T-contour. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Knots of amateur radio equipment. Filters and matching devices
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
To match a powerful output transistor with an antenna and filter the signal, in most cases, insufficiently perfect circuit solutions are used:
- ferrite transformers, which do not have filtering properties and are not easily accessible to radio amateurs;
- P-circuit, but it poorly matches the low output impedance of the transistor stage (2 ... 15 Ohms) with the output impedance of the antenna, while the losses are large.
One of the effective solutions to the problem that has arisen is the T-loop, the principle of which is clear from Fig. one.

Ris.1
It can be seen from the diagram that this is a two-circuit system. The input impedance of the antenna (Ra) is introduced into the K2 circuit. In this case, the reactive component of the input impedance of the antenna can be easily compensated by changing the value of Lc, which is very important when tuning the antenna. The input impedance of the K2 circuit at point "c" when tuned to resonance.

It has a value of the order of 100 ... 2000 Ohm, depending on the value of Lc, which, in turn, is selected depending on the operating frequency and output power of the cascade.
The transistor collector, operating as a current generator, is connected in series to the K1 circuit. The load of the circuit K1 (at point "b") is the input resistance of the circuit K1 - Rin2. To obtain a T-contour, it is enough to connect the points "b" and "c". In this case, the total capacity is C \u1d C2 + CXNUMX.
The input resistance of the K1 circuit at point "a" has the value

The presence of two circuits in the circuit allows you to qualitatively filter out unnecessary components in the signal, there is no need for additional filters.
In practice, the elements are selected from the following ratios:
С [pf]=(8...20)L,
where L is the average wavelength in m.
C - the more, the greater the power, i.e. at P=10 W C=8L, at P=200 W C=20L. Cp-separating capacitance for direct voltage between Ek and the antenna.

where Rin1, is the load resistance of the transistor.
A practically working cascade circuit for the ranges of 160, 80 and 40 m is shown in Fig. 2.
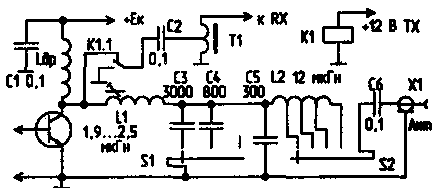 <Fig.2>
<Fig.2>
Coil L1 contains 16 turns of PESHO-0,5 wire, frame diameter - 16 mm, winding length - 16 mm, tuning - with a ferrite core with a diameter of 8 mm, a length of 20 mm. L2 contains 37 turns of PESHO-0,3, taps - from 25, 29 and 33 turns. Frame diameter - 10 mm, winding length - 12 mm. The coils are arranged so that there is no mutual inductance between them: shielding, perpendicularity of the axes of the coils.
S1 - range switch. The setting is as follows: using switch S2, a connection is established with the antenna, and the L1 core is used to tune the circuit to resonance at the maximum of the antenna indicator and the maximum current of the transistor collector. In general, the tuning resembles the tuning of a P-loop, but instead of variable capacitors, there are variable inductances and tuning for the maximum current of the transistor. Instead of L2 and S2, you can use a variometer with an inductance of 8...12 µH. It is possible to tune into resonance using a variable capacitor, then the inductance L1 is constant and is 2,1 μH, but the author's inductance tuning showed an excellent result, and the device turned out to be smaller than when using a variable capacitor.
When operating in the receive mode, the T-loop is an additional input band filter of the receiving device. Switching "reception-transmission" is carried out using a relay K1 type RES-55A or the like. Transformer T1 is wound on a ring measuring 8x4x2 mm with a permeability of 100 ... 1000 and contains 20 turns of PESHO-0,3 wire with a tap from the 5th turn, read from the grounded end (with the input resistance of the receiver 75 Ohm).
Literature
- Red E. Reference manual for high-frequency circuitry.
- Rivanenkov L. Output stages of HF transmitters on transistors. Radio amateur KB and VHF. - 1996. - No. 2.
Author: L. Rivanenkov (UA3LDW), Smolensk; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Knots of amateur radio equipment. Filters and matching devices.
See other articles Section Knots of amateur radio equipment. Filters and matching devices.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Shake before use
02.12.2000
The flashlight, launched in the US, does not have batteries or a light bulb.
In order for it to catch fire, it must be shaken several times. In this case, the magnet contained inside the body of the flashlight "runs" inside the coil, exciting an electric current in it, and its energy is stored in a miniature, but very capacious capacitor. From this energy, a white LED lights up, the service life of which is one hundred thousand hours.
After shaking for 25 seconds, the flashlight shines for five minutes, and at a distance of 10 meters an illuminated circle with a diameter of two meters is created. The operating temperature range - from minus 90 to plus 85 degrees - no battery could withstand.
Since nothing needs to be changed in the flashlight, it is made one-piece, sealed and can work underwater.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Friday Lock smart door lock
▪ Two mushrooms on chocolate
▪ Oversalted food harms the vessels of adolescents
▪ Cars go on rails
▪ Li-ion battery with sand anode
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Children's scientific laboratory. Article selection
▪ article Cracking process. History of invention and production
▪ How did the map of Europe change after the First World War? Detailed answer
▪ article Cranes maintenance mechanic. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Coordination of the antenna with the feeder. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Automotive laptop power supply without winding elements. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese




 <Fig.2>
<Fig.2> Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: