
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING GPA for IF 5,5 MHz. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
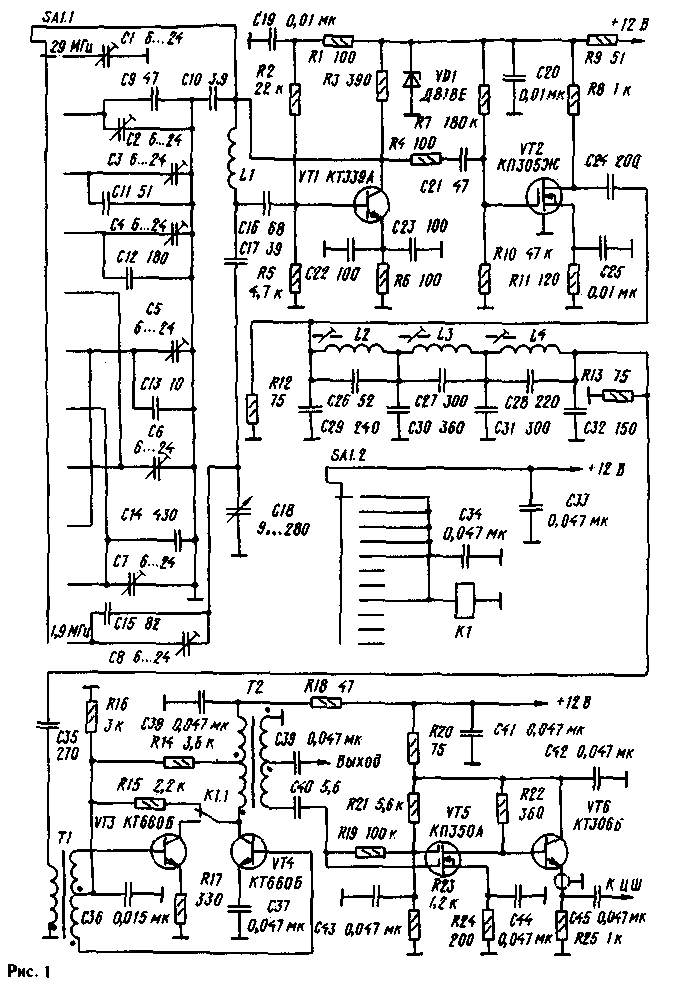
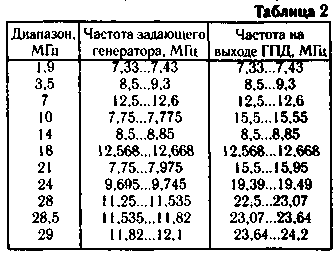
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Knots of amateur radio equipment. Generators, heterodynes The most important component, the "heart" of the transceiver equipment is a smooth range generator (GPA). In radios and transceivers with a fixed first intermediate frequency, the GPA must generate different frequencies according to the selected range. The quality of the device as a whole depends on the quality of its work. The output signal of the GPA must be stable when changing temperature, humidity, pressure, power supply voltage, etc. The negative impact of these factors can be reduced to a minimum by competent design of the GPA. Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the GPA, designed for use in transceiver equipment with a fixed first intermediate frequency of 5,5 MHz. It has a small number of switching circuits, has an increased stability of the output signal parameters, its high spectral purity and uniform amplitude over the ranges. The number of tuning elements compared to the number of ranges is reduced to a minimum. The effective output voltage of the generator is four volts into a 75 ohm load and has the shape of a sinusoid. The generator is made on the transistor VT1 according to the Vakar scheme. The parametric voltage regulator VD1, R9 and decoupling elements C 19, R1, C20 prevent leakage of high-frequency voltage in the power circuit and provide increased stability of the output signal parameters in the presence of small fluctuations in the supply voltage that occur during transients (transition from reception to transmission and vice versa). Resistor R4 improves the decoupling between the generator and the subsequent stage. A broadband radio frequency amplifier is made on the VT2 transistor. The low capacitance and high input impedance of the cascade contribute to a good decoupling of the generator from other cascades. The output of the GPA amplifier is loaded with an elliptical low-pass filter of the seventh order. The filter bandwidth is 7,33...12,6 MHz, the filter cutoff frequency is 12,65 MHz. All spurious products provide over 35 dB suppression. The input and output impedance of the filter is about 500m. The filter output is connected to the input of a cascade made on transistors VT3 and VT4, which is a switchable doubler amplifier. On the bands 1,9 MHz, 3,5 MHz, 7 MHz, 14 MHz, 18 MHz, it works as an amplifier, and on the bands 10 MHz, 21 MHz, 24 MHz, 28 MHz - as a doubler. When switching from the doubling mode to the amplification mode, the collector of the UTZ transistor is turned off, and the VT4 transistor is switched to the linear amplification mode (class A) by applying an additional positive bias to the base circuit due to the connection of the resistor R15. In the doubling mode, the signal from the input transformer T1 is supplied in antiphase to the bases of both transistors. In this case, the transistor collectors are connected in parallel and loaded on the input winding of the transformer T2. The output signal of the GPA is taken from the middle of the output winding of this transformer, and the cable decoupling amplifier with a digital scale is connected to the full winding. The latter is made on transistors VT5 (amplifier) and VT6 (emitter follower). Resistor R25 is installed directly in the digital scale. The emitter of the transistor VT6 is connected to the input of the digital scale by a piece of coaxial cable RK-75. This amplifier, having good buffer properties, has a gain of about 10 in the frequency band 100 kHz-50 MHz. The switching of the doubler amplifier (VT3.VT4) from the amplification mode to the doubling mode is performed by the node on the K1 relay, the SA1.2 jack switch and the capacitors C33, C34. Winding data of coils and transformers are given in Table. 1, and the frequencies generated by the generator in table.2.
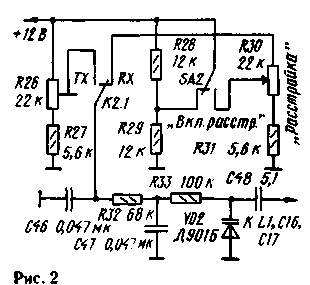
Transistor KT399A can be replaced with KT316B or similar. Transistors KT660B - on KT603B, KT608B; KP350A - on KP350B, KP306; KT306B - on KT316B. Trimmer capacitors C1-C8 with air dielectric type 1KPVM. Relay K1 type RES49 (passport RS4.569.424) or RES60 (passport RS4.569.438). Switch type PKG, PGG for 11 positions and 2 directions. The oscillator tuning begins with laying the 7 MHz range by selecting capacitor C13 and adjusting C5. After laying, thermal compensation is performed by replacing capacitors C 10, C13, C17, C22, C23 with capacitors of equal nominal value, but with different TKE. The remaining ranges are laid by selecting capacitors C9, C11, C12, C14, C15 and adjusting capacitors C1, C2, C3, C4, C6, C8, and then thermal compensation - replacing capacitors C9, C11, C12, C14, C15 according to the method described above. When laying the 29 MHz range, it may be necessary to install an additional capacitor with a capacity of 20 ... 30 pF in parallel with capacitor C1. Next, the cascade is set up on the transistor VT2 by selecting the resistor R8 according to the maximum signal at the drain of this transistor. To do this, temporarily replace the resistor R8 with a variable resistor with a nominal value of 1k0m, set up the cascade, and then, having measured the resistance of the resistor, replace it with a constant one - close in value. By rotating the trimmers of the coils L2, L3, L4, the low-pass filter is tuned in order to obtain a uniform characteristic in the frequency band of 7,33 ... 12,6 MHz and a cutoff frequency of 12,65 MHz. Control is carried out with an oscilloscope or a frequency response meter. The tuning of the doubler amplifier (VT3.VT4) is started in the doubling mode on the 10 MHz range by selecting the resistor R14 until the maximum signal amplitude and the correct shape of the sinusoid are obtained at the output (C39). Then, switching the generator to the 14 MHz range, in which this cascade operates in the 'amplification mode, the resistor R15 is selected until the maximum output signal and the correct shape of the sinusoid are obtained. The cascade on the transistor VT5 is adjusted to the maximum signal at the output (C45) by selecting the value of the resistor R22. If at the output of the generator there is unevenness in the amplitude of the output signal in different frequency ranges, then resistors R12, R13 with a high resistance - up to one kiloohm - should be taken. After that, irregularities in the form of humps and dips will appear in the frequency response of the generator. By rotating the trimmers of the coils L2, L3, L4, it is necessary to achieve a displacement of the humps of the characteristic in those areas where output frequency signals with low amplitude and dips were previously observed. By selecting resistors R12, R13, they adjust the height of the humps and the depth of the frequency response dips. You can reduce the output voltage of the GPA by selecting resistor R4. To introduce detuning, you can use the scheme shown in Fig.2. Positional designations of elements continue begun in fig. one.
The tuning resistor R26 is used to set the frequency of the GPA in the transmission mode, the same as in the reception. Turn on the detuning switch SA2. The variable resistor R30 controls the frequency change. The value of the tuning range depends on the value of the capacitor C48. It is the greater, the larger the capacitance of this capacitor. Author: Vladimir Rubtsov (UN7BV) Astana; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ TV Samsung UN105S9W for $120000 ▪ Hybrid crossover BMW Concept XM ▪ With a vacuum cleaner on the belt
▪ section of the site Amateur radio calculations. Article selection ▪ Arnold Joseph Toynbee article. Famous aphorisms ▪ What were the prerequisites, stages, results of the bourgeois revolution in England? Detailed answer ▪ article Secretary (dispatcher) of the educational unit. Job description
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: