
|
|
BUILDER, HOUSEHOLDER
Garden sofa. Tips for the home master
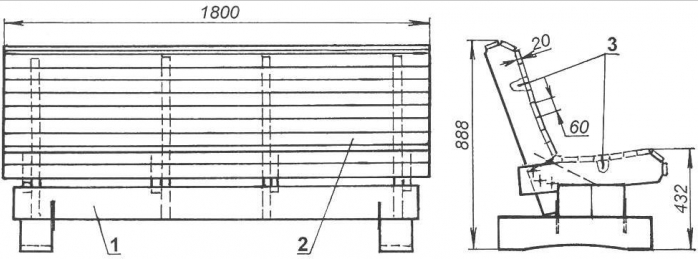
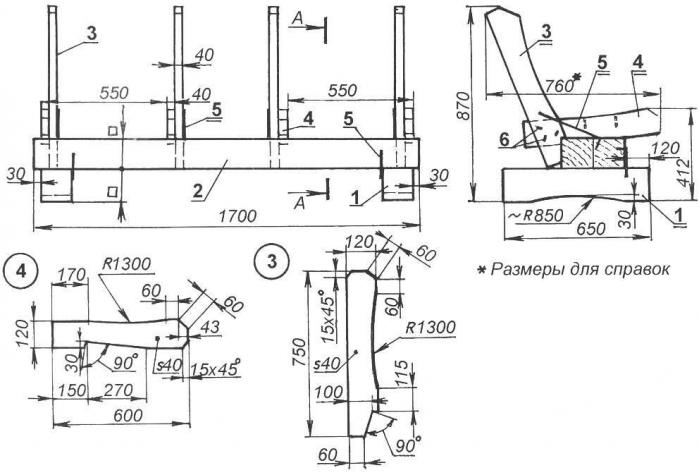
Directory / Builder, home master Mankind has made and described a huge number of different garden benches. But two reasons did not allow us to take advantage of centuries of experience: the lack of special materials and the availability of suitable materials. Almost always, after the construction of a more or less significant building, scraps of pine beams and boards remain. This happened to me too. It was from these that I decided to build a garden bench, or rather, a small but comfortable sofa. During the preliminary design, the idea of making a sofa in the style of the middle of the last century was visible - similar ones were installed in parks, squares and even train stations. On such a sofa (with smooth oval transitions in the profile between the seat and back), even hard, one could sit “tirelessly” for hours. Cast iron patterned cast sides with legs provided them not only with beauty and strength, but also gave them some special monumentality. Unfortunately, I didn’t have exactly such sidewalls. Therefore, the design had to be reworked and adapted to the available materials. As a load-bearing beam, I used a pair of cohesive (joined along the length) pine beams with a cross-section of 140x140 mm, their ends rest on two legs made of the same, but single beam. In the soles of the paws, I used an ax to cut out indentations with a radius of 850 mm, leaving rectangular heels at the ends - with such supports the sofa will be stable even on a not very level area. Instead of cast-iron sidewalls, I made wooden composite elements (I used magpie boards for them) and secured them with brackets on the beam not only on the sides, but also a couple more in the middle part. These elements (I’ll call them ribs) were also formative for the seat and back of the sofa. To do this, in their corresponding edges, I again carefully cut out smooth depressions along the marked radii with an ax, and sawed off large chamfers at the corners.
I first primed the legs, beam and ribs and then painted them with white acrylic paint for exterior use (the color doesn’t matter, I just had leftovers). I prepared a primer from the same paint, diluting it thinner with solvent. The seat and back of the sofa were made from planks with a section of 20x60 mm. I made the planks themselves from twenty boards, having first carefully planed them on one side, and then sawed them lengthwise into several pieces of 60 mm width (as many as would fit). The edges of the planks were also planed, and the upper ribs were blunted. The bottom of the planks was painted with the same white paint with a preliminary primer, and the front surface and edges were first impregnated with hot clear yacht varnish, and then (after drying) covered with another layer of “room” temperature varnish. Final assembly is not only not difficult, but even a pleasant experience - after all, a new product is born! Assembly order I laid the beam on its feet and fastened the parts with nails and staples. I made the staples from smooth reinforcing wire with a diameter of 6 mm with dimensions “in place”. I also “locally” determined the direction of the staples’ whiskers: in this case, I turned them 90 degrees relative to each other.
The finished sofa is installed in a beautiful and cozy corner of the garden or in a gazebo. There are no special requirements for the quality of the source materials: the length would be enough (by the way, one of the beam beams is composite, and the other is glued along a longitudinal crack), and there would only be fewer resin knots on the front surfaces of the seat and back trim strips. By the way, it would be nice to make planks from hardwood. The first tests - relaxing on the sofa - confirmed the ergonomics and convenience of the design. Even some massiveness is beneficial - the sofa does not move from an accidental push and does not break under a heavy rider. Having laid out a rug (and in cool weather, covered with a blanket), it is useful and pleasant to spend a quiet hour in the shade of the garden. Author: A.Matvejchuk
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ 3D printed objects change shape and color ▪ The neural network independently repeated the discovery of Copernicus ▪ Discovery of waves in Jupiter's magnetosphere ▪ durian antibacterial dressings
▪ website section Television. Article selection ▪ article Pass fire, water and copper pipes. Popular expression ▪ article Which planets rotate in the opposite direction? Detailed answer ▪ Article Librarian. Job description
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 