Application of PIN diodes as damping and switching elements. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Nodes of amateur radio equipment
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
An article by Max Perner, DM2AUO, discusses the use of PIN diodes as damping and switching elements, made possible by their high on-resistance and very low on-resistance. So, common PIN diodes VA182, VA282, VA479, VA482, VA679 (SMD) have an open resistance of 0,3 ... 0,5 Ohm and a dissipation power of 1 ... 2.5 W. The simplest application of PIN diodes would be as switches in series and parallel circuits (Figure 27, top and bottom, respectively).

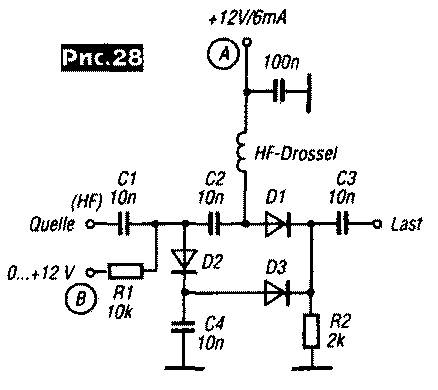
In a series circuit, the diode passes a signal from the source to the load in the open state when an appropriate bias voltage is applied, and in the parallel circuit, in the open state, the diode shunts the signal source, shorting the capacitors Sk to a common wire. Fig. 28 shows a combined diagram of a switch on D1, similar to Fig. 27, and an attenuation element on D2, D3. When a bias is applied to point A, the attenuation between the signal source and the load is minimal. If > 0 ... + 12 V is applied to point B, the current will flow through R1, D2, D3, R2 and, depending on its value, the resistance D2 will change, while part of the input RF signal is closed to ground through C4.
A simple switch of two RF signals is shown in Figure 29. When this circuit switches filters, mixers, etc. it should be taken into account that at the moment only one of the two sources can be turned on, and the other must be grounded.
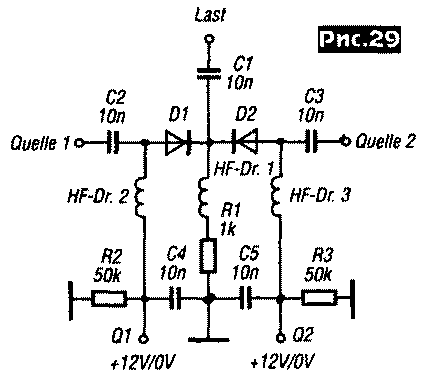
The resistance R1 is determined by the type of PIN diode. PIN diodes can be used as antenna receive/transmit switches (Fig. 30).
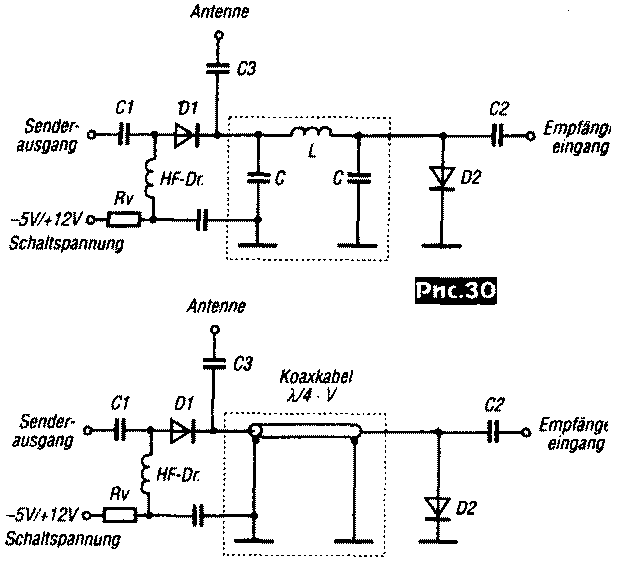
Usually, a quarter-wave strip line or a coaxial cable of the same length is connected between the receiver input and the transmitter output (Fig. 30, bottom), and on the KB - a U-shaped LC analog of a quarter-wave line (Fig. 30, top). The L and C values of this chain are calculated by the formulas:

where Zo is in ohms, f is in MHz, L is in µH, C is in pF. With an operating frequency of 28 MHz, a resistance of 50 ohms, we get L \u0,28d 113,7 μH and both capacitors are XNUMX pF each. The power loss is calculated by the formula:

With an output power of 20 W, the resistance of the diode D1 in direct connection is 0,5 ohms, the power loss will be 0,2 W. If the SWR (S) at the output is noticeably greater than 1, the power loss, taking into account the SWR (S), can be determined by the formula:

For the given example, with KCB=S=3, a power loss of 0,45 W can be expected. Thus, it becomes possible to use widely used PIN diodes in QRP transceivers. The use of switches on PIN diodes significantly reduces the time for switching from reception to transmission, which is especially important when working with digital modes of communication. In receive mode, to eliminate intermodulation distortion on D2, it is important to turn off the PIN diodes well by applying a negative bias to the circuits in Fig. 30
Author: Max Perner, DM2AUO; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Nodes of amateur radio equipment.
See other articles Section Nodes of amateur radio equipment.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024
In a modern technology world where distance is becoming increasingly commonplace, maintaining connection and a sense of closeness is important. Recent developments in artificial skin by German scientists from Saarland University represent a new era in virtual interactions. German researchers from Saarland University have developed ultra-thin films that can transmit the sensation of touch over a distance. This cutting-edge technology provides new opportunities for virtual communication, especially for those who find themselves far from their loved ones. The ultra-thin films developed by the researchers, just 50 micrometers thick, can be integrated into textiles and worn like a second skin. These films act as sensors that recognize tactile signals from mom or dad, and as actuators that transmit these movements to the baby. Parents' touch to the fabric activates sensors that react to pressure and deform the ultra-thin film. This ... >>
Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024
Taking care of pets can often be a challenge, especially when it comes to keeping your home clean. A new interesting solution from the Petgugu Global startup has been presented, which will make life easier for cat owners and help them keep their home perfectly clean and tidy. Startup Petgugu Global has unveiled a unique cat toilet that can automatically flush feces, keeping your home clean and fresh. This innovative device is equipped with various smart sensors that monitor your pet's toilet activity and activate to automatically clean after use. The device connects to the sewer system and ensures efficient waste removal without the need for intervention from the owner. Additionally, the toilet has a large flushable storage capacity, making it ideal for multi-cat households. The Petgugu cat litter bowl is designed for use with water-soluble litters and offers a range of additional ... >>
The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
The stereotype that women prefer "bad boys" has long been widespread. However, recent research conducted by British scientists from Monash University offers a new perspective on this issue. They looked at how women responded to men's emotional responsibility and willingness to help others. The study's findings could change our understanding of what makes men attractive to women. A study conducted by scientists from Monash University leads to new findings about men's attractiveness to women. In the experiment, women were shown photographs of men with brief stories about their behavior in various situations, including their reaction to an encounter with a homeless person. Some of the men ignored the homeless man, while others helped him, such as buying him food. A study found that men who showed empathy and kindness were more attractive to women compared to men who showed empathy and kindness. ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive The two-photon method made it possible to increase the accuracy of nanoscale measurements by a hundred times
14.05.2018
The accuracy of measuring the size of nanostructures has been increased by at least a hundred times, thanks to the work of researchers from the University of Warwick, the QuantIC center and the University of Glasgow. A new method using pairs of photons, the fundamental particles of light, makes it possible to measure the thickness of objects 100 times smaller than the diameter of a human hair, with an accuracy 100 times greater than any other method.
The new measurement method uses a source that emits pairs of photons that are almost identical in all respects. These photons are separated using a component called a light splitter, about 30 thousand pairs of photons are used to carry out one measurement cycle, and about 500 billion photons are used to carry out the entire measurement as a whole.
One of the photons, photon A, remains inside the light splitter, and the second photon, photon B, passes through the object, causing its speed to slow down somewhat. After that, photon B again returns to the light splitter and leaves it together with photon A. Measuring the delay between the exit of photons A and B from the splitter gives the value of the thickness of the object through which photon B passed. And the accuracy of such measurements is at least 100 times higher than the accuracy similar measurements made with only one photon.
With this method it is possible to measure objects made of transparent material. But even this is quite enough to study the structure and properties of cell membranes, DNA molecules. In addition, the new measurement method can be used for quality control in the production of graphene and other conventionally two-dimensional materials.
"The most interesting thing about this achievement is that the measurements are not carried out with the help of some unstable quantum technologies, but with the help of sensors based on time-tested conventional physical principles," says Dr George Knee, who developed the theoretical basis of the experiment. , - "A higher measurement accuracy was obtained by us due to the special adjustment of the interferometer and its constant recalibration, which made it possible to eliminate the slow time and temperature drift."
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Project Jacquard for creating electronic clothing
▪ Superconductor without limits
▪ White graphene for microcircuit cooling
▪ ZL60301 - transmitter for fiber optic systems
▪ Bacteria can survive interplanetary travel
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Normative documentation on labor protection. Article selection
▪ article Nestlings of Petrov's nest. Popular expression
▪ What country is named after Christopher Columbus? Detailed answer
▪ article Oliva cultural. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Universal radio signaling. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article 144 MHz power amplifier. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese







 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: