
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UHF amplifier from SKD-1. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Antenna amplifiers The use of an amplifier with high selectivity can significantly improve the reception of signals from UHF stations, as well as eliminate interference from neighboring nearby stations. The SK-D-1 block, which was used in tube-semiconductor TVs, was taken as the basis. A simple alteration of the SK-D-1, which even a novice radio amateur can perform, allows you to get a UHF signal amplifier with good performance characteristics:
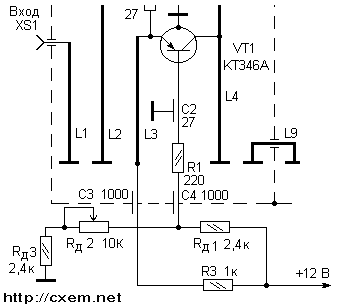
The advantages of such an amplifier include high selectivity, significant noise suppression on adjacent channels. There is also a drawback - this is the need for restructuring (by rotating the rotor knob) when switching to another channel. However, if reception is carried out on one UHF channel, then the need for restructuring is eliminated. Let's take a brief look at the original SK-D-1 scheme. In the first chamber there is the first stage of the block, made on the transistor T1, which operates in the amplification mode with OB. Resonator L1 provides input matching with the antenna, L2 with capacitances C11 and C12 forms a tunable input circuit for tuning to the desired channel. The collector of the transistor T1 is loaded on the circuit L4 C13 C14, which is located in the second chamber. Next, the signal passes to the circuit L5 C15 C18, located in the third chamber. Due to the inductance L6, the signal enters the emitter of the transistor T2. On the transistor T2, an RF signal converter is assembled into the IF of the TV. Transistor T2 is connected according to the capacitive three-point circuit, the load of the cascade is Dr1, which, together with C17, C18, C8, L7, C20, is located in the fourth chamber. Alteration SK-D-1 is as follows: - since in real conditions the first stage on the transistor T1 is controlled by the AGC system of the television receiver, it is necessary to set the normal, without AGC, operating mode by introducing a voltage divider across two resistors; - transfer of the second stage on the transistor T2 from the conversion mode to the amplification mode, which is achieved by removing several elements. Before starting work, remember that you need to handle the unit carefully, because. the slightest changes in the arrangement of parts with careless disassembly can cause detuning of circuits with resonant circuits. So, having removed the spring bar on the top of the cover, carefully remove the cover itself. The number of cameras (and there are only 5 of them) is counted starting from the antenna input socket. Carefully inspect the interior installation. There should be no obvious damage inside - burnt and broken resistors, capacitors. When the handle of the vernier mechanism is rotated, the movement of the plates of the quadruple capacitor must be free, without closing the plates between themselves or with other elements. When working with the block, it is impossible to change the position of the trimmer capacitors, made in the form of silver-plated plates and located in front of the sections of the variable capacitor, as well as resonant lines, made in the form of silver-plated tires and wire segments. Solder the following items carefully: - C8, C20, Dr1 - which are located in the 4th chamber; - L8, Dr2 and R7 - which are located in the 5th chamber. Resistor R7 may be missing in some instances of SK-D-1. Next, you need to determine the brand of transistors that are available in your SK-D-1 block. The fact is that instead of the transistors indicated in the diagram in Fig. 1, there may be others, for example, AF-239 and AF-139, which are analogues of the GT346A and GT346B transistors, respectively. If a GT2B or AF-346 transistor is installed as T139, then it will have to be removed and replaced with GT346A. Transistors of this type are used in almost all SK-D units, as well as in SK-M units with electronic tuning, so in principle it is not difficult to find such a transistor. Before installing a new transistor, it should be checked. If the test is carried out with an ohmmeter, it should be remembered that the supply voltage of the ohmmeter may exceed the allowable reverse voltage of the emitter junction. Therefore, when determining the health of the transistor with an ohmmeter, you should not use the low-resistance limits of the ohmmeter. If there is a choice of several transistors, then you should choose a transistor with the largest possible h21e. Before installing the transistor, it is necessary to connect its common output ("body") by soldering to the body of the transistor itself. Above the camera window, in which the transistor is located, there may be a piece of thin silver-plated wire. This segment is the "tail" of L6. Therefore, in no case do not try to remove it by soldering. Due to heating, the position of L6 in space may change, which will lead to a detuning of the circuit. Removal can be done by biting off the "tail" with side cutters. The body terminal of the transistor T2 should be inserted into a small hole that is under the resistor R8 and unsoldered from the side of the 4th chamber. The collector output should be soldered to the same point on L7 where the output of the removed transistor was soldered. Carefully solder the emitter and base leads without overheating the solder points, as the solder points are low-capacitance capacitors that can be destroyed if overheated. Next, you need to remove the resistors R6 and R4, thus disconnecting the second stage from the power circuits. Then it is necessary to install the resistors Rd1, Rd2 and Rd3, as shown in Fig. 3.
Set the slider of the resistor Rd2 to the middle position. By applying a voltage of +12 volts to the circuit, by rotating the slider of the resistor Rd1, a voltage of +9,5 V is set at the emitter and +9 V at the base of the transistor T1. Then, turning off the power, measure the total resistance of the resistors Rd2 and Rd3. A resistor of the MLT-0,125 type is selected with a value close to the measured one and installed as a resistor R8 in Fig. 2, Rd1 will remain in the circuit as R9. Power is supplied to the circuit, and the voltage at the terminals of the transistor T1 is monitored. The operation of the first stage can be checked visually, according to the image on the TV screen. To do this, tune the TV to one of the UHF channels, which is received with poor quality. Then, disconnecting the antenna cable from the TV input, connect it to the input of the amplifier. A piece of cable RK-75 with a plug soldered at one end is connected to the UHF input of the TV. The braid of the other end of the cable is soldered to the amplifier case, and the central core through a 4,7 pF capacitor. soldered at the place of desoldering the output of the collector of the transistor T1. Although the peak point of the signal is on L4 closer to the case, you should not solder in places where there is no factory soldering, in order to avoid deterioration of the circuit parameters. After turning on the power of the amplifier, by smooth rotation of the vernier mechanism, they are tuned until an image is received on the screen. The image should be of better quality compared to what it was before the antenna was turned on through the amplifier. Then check the operation of the circuit L5 C15 C18. To do this, turning off the power and unsoldering the "control" cable from L4, solder it to the junction of L5 and C15. Turn on the power to the amplifier again and monitor the signal for image quality, and no deterioration in image quality should be observed. The setting of the second stage is similar. After turning off the power to the amplifier, the resistor R6 is soldered in place, and instead of the removed resistor R4, a tuning resistor is installed, with a nominal value of 5,1 ... 10 kOhm, and its engine is set to the middle position. Then the "control" cable is soldered through a capacitance of 4,7 pF to the soldering point of the collector of transistor T2 and the power is turned on. By smoothly rotating the resistor engine, the modes of the transistor T2 are set with the same values as those of T1. Then the power is removed, the resistance of the variable resistor is measured and the MLT resistor with a value close to the measured one is soldered instead. In conclusion, the socket KT1 and the passage capacitor C9 are removed. The RK-75 cable is inserted into the holes formed, which will be connected to the TV. The cable braid is soldered to the "case", and the central core through the capacitor C to L7, choosing the soldering point experimentally, according to the best image quality. The amplifier can be enclosed in any suitable decorative case. If the amplifier will be used on several channels, then it is convenient to mark the desired channels on the case, and at risk on the tuning knob. And in conclusion about further improvement. The author does not consider it expedient to increase the sensitivity to include broadband amplifiers before the input of the device, because due to the uneven frequency response and the high noise level of such devices, the reception quality on high-frequency or even on all channels can sharply decrease. Good results can be obtained by turning on a one- or two-stage broadband amplifier after the output of this amplifier. In this case, you will have to carefully match the input / output of both amplifiers. Author: Sinitsky V.; Publication: cxem.net
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Motorola Project Ara Modular Smartphone Platform
▪ section of the site Security and safety. Article selection ▪ article Believe it or not. Popular expression ▪ article In which restaurant did Colonel Sanders eat the worst chicken of his life? Detailed answer ▪ article Use of the services of specialized organizations in the field of labor protection ▪ article Antenna orientation device. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: