
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Electronic starters. The principle of operation of the electronic starter on the UBA2000T chip. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Ballasts for fluorescent lamps Let us consider in more detail an electronic starter implemented on a specialized chip from PHILIPS - UBA2000T. The UBA2000T is an integrated circuit used in electronic starters for fluorescent lamps designed to replace conventional bimetal starters. The microcircuit controls the preheating of the lamp electrodes and its ignition. The warm-up time of the lamp is strictly defined by using a power frequency divider. When a lamp fails, the circuit automatically shuts off after seven failed ignition attempts, thus preventing the ballast from overheating. In the event of interruptions in the supply voltage, the circuit automatically resets to its original state and ensures that the lamp is re-ignited. The UBA2000T chip provides the sequence of actions necessary to ignite a fluorescent lamp. Ways to turn on the microcircuit in the lamp power circuit are shown in fig. 3.4, and the functional block diagram of the UBA2000T is shown in fig. 3.5. The mains voltage is rectified and divided by external resistors R1 and R2 to the required level. When the power is turned on, the buffer capacitor C1 is charged through a resistive divider and an internal switch S1; the voltage across the capacitor is used to power the chip. As long as the voltage across the buffer capacitor Vcc will not exceed trigger level Vcc (гst), the internal circuits of the microcircuit are initialized. When the supply voltage Vcc reaches the trigger threshold Vcc (gst), and the peak value of VlN becomes greater than FIGN (that is, the mains voltage is near its peak value), the external power switch opens. As a result, the heating current of the lamp electrodes begins to flow through the lamp electrodes, the power switch and the integral current sensor. Throughout the entire period of time, while the external power switch is closed, the microcircuit is powered by the buffer capacitor C1. Typical voltage waveform at pin 6 (Vcc) is shown in Fig. 3.6.
During the warm-up period of the lamp electrodes the capacitor is discharging. The voltage from the current sense resistor is fed to a comparator whose output is used as a clock signal for an internal counter. This counter determines the warm-up time of the lamp electrodes, equal to 1,52 s at a power supply frequency of 50 Hz. Thanks to the use of a counter, the warm-up time is kept very precisely, since it depends only on the frequency of the supply network. After preheating the lamp electrodes the external power switch opens at the moment when the voltage across the current-measuring resistor corresponds to the flowing current of at least 285 mA. As a result of current interruption in a circuit containing an inductive load, a high-voltage pulse is generated, which ignites the fluorescent lamp. After successful ignition of the lamp the voltage on it becomes much lower than the mains. As a result, the supply voltage of the microcircuit does not exceed the threshold level necessary for its operation. On fig. 3.6 shows the shape of the microcircuit supply voltage when the lamp is ignited after the second attempt. While warming up the lamp electrodes the microcircuit is powered by the energy stored in the buffer capacitor, and the supply voltage gradually decreases. If after applying a high-voltage pulse lamp did not ignite, then the external power switch remains closed, and the voltage on the buffer capacitor again rises above the starting level. The external power switch closes again, and the next cycle of warming up and ignition of the lamp begins. On all subsequent ignition attempts, except for the first, the warm-up time is reduced to 0,64 s, since the lamp electrodes have not yet cooled down after previous unsuccessful ignition attempts. An internal counter limits the number of failed ignition attempts to 7. This prevents the lamp from flashing at the end of its life. The UBA2000T chip contains built-in current protection circuits. When the current through the sensor resistor exceeds the protection threshold (IPROT), the power switch is closed, and the microcircuit goes into rest mode. Switching the supply voltage off and on again resets the protection circuits. The state diagram of the microcircuit during the ignition of the lamp is shown in fig. 3.7.
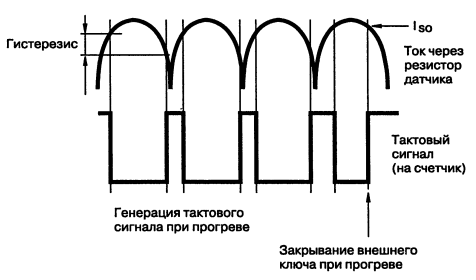
Source of power. When the supply voltage is applied to the microcircuit, the buffer capacitance is charged and the internal current source is allowed to work. The internal supply voltage of the microcircuit is stabilized and does not depend on the voltage on the buffer capacitor. The built-in zener diode limits the voltage at pin 6 (Vcc) at the Vcc (sl) level. Voltage comparators. Comparators monitor the voltage on the buffer capacitor and allow the operation of the internal circuits of the microcircuit when the supply voltage reaches the starting level - Vcc (sl). It takes a certain period of time t to initially charge the capacitorthis (See Figure 3.6). This time depends on the value of the capacitor C1, the current consumption of the microcircuit and the resistance of the external divider at the input Vin (R1IIR2). After the capacitor C1 is charged and provided that the mains voltage is close to its maximum value, a current pulse is generated that opens the external power switch. If the supply voltage drops to a level indicating the absence of mains voltage, the internal circuits of the microcircuit are reset, and it becomes ready to warm up and start the lamp when the mains voltage is turned on again. Trigger. The state of the internal trigger reflects the state of the external power switch. The process of setting the trigger is determined by the state of the voltage comparators, the counter of the number of ignitions and the rest mode of the microcircuit. The trigger reset is controlled by the timer, current sensor and current protection circuits. current sensor. The current sensor controls the moment when the power switch is turned off and generates clock pulses to control the internal counters of the microcircuit (Fig. 3.8).
For proper operation, the heating current of the lamp electrodes must be within the allowable range of IPR. Due to some hysteresis, individual peaks of the electrode heating current do not affect the state of the counter. In addition, the current sensor circuits carry out additional low-frequency filtering of the signal, which eliminates the influence of short current pulses on the warm-up time of the lamp electrodes. Front sensor. The front sensor ensures the closing of the external power switch on the falling edge of the rectified heating current. Counter. When a clock signal is applied to the counter with a doubled mains frequency, the counter sets the duration of the first warm-up of the lamp electrodes and, if necessary, the duration of the next six warm-ups. Warm-up time control circuit. Depending on the state of the counter of the number of runs, a large (tPRF = 1,25 s) or small (tPRN = 0,64 s) warm-up time. Run counter. The number of starts is counted by a separate counter. After seven unsuccessful start attempts, the microcircuit is transferred to a rest state. At rest, the current drawn increases, so that the buffer capacitor discharges quickly when the starter is disconnected from the power source. This provides an automatic starter reset when hot-swapping a defective bulb. Current protection circuits. If the current through the measuring resistor exceeds the threshold value IPROT, the external power key closes. During the first few periods of the open state of the power key (blocking time tD) the operation of current protection circuits is prohibited. Due to this, transient processes when opening the key do not lead to the operation of the current protection circuits. If the current exceeds the threshold value, the power switch is turned off, and the microcircuit is transferred to the rest state, preventing the subsequent opening of the key. The microcircuit can be brought out of this state only by turning off the supply voltage. output buffer. The output buffer is designed to control an external thyristor with a low input current or a powerful field-effect transistor. In the process of turning on the microcircuit, its output is maintained at a low level, which prevents the power switch from opening. Power switch on thyristor. As already mentioned, UBA2000T can work together with a high-voltage thyristor TN22 (Fig. 3.9). It is a high quality single-ended thyristor manufactured by high voltage pnpn diffusion planar technology. The manufacturer is STMicroelectronics (st.com). The thyristor is produced in IPAK (TO-251), DPAK (TO-252) plastic cases and is intended for use in electronic starting devices for fluorescent lamps. The main technical characteristics of the thyristor TN22:
Maximum values of parameters and modes TN22:
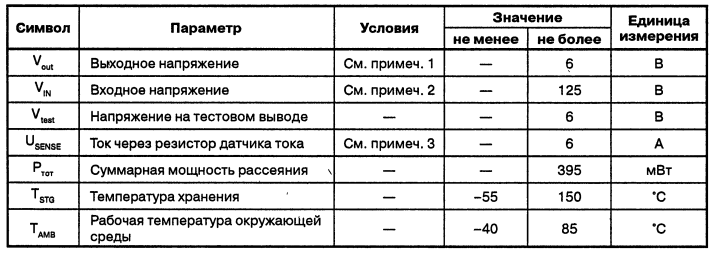
A typical example of using a microcircuit in conjunction with a thyristor with a small input current (type TN22) used as an external power switch is shown in fig. 3.4, a. In this case, the resistive input voltage divider is connected not to a common wire, but to the control electrode of the external switch. Since the voltage on the control electrode of the key is small, this does not lead to a noticeable change in the division factor. Output buffer amplifier generates a current pulse required to open the external key TH1. This current pulse is synchronized with the voltage at pin 4 (VIN). The power switch opens when the voltage VIN reaches level VIGN. In this case, the current through the divider R1 and R2 is an integral part of the current required to open the key. If necessary, the current pulse is repeated every half cycle of mains voltage. When it is required to close the foreign key, the output buffer is able to supply the large current flow required to close the key reliably. Sometimes it is necessary to limit the pulsed current flowing when the key is opened due to the discharge of the noise suppressing capacitor C2. To do this, a resistor R3 can be connected in series with the capacitor. Power key on a field effect transistor. A typical scheme for using the UBA2000T chip in conjunction with a power field-effect transistor switch is shown in fig. 3.4, b. In this case, the resistive divider is connected to the common wire. The output buffer of the microcircuit works similarly to the previous case. The output current pulse charges the gate of the field-effect transistor. As a result, the transistor opens. To hold the transistor in a conductive state, a high-resistance resistor is used, connected between the gate of the transistor and buffer capacitor C1. The need for this resistor is due to the fact that the output current is pulsed, not continuous. It should be notedthat the use of a resistor leads to an increase in the discharge current of the buffer capacitance C1. The internal zener diode limits the voltage at the output of the microcircuit, and, consequently, at the gate of the field-effect transistor, at a level of approximately 6,8 V. Both applications require the use of a power switch with breakdown voltage V(BR)AC or V(BR)DSexceeding the ignition voltage of the fluorescent lamp. In table. 3.1 are given limit values of UBA2000T chip parameters. Table 3.1. Limit values of UBA2000T chip parameters
Notes to the table. 1. The output is connected to an internal zener diode with a breakdown voltage of about 6,8 V. 2. The output is connected to an internal zener diode with a breakdown voltage of 130-230 V. The current through the output must be limited to 10 mA. 3. Impulse value with a pulse duration of 2 ms. Author: Koryakin-Chernyak S.L.
Alcohol content of warm beer
07.05.2024 Major risk factor for gambling addiction
07.05.2024 Traffic noise delays the growth of chicks
06.05.2024
▪ A new way of light propagation in glass ▪ Increasing the life of ultracold molecules ▪ Acer Extensa EX2510 and EX2509 laptops ▪ Lenovo Legion R7000P and R9000P gaming laptops
▪ site section Chargers, accumulators, batteries. Article selection ▪ article On one word of honor. Popular expression ▪ article Which languages don't distinguish between blue and green? Detailed answer ▪ article Juniper red. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Liquid crystal indicators. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese





 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: