Charging with stable current. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
There are several methods for charging batteries: direct current with voltage control on the battery being charged; at constant voltage, controlling the charging current; according to Woobbridge (ampere-hour rule), etc.
Each of these methods has both advantages and disadvantages. In fairness, it should be noted that the most common, and reliable, is still DC charging. The emergence of microcircuit voltage stabilizers that allow you to work in the current stabilization mode makes the use of this method even more attractive. In addition, only direct current charging provides the best recovery of battery capacity, when the process is divided, as a rule, into two stages: charging with rated current and half as much.
For example, the rated voltage of a battery of four D-0,25 batteries with a capacity of 250 mAh is 4,8 ... 5 V. The rated charging current is usually chosen to be 0,1 of the capacity - 25 mA. Charge with such a current until the voltage on the battery reaches 5,7 ... 5,8 V with the charger terminals connected, and then continue charging with a current of about 12 mA for two to three hours.
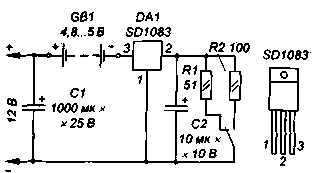
The charger (see diagram) is powered by a rectified voltage of 12V. The resistance of current-limiting resistors is calculated by the formula: R = Ust / I, where Ust is the stabilization voltage of the microcircuit stabilizer; I - charging current. In the case under consideration, Uct = 1,25 V; respectively, the resistance of the resistors - R1 \u1,25d 0,025 / 50 \u2d 1,25 Ohms, R0,0125 \u100d XNUMX / XNUMX \uXNUMXd XNUMX Ohms.
The device can use SD1083, SD1084, ND1083 or ND1084 chips. The stabilizer must be installed on the heat sink. It is possible to reduce the supply voltage of the charger and thereby reduce the power allocated to the stabilizer, however, it is advisable to supply it with such a voltage in order to be able to charge other types of batteries.
A close analogue of the SD1083 stabilizer is the domestic KR142EN22 microcircuit. The stabilizer KR142EN12 is also applicable.
Author: V. Sevastyanov, Voronezh; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Bilateral solar panels
22.01.2021
An international team from the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology in Saudi Arabia (KAUST) and the University of Toronto Engineering (Canada) has developed a solar cell that combines the best features of perovskite and silicon technologies.
Today there are tandem solar cells that combine perovskite and silicon. Compared to conventional silicon batteries, these cells are more efficient at converting sunlight into electricity by absorbing additional spectrum.
Specialists offer a two-way tandem configuration, which not only absorbs the widest possible spectrum of direct sunlight, but also captures scattered reflected light (albedo). This design allows the battery to generate a record amount of energy.
The new batteries are double sided. Their front part captures direct sunlight, and the back part captures the light that is reflected from the ground or other surfaces. It is important that such batteries can be produced on existing equipment without complicating the technology.
The potential for capturing indirect sunlight has been studied before, but so far it has not been possible to verify it experimentally. Now, researchers have finally been able to solve the scientific and engineering challenges required to absorb indirect light. Tests have shown that the bifacial tandem solar array generates nearly 25% more power than any commercially available solar panel.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Sony a42 II full frame 99MP camera
▪ Physical culture computer game EA SPORTS Active 2.0
▪ Y-chromosome deciphered
▪ Communication with sensors through the wall
▪ Nanodiamonds for LEDs and Semiconductors
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Power supplies. Article selection
▪ article A comrade flies to a distant land. Popular expression
▪ article Who is considered the world's first programmer? Detailed answer
▪ article Mother and stepmother ordinary. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Built-in digital voltmeter with a measurement range of -199,9 ... +199,9 mV. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Local oscillator for KB transceiver. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: