Antenna for operation on the range of 160 meters. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / HF antennas
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
On fig. Figure 1 shows the antenna I use on 160m. It consists of a tilted radiator A and three counterweights a, b, c, stretched parallel to the ground.
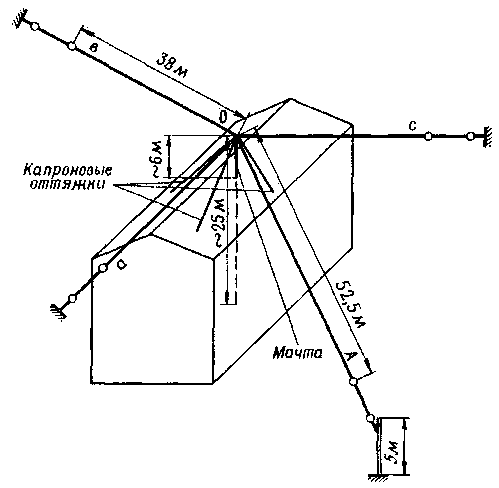
Fig. 1
The antenna is fed with an unbalanced coaxial cable with a characteristic impedance of 75 ohms. The central conductor is connected to a variable capacitor C1 (Fig. 2) of a matching device, which is placed in a moisture-proof box.
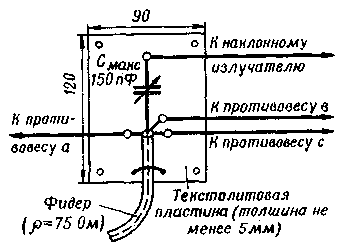
Fig. 2
An SWR meter is required to tune the antenna. First, all counterweights must be disabled. Then, a feeder with a characteristic impedance of 75 ohms is connected to two of them, for example a and c, and, having connected to the transmitter, the SWR is determined in the middle and at the edges of the range. If the SWR is high, then it is necessary to adjust the counterweights by changing their geometric dimensions. A similar operation is performed with the third counterweight, having previously turned off any of the previous ones. After adjusting all counterweights, they are connected to the cable sheath and the inclined emitter is adjusted. By changing the capacitance of a variable capacitor, a minimum SWR value is achieved in the middle of the range.
In the author's version, the SWR of the antenna in the middle of the range was equal to 1.3, at the edges of the range - no more than 1.6.
Author: V. Starostin (UA3PFC), Tula; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section HF antennas.
See other articles Section HF antennas.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Neutrino mass measured
14.10.2019
Neutrinos are responsible for many important processes that take place in stars. This particle was previously predicted only theoretically and was introduced to explain the excess energy that comes from the Sun when thermonuclear reactions take place on it. Observing neutrinos directly is very difficult, and for this, scientists carry out ultra-precise measurements in the water column of a huge volume.
Until recently, it was believed that the neutrino is a massless particle, the same as a photon. But the new study not only claims it has mass, it puts limits on its meaning. To do this, scientists used information from various sources, including space and ground-based telescopes that observe the first light of the universe (cosmic microwave background radiation), supernovae, the largest 3D map of galaxies in the universe, particle accelerators and nuclear reactors.
The analysis method they use can be applied to many other types of particles, the scientists say. With the help of it, it was possible to impose restrictions on the mass of all three types of neutrino - electron, muon and tau. Previously, the approximate total mass of all types of neutrinos was established. Now, scientists have gone further and, using the Grace supercomputer, have calculated the maximum mass of one of the types of particles.
It turned out that the mass of the electron neutrino is about a million times less than the electron itself - 1,5x10^-37 kilograms. According to the data, the measurement confidence interval is 95 percent - this is the probability that the real value will be close to the calculated value within the error.
Scientists were able to get this value using a huge array of modern measuring instruments. But even it is not enough to calculate the approximate value of the mass of the other two types of "ghost particles". According to experts, launching new space telescopes and obtaining data from Cherenkov radiation detectors will solve this problem.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Fish in a wind tunnel
▪ Fertility Coal
▪ Lemon and sun for water disinfection
▪ Dark Sky Conference
▪ Photoelectronic memory based on a colony of bacteria
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Signal limiters, compressors. Article selection
▪ article Shake the dust off your feet. Popular expression
▪ article Where did the word penal servitude come from? Detailed answer
▪ article Screwdriver. Directory
▪ article How to solder SMD. Part one. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article It's the other way around. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: