
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Car radio station in the range of 144 ... 146 MHz. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
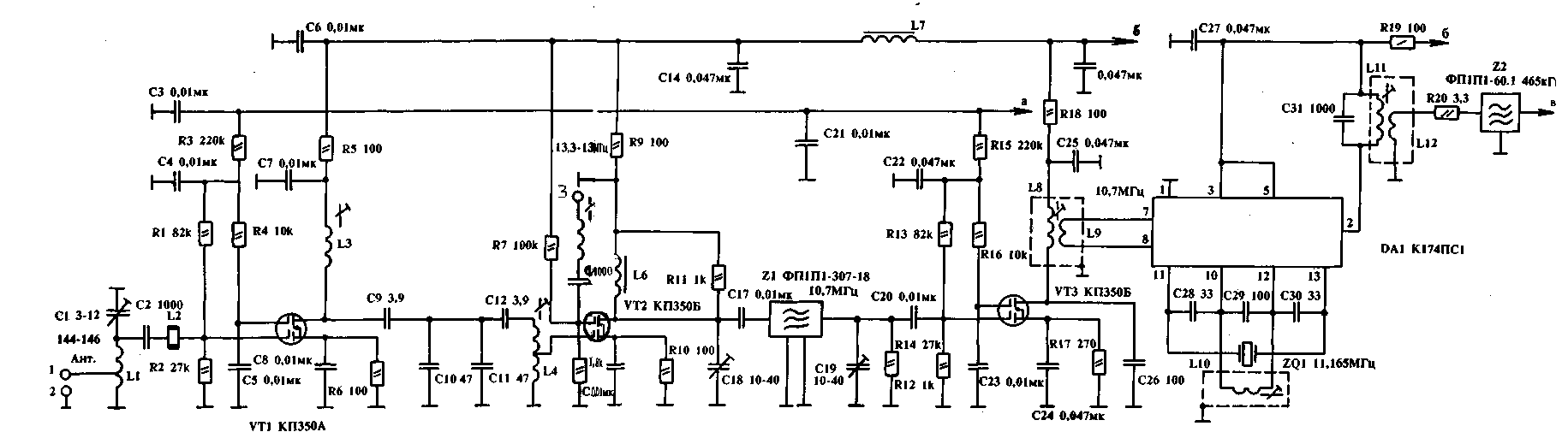
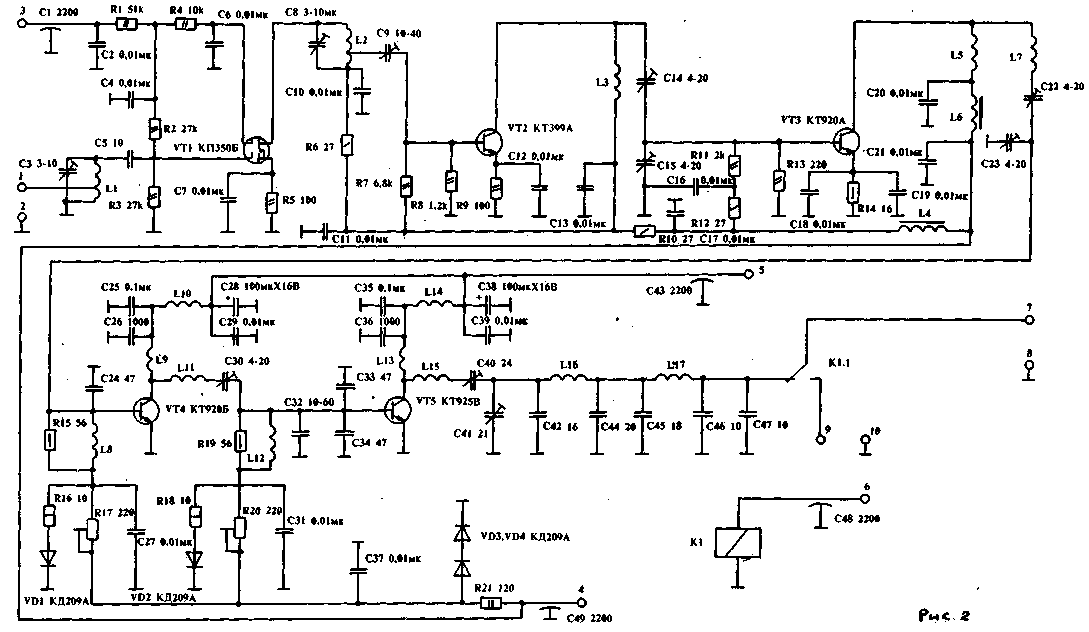
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Civil radio communications The radio station is designed for installation on a car and operates in the amateur band 144-146 MHz with frequency modulation. The frequency grid of the radio station coincides with their international division in this range. The frequency stability of the radio station is provided by a frequency synthesizer. When tested, it showed very good results. So, on the highway, the connection was stable between two cars at a distance of more than 40 km, and in a large city - 15-20 km. The radio station is easy to manufacture and operate, has small dimensions and does not contain scarce components. The parameters of the radio station are as follows: - the number of channels provided by the synthesizer - 160; - frequency grid step - 12,5 kHz; - frequency modulation with deviation - 3 kHz; - sensitivity of the radio receiver - 0,1 microvolts; - selectivity but side reception channels - 60 dB; - transmitter power - 5 W; - supply voltage - 12V; - dimensions - 200x200x50 mm; - whip antenna 5/8 wavelength; - there is a noise suppressor, a ringing device, an indication of the correct operation of the nodes; - it is possible to transmit digital information between two radio stations of the same type. The radio station receiver is built according to the superheterodyne scheme with double frequency conversion. The first intermediate frequency is 10,7 MHz, the second - 465 kHz. The circuit diagram of the receiver is shown in fig. one. The signal from the antenna through the antenna relay located on the transmitter board is fed to pin 1 of the receiver board. The input impedance of the board from this input is 50 ohms. The input circuit, made on the elements LI, C1, is tuned to the middle of the 145 MHz range. The high-frequency amplifier is built on a field-effect transistor VT1 of the KP350B type. A ferrite bead is put on the output of the capacitor C2, which acts as an inductance L2. This allows you to expand the dynamic range of the receiver by several decibels. The AGC voltage is supplied to the second gate of the UHF transistor. The signal amplified by the cascade is fed to a bandpass filter built on elements L3, C9, C10, C11, C12, L4. The connection of the filter contours is close to critical, and therefore the filter has the most flat top. The filtered signal from the tap of the coil L4 is fed to the mixer, made on the transistor VT2 type KP350B. The second gate of the mixer transistor receives a signal from a frequency synthesizer, which plays the role of the first local oscillator with frequencies of 133,3 - 135,3 MHz, depending on the selected channel. Coil L5 matches the synthesizer with the input of the mixer. The load of the mixer is coil L6. From the output of the mixer, a signal at an intermediate frequency of 10,7 MHz is fed to a Z1 quartz filter of the FP1P1-307-18 type. Resistors R11, R12 and capacitors C18, C19 are used to match the input impedance of the filter with the mixer output and the IF input. The filtered signal at the intermediate frequency through the capacitor C20 is fed to the first gate of the IF transistor VT3 type KP350B. The AGC voltage is also applied to the second gate of this transistor. The load of the IF is the circuit L8, C26. Through the coupling coil L9, the signal from the IF is fed to the DA1 microcircuit, which acts as a second mixer and a second local oscillator. The local oscillator is built on a part of the microcircuit and elements C28, C29, C30, L10, ZQ1. Quartz resonator ZQ 1 - at a frequency of 11,165 kHz. The L10 coil serves to improve the local oscillator voltage shape and is tuned to a frequency of 11,165 kHz. The load of the second mixer is the circuit L11, C31, tuned to the second intermediate frequency, equal to 465 kHz. Through the coupling coil L12, the signal at the frequency of the second IF is fed to the piezoceramic filter Z2 of the FP1P1-60.03 type. Resistors R20, R21 and the circuit L13, C32 match the input and output resistances of the filter with the output of the mixer and the input of the DA2 chip, respectively. The circuit L13, C32 is tuned to a frequency of 465 kHz. After filtering, the signal is fed to a multifunctional DA2 chip of the K174XA6 type, which acts as a second IF, frequency detector, and AGC detector. The reference circuit of the frequency detector L15, C46 is tuned to a frequency of 465 kHz. The internal level meter of the input signal of the DA2 chip is used as the AGC circuit. The output voltage from its output 14 will be supplied to the regulating transistor VT5 tin KT315I. From it, the AGC signal is fed to the second UHF gates VT1 and the amplifier of the first IF VT3. Resistor R22 is used to set the regulation range of the AGC system. The overall range of the AGC system is about 100 dB. Instead of resistor R25, you can turn on an S-meter, which can be used as a 300 μA microammeter, while resistor R23 can be used to adjust its sensitivity and further calibrate. The squelch is also built on part of the DA2 chip. As the working signal of the noise suppressor, the value of the input signal level is used, which is fed to the regulating transistor VT4 of the KT315B type. The output 9 of the printed circuit board is signaled to turn off the noise reduction system. From pin 7 of the DA2 chip, a low-frequency signal is fed to the volume control mounted on the front panel of the radio station, and from it to a low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 3 kHz, where high-frequency noise components are significantly reduced. The filter is built on transistors VT6, VT7 type KT315B and VT8 type KT316E. From the output of the filter, a low-frequency signal is fed to a low-frequency amplifier, the role of which is played by a DA3 chip of the K174UN7 type. The required amplification of the microcircuit can be adjusted by resistor R47. From pin 12 of the DA3 chip, the amplified signal is fed through the capacitor C65 to the headset or dynamic head. The schematic diagram of the transmitting part of the radio station is shown in Figure 2. The frequency-modulated signal from the frequency synthesizer is fed to point 1 of the transmitter board. The circuit L1, C3 is tuned to a frequency of 145 MHz. The adjustable buffer amplifier is assembled on a field-effect transistor VT1 of the KP3501B type. Its second gate will be supplied with control voltage from the output power level switch located on the front panel of the radio station. With this switch, the output power can be abruptly reduced to 0,5 watts. The load of the transistor VT1 is the circuit L2, C8, also tuned to a frequency of 145 MHz. From the tap of the L2 coil, the RF voltage through the capacitor C9, with which an optimal connection between the stages is established, is fed to the second amplification stage, built on a VT2 transistor of the KT399A type. The collector circuit of the transistor includes the circuit L3, C14, C15, tuned to the middle of the range. A line of power amplifiers was built on transistors VTZ, VT4, VT5 of the KT920A, KT920B and KT925V types, respectively. Cascades on transistors VT4 and VT5 operate in high efficiency mode. The mode of operation of these transistors is set by diode stabilizers VD1 - VD4 and resistors R17 and R20. When using this circuit to amplify a single-sideband signal, the cascades on transistors VT4, VT5 can be set to linear amplification mode using the same resistors. From the collector of the transistor VT5, the amplified signal at the operating frequency is fed to the band-pass filter on the elements L15 C40, C41, C42, L16, C44, C45, L17, C46, C47 and then through relay K1, switching the antenna signal, enters the antenna. The transmitting part is powered by a 12 V on-board vehicle battery or from another source. Author: V. Stasenko, Voronezh; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024 Controlling objects using air currents
04.05.2024 Purebred dogs get sick no more often than purebred dogs
03.05.2024
▪ The magnet stops you from lying ▪ Mini Robot for Moon Exploration
▪ site section Digital technology. Article selection ▪ article Control and revision. Lecture notes ▪ article Who gave the name to the city of Los Angeles? Detailed answer ▪ article Damn bush. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Automatic fan switch. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: