Bite alarm. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Home, household, hobby
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Fishermen are well aware of how difficult it is to keep track of bites on an elastic band or bottom. And if there are several of them, then even more so. As a rule, in such cases, bells are placed as a bite signaling device. But on night fishing it's hard to tell which bell is ringing. And night fishing is the most interesting and "profitable". Another option is when you take a few fishing rods and an elastic band with you. You direct all your attention to the floats of the fishing rods (even though it is small, but it bites!), And it is difficult to keep track of the rubber bands. I offer a variant of a bite signaling device with sound and light indication. The alarm time can be set up to 5 seconds. The signaling device circuit is shown in Figure 1.

(click to enlarge)
The signaling device is assembled on one microcircuit and functionally consists of two blocks. On the elements DD1.1 and DD1.2, a waiting single vibrator is assembled. The frequency-setting circuits of the single vibrator are the capacitor C1 and the resistor R2. With a capacitor value of 0,47 microfarads indicated on the diagram, the duration of the sound and light signal will be 1 second. By increasing the value of the capacitor to 2,2 microfarads, the duration will increase to 5 seconds. You can put different denominations on the signaling devices and determine by ear which gum is biting. True, if the fishing line is pulled, then the sound signal sounds continuously. A positive pulse of the waiting single vibrator starts the waiting multivibrator, assembled on the elements DD1.3 and DD1.4. The frequency-setting elements of the multivibrator are the resistor R3 and the piezoelectric element ЗП1. The multivibrator is excited at its own resonant frequency of the piezoelectric emitter. For a dozen assembled circuits with a ZP1 piezoelectric radiator, it was not necessary to select a resistor. If another piezo emitter is used, then it may be necessary to select a resistor for maximum volume. The zero potential of the waiting single vibrator turns on the HL1 LED. You can put any LED, but an LED with a diverging lens is better.
In standby mode, at the inputs 5,6 of the element DD1.2 there is a logic zero level, at pin 4 - a logic one level. LED HL1 is off. At the inputs 1,2 logic element DD1.1 high levels. Pin 3 is a logical zero. Capacitor C1 is discharged and the multivibrator does not work. When biting, switch SA1 closes and starts the waiting single vibrator and the waiting multivibrator. The capacitor C1 of the integrator will begin to recharge to a logic zero level at pins 5,6. The recharge time of the capacitor determines the duration of the single vibrator pulse. This means the time when the sound and light signal is turned on.
The signaling device is powered by 3-4 elements of the A10-A13 type. It is good to make a case for elements from the body of a disposable 5 ml syringe. The current consumption in standby mode is negligible (less than 1 microamp), so the power switch can be omitted. It is only necessary to ensure that in the transport position the lever does not close the switch. The printed circuit board of the signaling device is made of one-sided fiberglass. The topology of the board with the layout of the elements is shown in Figure 2. In practice, the size of the board must be increased by the size of the SA1 pushbutton switch. Since you can put miniature switches like MP-7 or larger switches like MP-3, MP11. Everything depends on "presence". The approximate location of the switch and the board is shown in Figure 3.
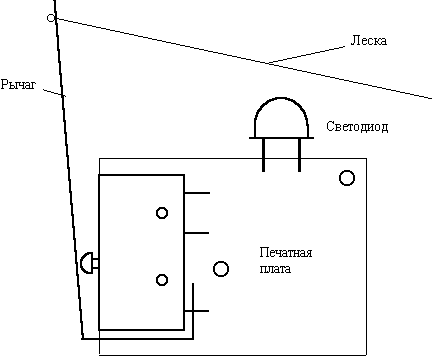
The lever for closing the switch is made from a soft plate from a large relay. The contact on the plate is pressed out, and a fishing line is inserted into the hole. The fishing line is wound on a match and stretched. The sensitivity of the bite alarm can be changed by increasing the length of the lever or by pulling the line. A strong wind or a wave for such a signaling device is not a hindrance. The signaling device is installed inside the box with the output of the lever and LED. The box is attached with screws to a stick with a pointed end.
Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section Home, household, hobby.
See other articles Section Home, household, hobby.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Methane on Mars is not a sign of life
13.06.2012
When 9 years ago, scientists discovered methane in the atmosphere of Mars, it became a sensation. Many considered the presence of this gas clear evidence of life on an inhospitable planet, since methane on Earth is formed mainly as a result of biological processes. Other scientists have suggested that the methane on Mars came from volcanic activity.
In 2003, observations of Mars revealed large amounts of methane in the atmosphere. One hypothesis claims that this is the result of the vital activity of Martian microorganisms, the other - that this is the result of geological activity. However, to date, none of the theories can definitively explain the large amount (200-300 tons) of methane that is annually released into the atmosphere of the Red Planet.
Scientists from the Max Planck Institute have found that Martian methane is most likely not a sign of life. The researchers irradiated the meteorite with ultraviolet light, similar to the conditions in the deserts of Mars, and found that methane gas was released from the stone. Thus, carbon compounds from interplanetary dust and meteorites, constantly deposited on the surface of Mars, under conditions of powerful UV radiation, release methane, which was mistakenly considered a sign of Martian life. A meteorite that fell in the Australian city of Murchison in 1969 was chosen for the study. This celestial rock is about 4,6 billion years old, contains a few percent carbon and is similar in chemical composition to most meteoritic matter on Mars.
As soon as the meteorite was placed in a chamber simulating Martian conditions (powerful UV light and temperatures from -143 to +17 Celsius), it began to emit methane.
Unlike Earth, Mars does not have a protective ozone layer that absorbs most of the ultraviolet radiation from space. In addition, the atmosphere of Mars is very thin, so that compared to the Earth, a much smaller part of the meteorite substance burns up in it. The theory of the meteoritic origin of methane is also consistent with the observations of orbital probes, which revealed an increased concentration of methane in the well-lit equatorial regions of Mars.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ New Nokia 3310 with 4G support
▪ Ultrafast photonic wires
▪ Huawei Smart Life Air Purifier 1Pro
▪ Smoking mother harms unborn child
▪ Smart Musical Sleep Mask Xiaomi Easy Air Brain Wave Sleeping Eye Mask
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Field strength detectors. Article selection
▪ article Wartime Emergencies. Basics of safe life
▪ article Why is the Nobel Prize not awarded for achievements in mathematics? Detailed answer
▪ article Desmodium hooked. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Meter R, C, L on microcircuits. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Standards for testing electrical equipment and devices for electrical installations of consumers. Stationary, mobile, complete portable test installations. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: