTT-0,08 / 4 engine with a power of 80 W was used. On fig. 4 shows a diagram of a device for controlling a single-phase motor.
Limit switches are located around the axis of rotation of the trays at the required angle. A bushing with an M8 thread is fixed on the axle, into which a bolt is screwed that closes the limit switches. More details on the design of the incubator from the body of a household refrigerator and recommendations for incubating eggs can be viewed on the website . Literature
Author: N.Zaets, Veidenevka village, Belgorod region.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Adam II - a tablet with a two-sided display ▪ Liquid laser that does not evaporate in air ▪ The gadget is powered only by the heat of the human body
▪ section of the site Instructions for use. Article selection ▪ article Marine chronometer. History of invention and production ▪ article How much can the heaviest cage weigh? Detailed answer ▪ article Gageya yellow. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Easy eight. Focus Secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: