 Free technical library
Free technical library
Blanket for concrete. Tips for the home master

Directory / Builder, home master
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Like a thick carpet measuring 400x1500x40 mm, it spreads on the surface of freshly laid concrete, warming it up and thereby accelerating setting, hardening and drying.
Portable building heating pads were proposed by the participants of the NTTM of the Kuibyshev Civil Engineering Institute named after A. I. Mikoyan. They have already found wide application at the construction sites of Kuibyshevgidrostroy, where they are used for active heat treatment of concrete and reinforced concrete structures up to 250 mm thick with one-sided heating and up to 500 mm with two-sided heating.
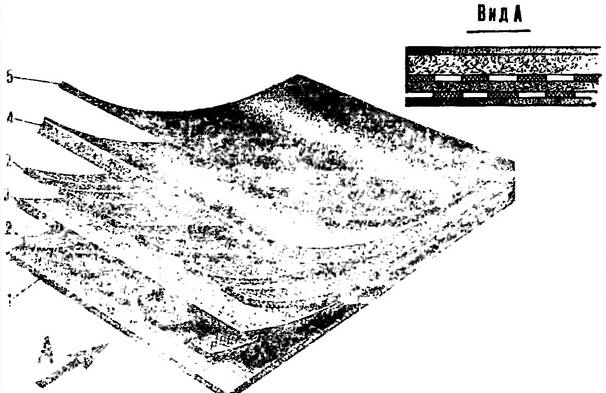
Construction heater: 1, 5 - rubberized fabric, 2 - mesh heaters, 3 - glass wool, 4 - moisture glass wool
In the context of the blanket is a multi-layered "pie". The role of "crusts" in it is performed by a rubberized fabric, which forms an outer moisture-proof shell. Immediately behind it are two layers of mesh heaters, separated by moisture-resistant glass wool. They are covered with a thick heat-insulating layer of glass wool. The heating elements are made in the form of mesh strips 250 mm wide, placed at a distance of 100 mm from each other and connected in series by soldered copper plates.
The maximum temperature reached by the heaters is 180 °C, at the contact surface "blanket - concrete" up to 80 °C.
The blanket can be successfully used for many other construction needs: warming up the soil in winter, drying and heating floors, bases for a soft roof.
 We recommend interesting articles Section Builder, home master:
We recommend interesting articles Section Builder, home master:
▪ weather indicator
▪ Corner mini fireplace
▪ Careful topping up of water in the aquarium
 See other articles Section Builder, home master.
See other articles Section Builder, home master.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Clean energy from the air
19.03.2023
Scientists have discovered that one of the "relatives" of the tuberculosis bacterium is an enzyme that converts hydrogen into an electric current.
The researchers believe that the discovery can be used for a new way to get energy from the air. This is Mycobacterium smegmatis, a bacterium that uses the Huc enzyme to generate energy from hydrogen in the atmosphere, allowing it to survive in extreme nutrient-deficient environments.
The scientists said they had discovered and studied an enzyme that could be used as a source of clean energy to power laptop computers.
"We believe that a power source containing the Huc enzyme could power a range of small portable devices, including biometric sensors, environmental monitoring devices, digital clocks, calculators, and even simple computers," said study lead author Reece. Grinter, a microbiologist at Monash University in Australia.
It is a rapidly growing, non-parasitic bacterial substance that is often used to study the cellular structure of the causative agent of tuberculosis, Mycobacterium smegmati. This bacterium has been known for years to convert hydrogen into electricity. Scientists have found that it is able to survive in harsh weather conditions such as Antarctica, volcanoes and deep oceans, where there are very few other sources of energy.
“If you provide the Huc enzyme with more concentrated hydrogen, it will produce more electrical current. This means that the Huc enzyme can be used in fuel cells to power more sophisticated devices such as smartwatches or smartphones, more sophisticated laptop computers, and perhaps even cars.” "Grinter explained.
The scientists found a charged structure in the center of the Huc enzyme containing nickel and iron ions. When a hydrogen molecule enters the active zone, protons and electrons find themselves in a chain between nickel and iron atoms. The enzyme then sends the electrons to "conductive pathways" that conduct electrical current.
Experiments have confirmed that Huc is able to persist for a long time and can absorb hydrogen in a negligible concentration, which is 0,00001% of the volume of air inhaled by a person. The scientists believe that these properties, combined with the bacteria's omnipresence, could be ideal candidates for a clean energy source for organic batteries.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Underwater photo will become clear
▪ Cocoa - protection against hypertension
▪ Alcatel OneTouch POP7 and POP8 tablets
▪ Sunscreens should be protected from chlorine
▪ More wives - fewer children
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Reference materials. Article selection
▪ article Morals of Rasteryaeva Street. Popular expression
▪ article What is the plague? Detailed answer
▪ article System Administrator. Job description
▪ article Autoguard. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Interference-proof telecontrol system. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 