Indoor magnetic antenna. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / HF antennas
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
For someone who is forced to abandon an outdoor antenna (for example, after moving), things are very bad for a shortwave radio amateur. However, something can always be done to still remain QRV.
A typical solution is a magnetic antenna. Despite satisfactory experience with two homemade indoor loop antennas for 80...10 m bands, there was very little hope that something similar could be done for 160 m.
Based on the well-known Annecke sketch and the loop made from it for 80...30 m, I just wanted to increase the number of turns to four (double). Then the 400 pF capacitor that was used before could be left unchanged.
But this is a theory. What if it fails? Four turns of copper tube with a cross section of 18 mm and a coil diameter of 17 cm - isn't it too expensive for a mistake? After some thought, I came up with a not very expensive solution - to use a thick coaxial cable. Total consumption of materials:
- 4 wooden planks 20 mmx40 mm;
- 12 m of RG-213 coaxial cable;
- 4m coaxial cable RG-58;
- 1 capacitor of variable capacitance 100 pF with a distance between the plates of 2...3 mm;
- 1 coaxial connector.
How the design looks like is shown in Fig.1...3. A cross of wooden planks with cross planks, in which I cut grooves, holds a resonant loop consisting of four turns of RG-213. The upper strips (for the resonant loop and the communication loop) have two holes at the edges to hold the ends of the cable and three grooves between them. The length of the side of the coaxial cable in an almost square suspension is 67 cm. To those who are very bothered that I do not give the dimensions of the wooden cross, I must say that I respect old Pythagoras very much and that, strictly speaking, only the dimensions of the coaxial cable are important.

The screen sheath of the coaxial cable forms the frame of the loop. The cable core is broken at a distance of 3,50 m from one of the ends. The result is a capacitance of about 353 pF connected in parallel to a variable capacitor.
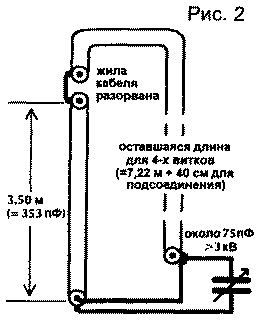
A variable capacitor is connected to both ends of the RG-213 cable sheath. For all connections and connections, a thick copper wire with a cross section of at least 10 mm must be used.2.

For reasons of convenience, the coupling coil is placed on the same strips and also has four turns at a distance of 8 cm from each other. The length of the side is 20 cm here. The RG-58 cable is connected to the input coaxial connector with both ends of the braid.
At resonance SWR = 1,2. The SWR<2 bandwidth is less than 9 kHz. Therefore, it is necessary to adjust the variable capacitor to resonance when tuning over the range. Perhaps this is the only drawback of the magnetic loop!
After going on the air for 15 days in a row (in January 1995) in the morning and in the evening for about one hour, I made 43 QSOs with stations from fourteen countries: DL, SM, SP, G, GL, GM, F , ON, 1, OK, OE, ON, 9A, S5. Unfortunately, I couldn't call many of the stations I heard because they purposefully called "CQ DX". Yet my own CQs only resulted in a few QSOs.
The existing noise level can be reduced by 2 ... 3 points by a slight change in the location of the antenna and its rotation. For a range of 160 m (and 80 m) - this is a true boon!
Since the antenna zeros (more precisely, almost zeros) are very narrow, the orientation of the antenna is completely uncritical.
In conclusion, I would draw the following conclusions:
-
it's not a super antenna, but I'm QRV again on 160m;
-
costs and space occupied by the antenna are negligible;
-
as a high quality symmetrical antenna, it greatly improves safety with respect to BCI/TVI (no RF stray currents);
-
atmospheric interference and local QRM are reduced;
-
accommodation does not depend on weather conditions.
When the antenna is transmitting, do not touch it, otherwise you may get burned.
Editorial note
Instead of the RG-213 cable, any 50 ohm cable with an outer diameter >13 mm can be used.
Literature
- CQ DL 12/96.
Author: W. Shreglman (DJ5QY); Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section HF antennas.
See other articles Section HF antennas.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Toyota BLAID: the wearable device of the future for the blind
10.03.2016
For visually impaired and completely blind people, Toyota plans to release a special wearable device designed to make life easier for them. The novelty is being developed as part of the BLAID project. Traditional walking sticks, trained guide dogs and GPS navigators are not always able to provide enough information about the environment. The new device, according to the developers, will make it easier for the blind to navigate in space, especially in enclosed spaces, such as office centers, shopping malls, and will help identify doors, escalators, stairs and various obstacles.
The novelty is an arc worn around the neck. The device is equipped with cameras that, using special software, recognize surrounding objects, including signs on doors and stores. The user receives information thanks to the speakers and vibration motors. You can use voice commands and buttons to communicate with the device. The BLAID project provides for the integration of mapping technologies, object identification and face recognition.
The manufacturer has already created an early working sample that is being tested by a blind person. The shape of the device may be really convenient, but it will be of interest only in the case of a really high-quality implementation of recognition technologies.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Cell death rate measured
▪ Light leads to the quantum world and the acceleration of supercurrents
▪ The polymer changes color under mechanical stress
▪ Non-contact lie detector
▪ The benefits and harms of video games
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Application of microcircuits. Article selection
▪ article Psychology of work. Crib
▪ article What agricultural output increases when exposed to lightning? Detailed answer
▪ article Mordovnik ordinary. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Logical elements and truth tables. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Battery charger, 2,5 amps. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: