
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Apparatus for magnetothermy. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Electronics in medicine Popular in the sixties and eighties, high-frequency therapy (heating body tissues in a high-frequency electromagnetic field) is now practically “dead” - firstly, due to the dominance of drug advertising, and secondly, due to the cessation of the production of HF devices. These devices ("Ekran", UHF-30, UHF-80) were produced with state subsidies, and in the conditions of the market they turned out to be commercially untenable. They also had an operational drawback - their inductive emitters gave the same electrical heating as capacitive ones. As you know, there are two types of ideal emitters - electric and magnetic dipoles. The first one consists of two conductors, to which a voltage is applied, which creates an electric field. The second is a current-carrying conductor around which a magnetic field is created. Real emitters are very close to the first and very far from the second. Conductors have a finite resistance, on which the voltage drops, creating an electric field that is strongly absorbed by living tissues. The resistance of electrical losses weakens the current in the conductor and, accordingly, the magnetic component of the field. Therefore, it is possible to obtain magnetic heating (magnetothermy) only with low-resistance, high-quality and tuned in resonance with the generator frequency emitter frames. This condition is not met in the listed HF devices, since they use a multi-loop circuit, and in the general case, the output circuit (coil) is not tuned to resonance with the generator - the presence of the patient and his movements upset the circuit. Meanwhile, magnetothermy has its advantages. If, under a potential electric field, linear currents arise in the body, from which the skin, fat, bones and brain are heated most of all, which have high resistance in a series circuit, then the magnetic field creates eddy currents in the physiological fluid around insulator particles (for example, cell membranes). The blood and blood-filled tissues are heated to the maximum. In addition, the magnetic field does not change its shape in the body and penetrates into it, as into air. Inflamed, edematous and tumor tissues are heated in a magnetic field to the greatest extent, which achieves selective safe treatment. Overheating of healthy tissue is impossible, because. The body regulates temperature by increasing blood flow to carry heat away. Capillaries open, most of which are closed at rest. In this case, the drug introduced into the blood irrigates the tissues better and becomes more effective (for example, antibiotics). Therefore, magnetothermia is used as an additional enhancer of drug therapy. I offer a device for magnetothermy, designed for individual use. It is simple, has small dimensions, but is not adapted for continuous clinical work (it overheats). The scheme of the apparatus is shown in fig. one.
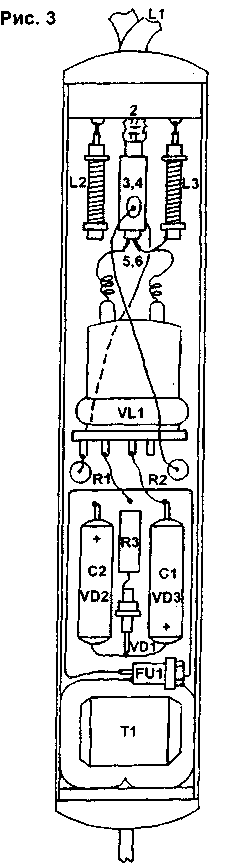
Circuit elements L1 - emitter-frame, combined with the generator circuit. L2, L3 - high-frequency chokes. VL1.1, VL1.2 - half of the generator lamp GU-29. R1, R2 - bias resistors, R3 - ballast resistor in the screen grid circuit. VD1 - a zener diode that extinguishes the voltage on the screen grid of a cold lamp. VD2, VD3 - rectifier diodes (any 1000V and current 2...3A). C1, C2 - filter capacitors. T1 - filament transformer 220 / 12,6 V (1,25 A).
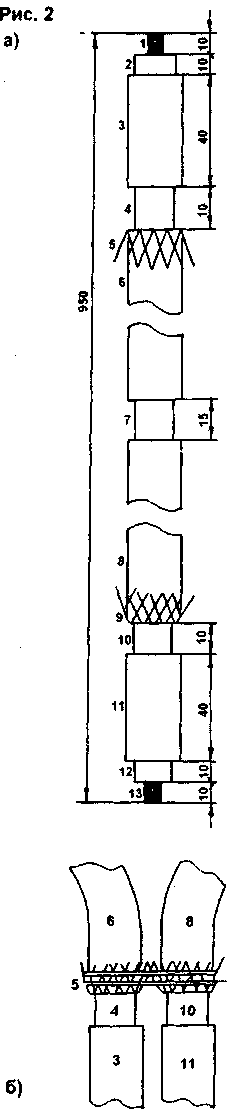
The circuit is a push-pull generator with a power of 100 W at a frequency of 40 MHz. The emitter is a frame with a diameter of 20 ... 23 cm. The basis of the design is a piece of coaxial cable with an internal insulation diameter of 4 ... 9 mm (L1). The numbers indicate: 1 - breaks in the braid, 2 - closure of the ends of the braid, 3, 4 - insulated segments of the braid, 5, 6 - insulated ends of the core. With this cutting, the cable core remains intact and insulated. Its ends 5, 6 are connected to the anodes of the lamps, and the core serves as a communication coil - the primary winding of an isolating transformer. The frame-emitter is an insulated braid, closed at point 2. The feed point of the frame is a break in the upper part (1). With this inclusion, the capacitance acting between the core cable and the inner surface of the braid is applied to the ends of the frame and serves as the capacitance of the oscillatory circuit (ideally shielded and allowing high reactive power, since this capacitance is distributed along the entire length of the cable and has good insulation). The linear capacitance of a thick coaxial cable is usually 1 ... 2 pF per centimeter, i.e. the total capacitance of the circuit is 100 ... 200 pF, which would be unattainable in an air condenser. A low-resistance circuit drops less voltage, which means it creates a smaller parasitic electric field. In addition, it is not affected by the output capacitance of the lamp, which reduces efficiency. Short insulated braids (3 and 4) serve as plates for the feedback capacitors. The other lining is the cable core. But this is not only its function. The linings also shield the ends of the core, due to which the inductive resistance of the ends is minimal, and their equivalent diameter is equal to the diameter of the braid. This eliminates the feeder that introduces losses. An unloaded oscillating circuit made of a cable has a quality factor of several hundred, and a loaded by the patient - about 50. The resonant frequency of the emitter in a single-circuit circuit always coincides with the frequency of the generator and determines it, therefore the circuit provides almost pure magnetic heating. The cable termination scheme is shown in Fig. 2a. The length of the blank is 95 cm. At the ends of the segment, the vein is exposed (sections 1,13). In sections 2,12, the outer insulation and braiding were removed, while the inner insulation was retained. Segments 3, 11 - untouched sections of the cable. They are followed by breaks in the braid (sections 4, 10), but the braid here is cut only from the side of the ends of the cable, and its bare ends are wound into sections 5, 9 over the outer insulation. At the same time, the veins of the braid are untwisted. The braid is also torn strictly in the middle of the cable segment (section 7). The places where the braid is removed are insulated with rings from the removed external insulation, and in sections 4, 7, 10 these rings are cut along the generatrix. Over the rings, the places of braid breaks are wrapped with adhesive tape. A piece of a corrugated plastic tube 7 0 mm long, 20 ... 7 cm long, is put on the middle gap 8. The ends of the tube are wound with PVC tape. The ends of the cable are folded into a frame, and the places with unfolded braids (5, 9) are wrapped with bare wire and soldered, as shown in Fig. 26. After cutting the segment, a piece of insulation is removed on the surface of sections 3, 11 to solder the conductors from the grids of the lamps. High-frequency chokes L2, L3 are made on cable sections with outer insulation and braid removed, i.e. the frame is internal insulation with a preserved core. A coil to coil of MGTF-0,12 wire or another with heat-resistant insulation, 2,2 m long, is wound on this frame. The ends of the winding are fastened with rubber rings. A lobe is made from the end of the core for fastening, a throttle. The circuit is mounted in an oblong case of two metal covers with holes for ventilation and two end caps made of caprolon, plexiglass or wood. The ends of the frame pass through one plug, and the power cord through the other. The layout of the elements in the case is shown in Fig.3. The elements can be fastened with screws and brackets or with a glue gun. All current-carrying circuits of the circuit must be well insulated from the case!
The device’s performance is checked using an electric lamp with a power of 100 ... 150 W (220 V) connected to two or three turns of a cable (a braid is used) 0 20 cm. When the indicator approaches the frame of the device, the lamp should light up with full heat. In this case, there is a maximum glow at a distance of 3 ... 5 cm, corresponding to the optimal load of the generator. Working with the device is reduced to combining the field of the frame, which has the form of a sphere resting on the frame, with the area of pathology. The round frame acts to a depth of approximately 10 cm, i.e. it is good to treat inflammations such as bronchitis, nephritis, arthritis. For greater localization, the frame can be narrowed, and for otolaryngology, for example, it is advantageous to bend it like a poker. At the same time, while holding the body of the device vertically, the part of the frame closest to the body is brought under the chin close to the neck, and the bent part covers the face at the level of the nose. In this position, the nasopharynx and ears are treated. Relief occurs immediately after a session lasting 10-15 minutes. For other diseases, the session is longer - 20 ... 30 minutes. In the acute form of inflammation, sessions can be repeated after a few hours, in chronic inflammation - every day or every other day. The course of magnetothermy consists of several sessions. The exception is fractures and arthritis, when the effective number of sessions is more than 10.
Magnetothermia can be used in all cases where physiotherapy is indicated. Ten years of experience using this method by dozens of doctors on thousands of patients has not revealed any side effects, but it is still recommended to consult a doctor before using it. Author: Y. Medinets (UB5UG), Kiev; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Why food photography is appetizing ▪ No dark matter found around the sun ▪ Angry Birds brought in $67,6 million in revenue
▪ section of the site Aphorisms of famous people. Article selection ▪ Public Relations article. Crib ▪ article Unusual ball. Focus secret
Comments on the article: Alexander Blessed memory of Yu.R. Medints. Thanks for the device.
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: