Flashing lamp. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Lighting
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Based on the "flashing" VD3 LED, the author developed a "flashing" network lamp (Fig. 1), which can be used in discos, for Christmas trees, etc.
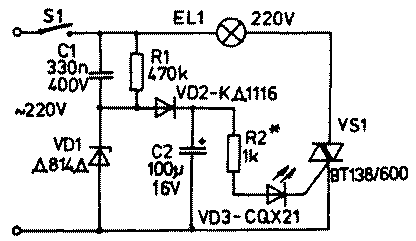
C1VD1R1VD2C2 form a rectifier to power the "flashing" LED with constant voltage, R2 limits the current of the control electrode of the triac VS1. The switching period is determined by the properties of VD3. In general, the circuit is capable of auto-switching loads up to 3500 watts.
Author: Tsvetam Manoilov; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Lighting.
See other articles Section Lighting.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Interesting life improves immunity
06.10.2016
It is known that sometimes environment and lifestyle influence the immune system more than genes. For example, scientists, comparing the state of the immune system in identical and fraternal twins, found that non-hereditary factors overlap hereditary in 3/4 of cases; that is, vaccinations in the past, germs and toxins that once had to fight, diet, and even how much a person took care of his teeth - all this determines the state of the immune system to a much greater extent than the genetic instructions inherited from parents . But after all, non-genetic factors are not limited to toxins, bacteria, diet and bad teeth.
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London found that the activity of T-lymphocytes largely depends on how diverse the environment around the individual is. T-lymphocytes are one of the best known immune cells; it is they who recognize foreign molecules, they kill infected and cancer cells, and they, by the way, regulate the strength of the immune response.
What does "diverse environment" mean? The experiments were carried out on mice that naturally lived in special cages. Usually the mice had nothing but sawdust on the floor of the "apartment" and some other material for the nest. But for some animals, not only were they given a bigger cage, they also piled all sorts of useless rubbish in the form of large wood chips, multi-colored boxes, some kind of fabric tubes; in addition, mice were given useful objects, such as a squirrel wheel, with which they could play. That is, the landscape around the animals was made extremely diverse.
After two weeks of such an interesting life, the immunity of animals changed: when T-cells isolated from them were stimulated with substances that supposedly indicated the invasion of infectious agents, then T-lymphocytes in response synthesized more interleukin-20 and interleukin-17 - signal proteins, on which they depend immune response to infection. In addition, the T cells of mice that lived in a diverse landscape increased the activity of 56 genes, again associated with anti-infective processes and with the regulation of autoimmune processes. That is, life in a diverse environment clearly benefited the immune system.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ A new island has appeared
▪ Water cannons for submarines
▪ Silicon Carbide Mass Production Plant
▪ A new method for fast optical distance measurement
▪ The doctor who is always with you
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Tools and mechanisms for agriculture. Article selection
▪ article Science to win. Popular expression
▪ article Where and when was the person who committed the murder in front of witnesses fully acquitted? Detailed answer
▪ Boat driver article. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Luminaire dimmer. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Power amplifier control unit. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: