
|
|
OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH
Instructions for labor protection when working with fiberglass, fiberglass, fiberglass. Full document
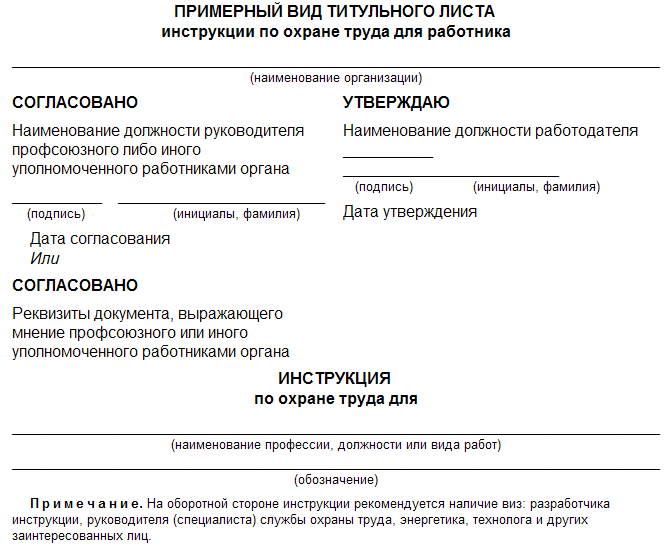
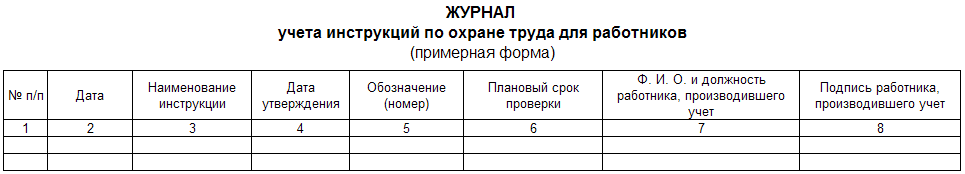
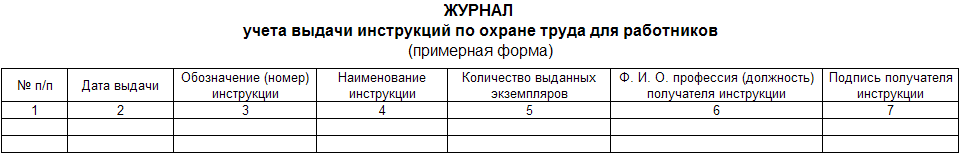
Occupational Safety and Health / Standard instructions for labor protection Abstract Guidelines for the development of instructions for labor protection when using fiberglass, fiberglass and fiberglass. - M.: Publishing house of NTs ENAS, 2004. These guidelines have been developed in accordance with the Guidelines for the development of state regulatory requirements for labor protection, approved by the Decree of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 17, 2002 No. 80, and other current regulatory legal acts containing requirements and norms for labor protection, in order to develop instructions for labor protection labor for employees of various positions and professions associated with the use of fiberglass, fiberglass and fiberglass in the production. The recommendations contain a list and examples of labor protection instructions. On the basis of these recommendations and sample instructions in organizations, regardless of ownership and organizational and legal forms, instructions on labor protection for employees should be developed and approved in the prescribed manner. These guidelines were issued on behalf of the Ministry of Labor and Social Development of the Russian Federation (letter dated May 25.05.2004, 468 No. 7-XNUMX) Introduction In accordance with Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, one of the obligations of the employer is to develop and approve, taking into account the opinion of an elected trade union or other body authorized by employees, instructions on labor protection for employees. Guidelines for the development of instructions for labor protection when using fiberglass, fiberglass and fiberglass (hereinafter referred to as the Recommendations) were developed by LLC "Analysis. Separation. Cleaning." Aeroflot commissioned by the Ministry of Labor of Russia in accordance with the Guidelines for the development of state regulatory requirements for labor protection, approved by the Decree of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 17, 2002 No. 80, and other applicable regulatory legal acts containing requirements and norms for labor protection, in order to develop instructions for labor protection for employees of various positions and professions associated with the use of fiberglass, fiberglass and fiberglass in the production. Currently, in many areas of technology and industry, products made of fiberglass, fiberglass and fiberglass are widely used. These materials are used in industrial construction and engineering industries, in the production of aviation and space technology, laboratory equipment, etc. In addition, fiberglass is used in the manufacture of a wide range of sports products and household appliances. Fiberglass is used on a large scale in the production of glass fabrics, fiberglass, as well as for thermal insulation of pipelines and other objects and products. Fiberglass fabrics are used in the production of glass-reinforced plastics, including as filter materials, especially when filtering aggressive media. The recommendations contain a list and examples of labor protection instructions for workers (Appendix 4), which take into account the basic requirements for labor protection when using fiberglass, fiberglass and fiberglass. The recommendations are intended to assist in the development of labor protection instructions for employees in organizations and employers - individuals, regardless of organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership. Development and approval of labor protection instructions for employees 1. An instruction on labor protection for an employee is developed based on his position, profession or type of work performed. 2. The development of an instruction on labor protection for an employee is carried out taking into account Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. 3. An instruction on labor protection for an employee is developed on the basis of an intersectoral or industry standard instruction on labor protection (and in its absence, intersectoral or sectoral rules on labor protection), safety requirements set forth in the operational and repair documentation of equipment manufacturers, as well as in the technological documentation of the organization, taking into account specific production conditions. These requirements are set out in relation to the position, profession of the employee or type of work performed. An approximate view of the title page of labor protection instructions for employees is recommended to be drawn up in accordance with Appendix 1 to these Guidelines. 4. The employer ensures the development and approval of labor protection instructions for employees, taking into account the written opinion of an elected trade union or other body authorized by employees. A collective agreement or agreement may provide for the adoption of instructions on labor protection in agreement with the representative body of employees. 5. For new and reconstructed productions put into operation, it is allowed to develop temporary labor protection instructions for employees. Temporary labor protection instructions for employees ensure the safe conduct of technological processes (works) and the safe operation of equipment. They are developed for a period until the acceptance of these productions into operation. 6. The employer shall organize the verification and revision of labor protection instructions for employees. The instructions must be reviewed at least once every 5 years. 7. Labor protection instructions for employees may be revised ahead of schedule: a) when revising intersectoral and sectoral rules and standard instructions for labor protection; b) when working conditions of employees change; c) when introducing new equipment and technology; d) based on the results of the analysis of the materials of the investigation of accidents, industrial accidents and occupational diseases; e) at the request of representatives of the labor authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation or the federal labor inspectorate. 8. If during the period of validity of the instruction on labor protection for the employee, the conditions of his work have not changed, then its validity is extended for the next period. 9. The current instructions on labor protection for employees of the structural unit of the organization, as well as a list of these instructions, is kept by the head of the unit. 10. The location of labor protection instructions for employees is recommended to be determined by the head of the structural unit of the organization, taking into account ensuring accessibility and ease of familiarization with them. Labor protection instructions for employees can be handed out to them for study during the initial briefing, or posted at workplaces or sites, or stored in another place accessible to employees. The recommended forms of registers for recording labor protection instructions for employees and recording the issuance of labor protection instructions for employees of organizational units are given in Appendixes 2 and 3 to these Methodological Recommendations. Appendix 1 Appendix 2 Appendix 3 Appendix 4 Sample instructions for labor protection when using fiberglass, fiberglass and fiberglass List of labor protection instructions
Instructions for labor protection when using fiberglass 1. General requirements for labor protection 1.1. On the basis of this Instruction, instructions are developed for labor protection of workers employed in industries using fiberglass. 1.2. During the mechanical processing of fiberglass, glass dust and dust of hardening and binding substances are released into the air zone of industrial premises. The complex of substances released into the air of the working area of fiberglass production depends on the formulation of the binders and other types of raw materials used. 1.3. In the production of fiberglass products using mechanical processing, dust of fiberglass materials, finished fiberglass, talc, silumin, dyes enter the air of the working area. 1.4. When processing fiberglass based on polyester resins, styrene or methyl ethyl ketone peroxide, phthalic and maleic anhydrides, methacrylic acid can be released into the air. From fiberglass based on phenol-formaldehyde resins, phenol, formaldehyde, and aniline are released during processing. If the processed fiberglass was obtained on the basis of epoxy resins, epichlorohydrin, butyl alcohol, and toluene are released. 1.5. When used, including during mechanical or other processing of fiberglass, a worker may be exposed to dangerous and harmful production factors:
1.6. An employee involved in the process associated with the use of fiberglass can also be affected by other hazardous and harmful production factors: moving parts of mechanical equipment, moving raw materials, semi-finished products, containers, elevated temperature of equipment surfaces, elevated air temperature of the working area, increased air mobility, increased electric circuit voltage value, physical overloads. 1.7. To perform work in which fiberglass is used, persons are allowed at least 18 years old who have been trained, instructed and tested on labor protection, who have mastered safe methods and techniques of work, including methods and techniques for the correct handling of fiberglass and those used when working with them chemicals, as well as those who have mastered the methods and techniques for the proper handling of mechanisms, devices, tools and loads. 1.8. When working with fiberglass, including any processes, it is necessary to follow the accepted technology for their processing. It is not allowed to use methods that lead to violation of labor protection requirements. 1.9. If in the course of work there are any questions related to its safe performance, you must contact your immediate or higher manager. 1.10. It is necessary to follow the accepted technologies for cleaning glass-reinforced plastic blanks and parts with organic solvents. 1.11. Employees must comply with the internal labor regulations of the organization. 1.12. Workers working with fiberglass must be provided with overalls and personal protective equipment in accordance with established standards: cotton semi-overalls, a respirator, antistatic shoes. 1.13. The air removed from the place of mechanical processing of fiberglass should be cleaned. 1.14. The room in which work is carried out with fiberglass or products made from them should be isolated from other production areas and equipped with a supply and exhaust ventilation system with air purification and collection of waste generated during the processing of these materials. 1.15. Chambers for work must be sealed and equipped with devices for moving parts. Such devices must be controlled from the outside of the chamber. Observation of the processes in the chamber should be carried out through special windows with glasses of the required strength. 1.16. Hand holes in a closed chamber should not have gaps through which small particles or vapors of toxic substances can enter the room. Elastic gloves and sleeves in the hand holes must be made as one piece. 1.17. In the event of a fire, fire extinguishing agents should be used: foam, water spray, sand, felt mat, carbon dioxide or foam fire extinguishers. 1.18. Upon admission to a job where fiberglass is used, an employee must be instructed on labor protection at the workplace. Conducting an introductory and primary briefing is recorded in the register of briefings on labor protection in the prescribed manner. Repeated briefings and testing of knowledge on labor protection are carried out once every three months with registration in the briefing register. 1.19. The duties of an employee include:
Smoking and consumption of alcoholic beverages in the workplace is not allowed. 1.20. In the event of an accident, the employee must stop work, notify their immediate or superior supervisor and seek medical attention. 1.21. The employee must observe the rules of personal hygiene: before eating and after finishing work, wash hands with warm water and soap; food should be taken in rooms specially equipped for this purpose. 1.22. Employees are responsible for violation of the requirements of this instruction in accordance with applicable law. 1.23. Instructions on labor protection after the employee has passed the initial briefing at the workplace is issued to him against receipt or posted at the workplace. 2. Labor protection requirements before starting work 2.1. Obtain instructions on labor protection from the manager before performing new types of work and when working conditions change. 2.2. Inspect the workplace, put it in order, clear the aisles and do not clutter them up. 2.3. Put on overalls, inspect, tidy up and put on personal protective equipment. 2.4. Arrange the working tool, materials, devices in a convenient and safe order for use. 2.5. Check the serviceability of the valves of the steam pipelines, air pipelines, water supply. 2.6. Check the tightness of the fastening and connection of the hoses. 2.7. Turn on and check ventilation. All work with fiberglass should be carried out only with effective ventilation. Turn on ventilation at least 5 minutes before starting work. 2.8. Check availability and serviceability:
2.9. Check the illumination of the workplace. The voltage for local lighting should not exceed 50 V. 2.10. When working with lifting mechanisms, check their serviceability and comply with the requirements of the relevant labor protection instructions. 3. Labor protection requirements during work 3.1. Keep the workplace clean and free from clutter. 3.2. It is not allowed to work with the use of damaged personal protective equipment. 3.3. Fiberglass cutting must be done with the ventilation turned on and only inside fume hoods. 3.4. When cleaning fiberglass or a product made of it, do not allow solvents to spill onto the floor, and in case of a spill, remove them immediately. 3.5. Cleaning of fiberglass or products from it with chlorinated hydrocarbons must be carried out in sealed installations. 3.6. The use of electric heaters and smoking in the workplace, as well as the performance of any work related to the appearance of a spark or flame, is not allowed. 3.7. It is necessary to wash the fiberglass parts in the bath only with rubber gloves. 3.8. During the lunch break, rinsing baths and solvent containers should be covered with a lid. 3.9. Cleaned blanks and parts made of fiberglass should be transported to the area allocated for the next operation using a lifting mechanism. 3.10. GRP parts should be laid in such a way that they are in a stable position. 3.11. It is necessary to constantly monitor the serviceability of the system of interlocks, alarms, limit switches, chains, hooks and devices for hanging parts and the reliability of their fastening. 3.12. Cleaning and repair of equipment containing residues of organic solvents should be carried out after blowing it with air or steam until the solvent vapors are completely removed. When purging, it is necessary to turn on ventilation devices that prevent pollution of the room air with vapors of organic solvents. 3.13. Do not allow unauthorized persons to work on the installation for cleaning with organic solvents. 3.14. Products and raw materials should be transferred only in serviceable containers. It is not allowed to load containers in excess of the mass allowed by the instruction. 3.15. When preparing cleaning solutions, only detergents approved by the health authorities should be used. 3.16. In the event of a voltage (“shocking” current) on the equipment case, the casing of the ballast, extraneous noise, the smell of burning insulation, spontaneous stop or improper operation of mechanisms and equipment elements, it should be stopped (switched off) by the “Stop” button of the switch and disconnected from the mains using a launcher. Report this to the immediate supervisor and do not turn it on until the malfunction is eliminated. 3.17. When using water to remove dust from walls, windows and structures, electrical devices must be disconnected from the mains during cleaning. 4. Labor protection requirements in emergency situations 4.1. In the event of equipment failure, you must:
4.2. In the event of an accident, you must:
4.3. In case of electric shock, it is necessary to take measures to release the victim from the action of the current as soon as possible and provide him with first aid. 4.4. When rotating parts of machines, slings, load hooks or other equipment capture parts of the body or clothing, give a signal to stop work and, if possible, take measures to stop the machine (equipment). You should not try to free yourself from the grip if it is possible to attract others. 4.5. In the event of a fire, you must:
5. Labor protection requirements at the end of work 5.1. Turn off the unit and other equipment. 5.2. Turn off ventilation. 5.3. Disconnect electrical equipment from the network. 5.4. Close the valves of the steam pipeline, air pipeline and water pipeline. 5.5. Before handing over the shift, check the serviceability of the installation and record the results of the check in the shift acceptance and delivery log, inform the manager about the malfunctions. 5.6. Tidy up the workplace, put the tools and fixtures in the tool box. 5.7. Take off overalls and other personal protective equipment and hang them in a specially designed place. 5.8. Wash hands and face with warm soapy water and take a shower. Instructions for labor protection when using fiberglass 1. General requirements for labor protection 1.1. On the basis of this Instruction, instructions are developed for labor protection of workers employed in industries using glass fiber. 1.2. During the production and textile processing of fiberglass, the air of the working area is polluted with a vapor-gas-aerosol mixture of lubricants, their components and degradation products. 1.3. When working with fiberglass, in particular, its textile processing, glass fiber dust enters the air of the working area. 1.4. Glass fiber dust also enters the air of the working area during thermal insulation work. 1.5. Workers involved in processes involving the use of fiberglass may also be exposed to such harmful and hazardous production factors as moving parts of mechanical equipment, transported or transported raw materials, semi-finished products, containers, elevated temperatures from equipment, heated air, air currents, harmful substances in air and increased physical activity. 1.6. Persons at least 18 years of age who have been instructed and tested on labor protection, have mastered safe work practices, including the correct handling of fiberglass and the chemicals used when working with it, as well as mastered the methods and techniques of correct handling tools, loads, fixtures and mechanisms. 1.7. When working with fiberglass, including any processes that lead to the release of dust and particles of this material into the atmosphere, it is necessary to follow the accepted technology for its processing. It is not allowed to use methods and techniques that lead to violation of labor protection requirements. 1.8. If in the process of work there are questions related to its safe performance, the employee should contact his immediate or higher supervisor. 1.9. Employees must comply with the internal labor regulations of the organization. 1.10. When applying for a job, an employee must undergo an introductory and primary briefing on labor protection at the workplace. Conducting an introductory and primary briefing is recorded in the register of briefings on labor protection in the prescribed manner. Repeated briefings and testing of knowledge on labor protection are carried out once every three months with registration in the briefing register. 1.11. The duties of an employee include:
Smoking and consumption of alcoholic beverages in the workplace is not allowed. 1.12. Workers working with fiberglass must be provided with overalls and personal protective equipment in accordance with established standards. 1.13. The room in which work with glass fiber or products from it is carried out must be isolated from other production areas and equipped with a supply and exhaust ventilation system with air purification and collection of waste generated during the processing of this material. 1.14. Hermetically sealed chambers for working with glass fiber must be equipped with devices for moving parts inside the chamber. These devices are controlled from the outside of the chamber. Observation of the processes in the chamber should be carried out through special windows with glasses of the required strength. 1.15. Hand holes in the closed chamber should not have gaps through which fiberglass dust can enter the room. Elastic gloves and sleeves in the hand holes must be made as one piece. 1.16. In the event of an accident, the employee must stop work, notify their immediate or superior supervisor and seek medical attention. 1.17. An employee working with fiberglass must observe the rules of personal hygiene: before eating and after finishing work, wash hands with warm water and soap; food should be taken in rooms specially equipped for this purpose. 1.18. Employees are responsible for violation of the requirements of this instruction in accordance with applicable law. 1.19. Instructions on labor protection after the employee has passed the initial briefing at the workplace is issued to him against receipt or posted at the workplace. 2. Labor protection requirements before starting work 2.1. Obtain instructions on labor protection from the manager before performing new types of work or when working conditions change. 2.2. Inspect the workplace, put it in order, clear the aisles and do not clutter them up. 2.3. Put on overalls, inspect, tidy up and put on personal protective equipment. 2.4. Arrange the working tool, materials, devices in a convenient and safe order for use. 2.5. Check the serviceability of the valves of the steam pipelines, air pipelines, water supply. 2.6. Check the tightness of the fastening and connection of the hoses. 2.7. Turn on and check ventilation. All work with fiberglass should be carried out only with effective ventilation. Ventilation should be turned on at least 5 minutes before starting work. 2.8. Check availability and serviceability:
2.9. Check the illumination of the workplace. The voltage for local lighting should not exceed 50 V. 2.10. When working with lifting mechanisms, check their serviceability and comply with the requirements of the relevant labor protection instructions. 3. Labor protection requirements during work 3.1. Keep the workplace clean and free from clutter. 3.2. It is not allowed to work with the use of damaged personal protective equipment. 3.3. Fiberglass cutting must be done with the ventilation turned on and only inside fume hoods. 3.4. The use of electric heaters and smoking in the workplace, as well as the performance of any work related to the appearance of a spark or flame, is not allowed. 3.5. It is necessary to wash parts in baths only with protective gloves. 3.6. During the lunch break, solvent containers and rinsing baths must be covered with a lid. 3.7. Fiberglass parts should be transported to the area allocated for the next operation using a lifting mechanism. 3.8. Fiberglass products must be laid in such a way that they are stable. 3.9. It is necessary to constantly monitor the serviceability of the system of interlocks, alarms, limit switches, chains, hooks and devices for hanging parts and the reliability of their fastening. 3.10. Cleaning and repair of equipment on which work with fiberglass was performed should be carried out after blowing it with air until the fiberglass particles are completely removed. When purging, ventilation devices must be turned on to prevent contamination of the room air with glass fiber particles. 3.11. Do not allow unauthorized persons to work on fiberglass processing plants. 3.12. Products and raw materials should be transferred only in serviceable containers. It is not allowed to load containers in excess of the mass allowed by the instruction. 3.13. When using cleaning solutions, only detergents approved by the health authorities should be used. 3.14. In the event of a voltage (“shocking” current) on the equipment case, the casing of the ballast, extraneous noise, the smell of burning insulation, spontaneous stop or improper operation of mechanisms and equipment elements, it should be stopped (switched off) by the “Stop” button of the switch and disconnected from the mains using a launcher. Report this to the immediate supervisor and do not turn it on until the malfunction is eliminated. 3.15. During wet cleaning in the production area, electrical equipment must be disconnected from the mains during cleaning. 4. Labor protection requirements in emergency situations 4.1. In the event of equipment failure, you must:
4.2. In the event of an accident, you must:
4.3. In case of electric shock, it is necessary to take measures to release the victim from the action of the current as soon as possible and provide him with first aid. 4.4. When rotating parts of machines, slings, load hooks or other equipment capture parts of the body or clothing, give a signal to stop work and, if possible, take measures to stop the machine (equipment). You should not try to free yourself from the grip if it is possible to attract others. 4.5. In the event of a fire, you must:
5. Labor protection requirements at the end of work 5.1. Turn off the unit and other equipment. 5.2. Turn off ventilation. 5.3. Disconnect electrical equipment from the network. 5.4. Close the valves of the steam pipeline, air pipeline and water pipeline. 5.5. Before handing over the shift, check the serviceability of the installation and record the results of the check in the shift acceptance and delivery log, inform the manager about the malfunctions. 5.6. Tidy up the workplace, put the tools and fixtures in the tool box. 5.7. Take off overalls and other personal protective equipment and hang them in a specially designed place. 5.8. Wash hands and face with warm soapy water and take a shower. Instructions for labor protection when using fiberglass 1. General requirements for labor protection 1.1. On the basis of this Instruction, instructions are developed for labor protection of workers employed in industries using fiberglass. 1.2. When using glass fabrics, including during their mechanical or other processing, a worker may be exposed to dangerous and harmful production factors:
1.3. When processing fiberglass, the air of the working area is also polluted with a vapor-aerosol mixture of lubricants, their components and degradation products. 1.4. With any type of fiberglass processing, fiberglass and fiberglass dust enters the air of the working area. 1.5. Glass fiber dust from glass fabric also enters the air of the working area when performing thermal insulation work using glass fabric. 1.6. An employee in processes involving the use of fiberglass may be additionally affected by harmful and dangerous production factors: moving parts of mechanical equipment, moving raw materials, semi-finished products, containers, heated equipment, drafts, physical overload. 1.7. To work with the use of glass fabrics, persons are allowed at least 18 years old who have been trained, instructed and tested on labor protection, who have mastered safe methods and techniques of work, including methods and techniques for the correct handling of glass fabrics, chemicals used when working with them, and also mastered the methods and techniques of proper handling of mechanisms, devices, tools and loads. 1.8. When applying for a job, an employee must undergo an introductory and primary briefing on labor protection at the workplace. Conducting an introductory and primary briefing is recorded in the register of briefings on labor protection in the prescribed manner. Repeated briefings and testing of knowledge on labor protection are carried out once every three months with registration in the briefing register. 1.9. The duties of an employee include:
1.10. When working with glass fabrics, including any processes that lead to the ingress of dust and particles of these materials into the atmosphere, it is necessary to follow the accepted technology for their processing. It is not allowed to use methods that violate the requirements of labor protection. 1.11. If in the course of work there are questions related to its safe performance, you must contact your immediate or higher manager. 1.12. Employees must comply with the internal labor regulations of the organization. 1.13. Workers working with fiberglass must be provided with overalls and personal protective equipment in accordance with established standards: cotton semi-overalls or overalls, a respirator, antistatic shoes. 1.14. The room in which work with glass fabrics or products made from them is carried out must be isolated from other production areas and equipped with a supply and exhaust ventilation system with air purification and collection of waste generated during the processing of these materials. 1.15. Chambers for working with glass fabrics must be sufficiently sealed and equipped with special devices for moving parts. Such devices must be controlled from the outside of the chamber. Observations of the processes in the chamber are made through special windows with glasses of the required strength. 1.16. Hand holes in a closed chamber should not have gaps through which small particles of fiberglass and vapors of toxic substances can enter the room. Elastic gloves and sleeves in the handholes must be made as one piece. 1.17. In the event of an accident, the employee must stop work, notify their immediate or superior supervisor and seek medical attention. 1.18. An employee working with fiberglass must observe the rules of personal hygiene: before eating and after finishing work, wash hands with warm water and soap; food should be taken in rooms specially equipped for this purpose. 1.19. Employees are responsible for violation of the requirements of this instruction in accordance with applicable law. 1.20. Instructions on labor protection after the employee has passed the initial briefing at the workplace is issued to him against receipt or posted at the workplace. 2. Labor protection requirements before starting work 2.1. Get a preliminary briefing on labor protection before performing new types of work and when working conditions change from the manager. 2.2. Tidy up the workplace, clear the aisles. 2.3. Put on overalls, inspect, tidy up and put on personal protective equipment. 2.4. Arrange the working tool, materials, devices in a convenient and safe order for use. 2.5. Check the taps of steam pipelines, air pipelines, water pipelines for serviceability. 2.6. Check the tightness of fastening and connection of hoses. 2.7. Turn on the ventilation and check its operation. All work with fiberglass should be carried out only with active ventilation. Ventilation must be turned on at least 5 minutes before starting work. 2.8. Check for correctness:
2.9. Check the illumination of the workplace. The voltage for local lighting should not exceed 50 V. 2.10. When working with mechanisms for lifting and transporting goods, check their serviceability and comply with the requirements of the relevant labor protection instructions. 3. Labor protection requirements during work 3.1. Avoid cluttering the workplace and keep it clean. 3.2. It is not allowed to work with faulty personal protective equipment. 3.3. Fiberglass cutting must be done with the ventilation turned on and only inside fume hoods. 3.4. When cleaning fiberglass or products made from it, do not allow solvents to spill onto the floor, and in case of a spill, clean them up. 3.5. Cleaning of glass fabric or products from it in chlorinated hydrocarbons must be carried out in sealed installations. 3.6. The use of electric heaters and smoking in the workplace, as well as the performance of any work related to the appearance of a spark or flame, is not allowed. 3.7. It is necessary to wash the parts in the bath only with rubber gloves. 3.8. During the lunch break, rinsing baths and solvent containers should be covered with a lid. 3.9. The cleaned fiberglass parts should be transported to the designated area for the next operation using a lifting mechanism. 3.10. Fiberglass parts must be laid in such a way that they are in a stable position. 3.11. It is necessary to constantly monitor the serviceability of the system of interlocks, alarms, limit switches, chains, hooks and devices for hanging parts and the reliability of their fastening. 3.12. Cleaning and repair of equipment containing remnants of fiberglass particles should be carried out after blowing it with air or steam until they are completely removed. When purging, it is necessary to turn on ventilation devices that prevent contamination of the room air with glass fiber particles. 3.13. Do not allow unauthorized persons to work with the use of fiberglass. 3.14. Products and raw materials should be transferred only in serviceable containers. It is not allowed to load containers in excess of the mass allowed by the instruction. 3.15. When preparing cleaning solutions, only detergents approved by the health authorities should be used. 3.16. In the event of a voltage (“shocking” current) on the equipment case, the casing of the ballast, extraneous noise, the smell of burning insulation, spontaneous stop or improper operation of mechanisms and equipment elements, it should be stopped (switched off) by the “Stop” button of the switch and disconnected from the mains using a launcher. Report this to the immediate supervisor and do not turn it on until the malfunction is eliminated. 3.17. When wet cleaning the working area, electrical devices must be turned off. 4. Labor protection requirements in emergency situations 4.1. In the event of equipment failure, you must:
4.2. In the event of an accident, you must:
4.3. In case of electric shock, it is necessary to take measures to release the victim from the action of the current as soon as possible and provide him with first aid. 4.4. When rotating parts of machines, slings, load hooks or other equipment capture parts of the body or clothing, give a signal to stop work and, if possible, take measures to stop the machine (equipment). You should not try to free yourself from the grip if it is possible to attract others. 4.5. In the event of a fire, you must:
5. Labor protection requirements at the end of work 5.1. Turn off the unit and other equipment. 5.2. Turn off ventilation. 5.3. Disconnect electrical equipment from the network. 5.4. Close the valves of the steam pipeline, air pipeline and water pipeline. 5.5. Before handing over the shift, check the serviceability of the installation and record the results of the check in the shift acceptance and delivery log, inform the manager about the malfunctions. 5.6. Tidy up the workplace, put the tools and fixtures in the tool box. 5.7. Take off overalls and other personal protective equipment and hang them in a specially designed place. 5.8. Wash hands and face with warm soapy water and take a shower.
▪ Pickup of parts and products per stream (launcher). Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ Cutter. Standard instruction on labor protection
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ Microcontrollers Texas Instruments MSP432 ▪ 1600W chargers with 19" rack version
▪ section of the site Winged words, phraseological units. Selection of articles ▪ article Slavic promiscuity. Popular expression ▪ article Is it true that water in which a silver object is immersed kills germs? Detailed answer ▪ May lily of the valley article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 