 Free technical library
Free technical library
Hay lift. Drawing, description

Directory / Tools and mechanisms for agriculture
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
With the growth of livestock on farmsteads, it became necessary to increase the fodder base. Forage harvesting is a very laborious process, requiring great effort, and the weather does not allow enough fine days for this. Manually, in the old fashioned way with a scythe and a rake, it became increasingly difficult to cope with this task. Meanwhile, trucks and tractors gradually began to appear in private households. They needed various agricultural implements, trailed and mounted units. In particular, balers began to be used for harvesting hay. Now hay is pressed into rolls of about 200 - 300 kg. They have to be transported from the field to the storage area. But try to lift such a weight and throw it into the back of a truck or even lift it onto a tractor cart! Therefore, the idea arose to make the so-called tractor bale lift - a rear-mounted unit powered by a tractor hitch.
This idea was brought to life last year. It turned out, in my opinion (and neighbors too), a simple and very easy-to-use loader. The main details in it are a fork-grip, a mast, an arrow and traction, a base, and even a power cylinder, which, however, you cannot do yourself. Of course, I had to make things from what was available or came to hand, mainly at a scrap yard.
The main part of the mechanism - the mast - was built from the pushing beam ("carrier") of the bulldozer knife of the DT-75 tractor. It was a box-shaped thick-walled beam with a section of 140x120 mm and a length of more than 3500 mm. I cut it to the desired length - 2007 mm. I was lucky, not having such a pipe, I would have to weld it from channels or corners.
Under the mast base - a horizontal support, I took a rectangular pipe 120x100 mm 800 mm long - according to the dimensions of the tractor hitch. I put plugs with pins on both ends of it - they are needed to connect the base to the hinge.
The welded connection of the mast with the support was reinforced with scarves, in order to avoid breaking this place when lifting the load.

Lift scheme: 1 - fork; 2 - copying rod (O50); 3 - arrow (100x100x4); 4 - mast (140x120x6); 5 - main thrust (40x40x4); 6 - base beam (120x100x4); 7 - slope (60x60x3); 8 - power hydraulic cylinder; a - h - splints of arrows and bases

Mast base and guide rod

Fork grip. Above the main beam fastening of an arrow and a copy rod
The mast also needs a lifting boom. For it, I used a wheel support balancer from an LDG-10 cultivator with a profile measuring 100x100 mm, from which I made a blank for such an arrow 1250 mm long. Now it's the turn to articulate both parts in the upper part. To do this, two plates with holes for the pin were welded to the walls at the end of the boom. I welded a sleeve under the same cotter pin to the main mast. By connecting the boom and the mast, I got, as it were, one folding part, made up of two parts.
I took the hydraulic cylinder for lifting the boom from the PKU-08 front loader. Its weight is about 30 kg. For my lift, it was important that its center distance was at least 940 mm, and the piston could extend up to 630 mm.
For the manufacture of the fork, I used part of the KPS-4 trailed cultivator and the GAZ-53 axle shaft. From the trimming of the trailer, I received the base of the grip - a beam with a section of 110x70 mm and a length of 500 mm. Two axle shafts with a diameter of 40 mm and a length of 78 mm went to the teeth. For articulation with traction and boom, I cut out lugs with holes for cotter pins. All connections between these parts are welded. In addition, a metal strip additionally strengthened the teeth with the base, in order to avoid their deflection under the weight of hay rolls.
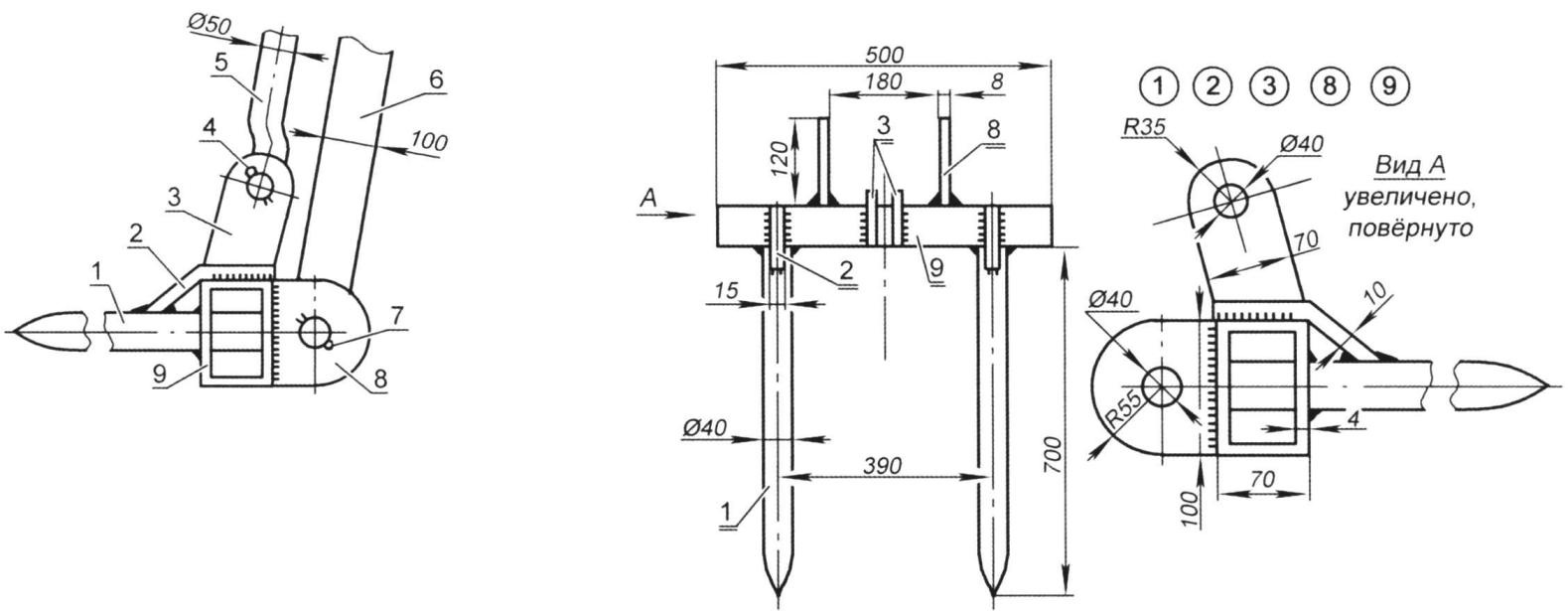
Link, boom and fork connection unit (click to enlarge): 1 - grip tooth; 2 - overlay; 3 - thrust eye; 4,7 - cotter pins; 5 - copying thrust; 6 - arrow; 8 - boom eye; 9 - base

Mast base (click to enlarge): 1 - mast; 2 - slope; 3 - base beam; 4 - plug; 5 - pin
It was also necessary to make sure that the gripper constantly kept a horizontal position during raising and lowering the boom. To do this, I took a piece of a thick-walled pipe 1350 mm long and welded its eyes to both ends. The result was a "copying" arrow thrust (passing parallel to the arrow from the top of the mast to the grip). For fastening the thrust, it was necessary to weld lugs to the end of the mast - from two more metal plates 8 mm thick and 23 mm high.
The lower end of the rod was bent at a slight angle and connected to the base of the fork. This is done so that when the boom is fully raised, the grip is somewhat lowered down from the horizontal position. This made it possible to put the roll in the body of a car, trailer, both lying down and standing up.
From another thick-walled square pipe with dimensions of 40x40 mm, I made the main thrust 2100 mm long. It had to pass from the top of the mast to the bracket of the central link of the tractor linkage. Therefore, I again welded lugs to its upper end, and a hinge with a fastening screw to its lower end. Such a long thrust helped to increase the travel of the mast.

Tractor bale lifter, rear-mounted unit powered by a tractor hitch

The "carrier" (shown by the arrow) of the bulldozer knife of the DT-75 tractor. Similar was used to make the lift mast

The balancer (shown by the arrow) of the wheel support of the ploughshare LDG-10. The same was used to make
Acting with a tractor linkage, I got the opportunity, due to the work of a long traction, to tilt the mast of the lift at a certain angle as needed, and with the help of a power cylinder, to control the boom. The parallelogram formed by the boom, the copying rod and both sides of their attachment, allows you to keep the fork in a horizontal position under the load. In the future, with the fork removed, it is possible to make and insert a removable extension with a hook inside the boom, which will make it possible to lift not only hay rolls, but also other various loads weighing up to 700 kg.
In conclusion, I must note that the labor I spent on the manufacture of such a lift was fully justified. The mechanism showed itself well in operation, allowing us to minimize the time required for hay harvesting in our farm.
Author: N.Golovanov
 We recommend interesting articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture:
We recommend interesting articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture:
▪ Dirt cleaning machine for a well
▪ Electric grater
▪ Auger juicer
 See other articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture.
See other articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Optical relay will help speed up the Internet
13.10.2012
A new micro-optical device, developed by researchers at the University of Minnesota, could significantly increase the speed of downloading files from the Internet, as well as reduce the cost of transferring data over the global network. The tiny device uses the power of light to switch a microscopic trigger at high speed. This allows the signal to be processed using light rather than electrical current, resulting in higher performance and lower power consumption.
The development of scientists is based on the discovery of 2008, when it was found that nanoscale channels can be used to create a force sufficient to mechanically move the optical waveguide. The new device succeeded in amplifying this effect so much that with the help of light it is possible to completely control the mechanics of the optical analogue of an electromechanical relay. In other words, scientists were the first to use the optical-mechanical effect to amplify optical signals without converting them to electrical ones. The new device has two optical waveguides, between which is placed a donut-shaped microscale resonator. This optical resonator amplifies light hundreds of times.
Due to the resonance effect, the optical signal in the first waveguide is greatly amplified in the resonator and generates a very strong optical power in the second waveguide. The second waveguide oscillates like a tuning fork and changes the properties of the optical signal. Since the power of the second optical signal can be many times higher than the first, the device functions as a mechanical relay that amplifies the input signal.
So far, the new optical relay operates at a frequency of a million cycles per second. The researchers plan to increase the frequency to several billion cycles per second. Although, it should be noted that the current indicators are high enough so that the optical relay can significantly increase the speed of information transfer.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Bloodhound Mouse
▪ Sega is ditching blockchain games in favor of classics
▪ The danger of crab sticks
▪ New family of multi-channel DACs
▪ Tetris against psychological trauma
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Labor protection. Selection of articles
▪ article Ministerial leapfrog. Popular expression
▪ article How big is the solar system? Detailed answer
▪ auto electrician article. Job description
▪ article Homemade wind power plant. Springs. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Amplifier at 144 MHz (on a GU35b lamp). Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese









 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 