
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING The use of the K174PS1 chip. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Application of microcircuits The widespread introduction of microcircuits in radio devices has made it possible to significantly improve their parameters, reduce dimensions, and simplify installation. Particularly convenient are universal microcircuits that can be used in a wide variety of radio equipment nodes. These include, for example, general-purpose op amps that successfully operate in low-frequency equipment and automation devices. The same versatility, according to the authors, has a functional microcircuit K174PS1. Since it can operate over a wide frequency range, it can be used not only in low-frequency radio equipment, but also in broadcasting and television devices. In the published article, readers are offered some of the possible options for using this microcircuit. The electrical circuit of K174PS1 is shown in fig. 1.
It is a balanced mixer with the following main technical characteristics. Conversion rate, mA/V, not less....... 4,5
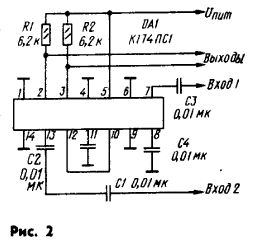
On fig. 2 shows a differential amplifier circuit with adjustable bandwidth and gain. When the maximum (~ 10 V) control voltage is applied through the R3R2 divider to the base of the VTI transistor, the collector current flowing through it completely closes the transistor VT5 of the DA1 microcircuit (see Fig. 1) and excludes the differential stage on transistors VT4, VT6 from its amplifying path. In this mode, the DA1 chip has a maximum (at least 20 dB) transfer coefficient. As the control voltage decreases, the collector current of transistor VT1 will decrease, transistor VT5 of the microcircuit will begin to open and gradually turn on the differential cascade on transistors VT4, VT6. Working in antiphase with the cascade on transistors VT1, VT3, this cascade will reduce the transfer coefficient of the DA1 chip. With a regulating voltage of less than 0,6 V, the transistor VT1 will completely close, the collector currents of the transistors VT2 and VT5 of the DA1 microcircuit will equalize and its transfer coefficient will become equal to zero. The described amplifying device can perform the functions of high-speed 3H amplifiers, RF and AGC amplifiers for radio receivers, and volume controls. The gain adjustment depth is at least 40 dB. The bandwidth can be adjusted by the resistor R3, and the widest (200 MHz) band corresponds to the upper (according to the diagram) position of the slider of this resistor.
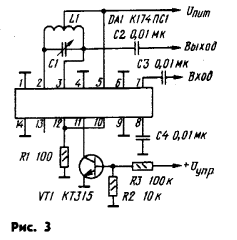
On fig. 3 shows a diagram of a resonant RF amplifier, its transmission coefficient is about 20 dB, the tuning frequency within 160 kHz ... 230 MHz is changed by a variable capacitor C1 included in the L1C1 circuit. The gain of the amplifier depends on the mode of operation of the cascade on the transistor VT1, which allows you to enter the AGC into the amplifier with an adjustment depth of up to 40 dB,
On fig. 4 shows the use of the K174PS1 chip in the frequency converter of a broadcasting receiver. The L1C1 circuit is tuned to an intermediate frequency, the local oscillator setting is determined by the L2C3C4C7VD1 circuit. In the absence of a varicap, elements C7, C1, R2, R2 can be excluded and the local oscillator circuit can be tuned with a variable capacitor connected in parallel with the inductor LXNUMX.
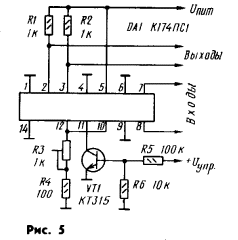
The K174PS1 microcircuit can also be successfully used for detecting balanced-modulated signals in synchronous detectors of color decoders for PAL and NTSC television systems. The scheme of such a detector is shown in Fig. 5. Input 1 is supplied with a color subcarrier signal, and input 2 is a signal from the decoder crystal oscillator. Anti-phase detected signals are taken from resistors R1 and R2. At the output of such a detector, one of the color difference signals is obtained. For another signal, a second detector is needed. This device can also be a frequency doubler, for which it is necessary to combine inputs 1 and 2. Then signals with a double frequency can be taken from the outputs.
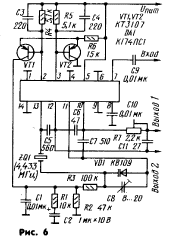
The authors of the article also tested the operation of the K174PS1 microcircuit as a crystal oscillator with a PLL for the color decoder of the PAL system (Fig. 6). The quartz oscillator is assembled on transistors VT2, VT5, and the phase detector on transistors VT1, VT3, VT4, VT6 of the microcircuit (Fig. 1). At the input of the generator through the capacitor C9, a flash signal of the color subcarrier is applied. The phase error voltage of the flash signals of the color subcarrier and the crystal oscillator is integrated by the elements R4, R5, C4, C1, amplified by the differential cascade on transistors VT2, VT1, then reintegrated by the C2C1R1 circuit with a long integration time and fed to the VD10 varicap, thus ensuring the adjustment of the crystal oscillator . At outputs 12 and 180 of the microcircuit, there are two subcarrier signals, shifted one relative to the other by 12 °. The signal is taken directly from terminal 7 to the synchronous detector of the "red" color difference signal, and to the synchronous detector of the "blue" color difference signal - after the R11C90 chain, which shifts the phase of the subcarrier signal by XNUMX °. Literature
Authors: V. Bondarev, A. Rukavishnikov, Moscow; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ ViewSonic VX28ml 2880" 4K Monitor ▪ MAX77801 - new buck-boost regulator for battery power ▪ Panasonic will create TVs 16 times clearer than Full HD ▪ Self-driving cars from Google
▪ site section Batteries, chargers. Article selection ▪ article by Walter Scott. Famous aphorisms ▪ article Why is a mirror considered dangerous? Detailed answer ▪ article Buer Blue bird. Personal transport
Comments on the article: Georgy The author should be more attentive to the information, in the aforementioned Radio magazine, the drawings and links to them were mixed up. Everything got here with errors. Thank you. Maksim Good and useful thing [up]
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: