Protective microassemblies FOR-0, FOR-1. Reference data

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Reference materials
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Protective microassemblies are designed to reduce to a safe level high-voltage (amplitude 1 kV or more) pulses in household and industrial AC networks with a voltage of 220 V. In "Radio", 1998, No. 7, p. 52, 53 published an article by V. Kolosov and A. Muratov "Protection of electronic equipment from high-voltage pulses in the network", which discusses the principle of operation of semiconductor voltage limiters and microassemblies based on them, and application features.
Below are the characteristics of protective microassemblies produced by the domestic industry. At present, two of their series have been mastered - ZA-0 and ZA-1. Devices ZA-0 (Fig. 1) have wire leads and are designed to be built into the equipment, and ZA-1 are designed in the form of a plastic power plug (Fig. 2) with rigid pins for installation in a standard power outlet. Option ZA-01, described as an example in the mentioned article, was recognized as unpromising and discontinued.
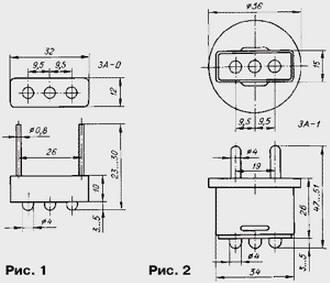
Three LED indicators are displayed on the front side of the microassemblies. Medium - green glow - shines in the presence of mains voltage and with serviceable voltage limiters. "Red" LEDs (both or one of them) turn on when both or one limiter fails, respectively.
Technical characteristics of microassemblies ZA-0 and ZA-1 are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1
| microassembly |
impulse max. permissible power(1), kW |
Opening voltage, V |
Opening voltage spread, % |
Maximum non-opening voltage(2) , V, no more |
Weight, g, no more |
| FOR-0-1,5-400A |
1,5 |
400 |
5 |
320 |
10 |
| ZA-0-1,5-400B |
10 |
| FOR-0-1,5-450A |
450 |
5 |
360 |
| ZA-0-1,5-450B |
10 |
| FOR-0-1,5-540A |
540 |
5 |
430 |
| ZA-0-1,5-540B |
10 |
| FOR-0-1,5-630A |
630 |
5 |
500 |
| ZA-0-1,5-630B |
10 |
| FOR-0-1,5-720A |
720 |
5 |
580 |
| ZA-0-1,5-720B |
10 |
| FOR-0-1,5-800A |
800 |
5 |
640 |
| ZA-0-1,5-800B |
10 |
| FOR-1-1,5-400A |
1,5 |
400 |
5 |
320 |
30 |
| ZA-1-1,5-400B |
10 |
| FOR-1-1,5-450A |
450 |
5 |
360 |
| ZA-1-1,5-450B |
10 |
| FOR-1-1,5-540A |
540 |
5 |
430 |
| ZA-1-1,5-540B |
10 |
| FOR-1-1,5-630A |
630 |
5 |
500 |
| ZA-1-1,5-630B |
10 |
| FOR-1-1,5-720A |
720 |
5 |
580 |
| ZA-1-1,5-720B |
10 |
| FOR-1-1,5-800A |
800 |
5 |
640 |
| ZA-1-1,5-800B |
10 |
Notes
(1) With a pulse with a steep front with a duration of not more than 10 µs, decreasing when the amplitude value is reached exponentially; the pulse duration at a level of 0,5 of the amplitude is not more than 1 ms with a duty cycle of 10. With a rectangular pulse shape, the power is reduced by 000 times, and with a shape close to half-sinusoidal, by 2 times.
(2) The operating voltage amplitude should not exceed the maximum non-opening voltage.
Power consumed by microassemblies in the absence of high-voltage pulses in the network, not more than 0,5 W for devices ZA-0-1,5-400A, ZA-0-1,5-400B, ZA-01,5-450A, ZA-0 -1,5-450B and no more than 1 W for the rest. The light intensity of the LEDs is at least 0,5 mcd at an operating voltage of at least 0,8 of the maximum non-opening voltage.
The dependences of the pulsed maximum allowable power Rmp max on the pulse duration t and with the pulse shape "decreasing exponential" and various values of the duty cycle Kz are shown in fig. 3.
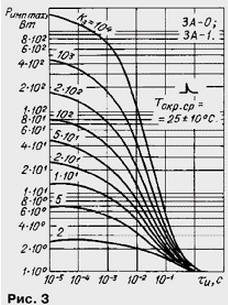
Dependence of the pulsed maximum allowable power Rimp max on the ambient temperature Tamb. cf for a rectangular pulse is shown in Fig. 4.

Author: R. Tolkacheva, Moscow
 See other articles Section Reference materials.
See other articles Section Reference materials.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024
The modern world of science and technology is developing rapidly, and every day new methods and technologies appear that open up new prospects for us in various fields. One such innovation is the development by German scientists of a new way to control optical signals, which could lead to significant progress in the field of photonics. Recent research has allowed German scientists to create a tunable waveplate inside a fused silica waveguide. This method, based on the use of a liquid crystal layer, allows one to effectively change the polarization of light passing through a waveguide. This technological breakthrough opens up new prospects for the development of compact and efficient photonic devices capable of processing large volumes of data. The electro-optical control of polarization provided by the new method could provide the basis for a new class of integrated photonic devices. This opens up great opportunities for ... >>
Primium Seneca keyboard
05.05.2024
Keyboards are an integral part of our daily computer work. However, one of the main problems that users face is noise, especially in the case of premium models. But with the new Seneca keyboard from Norbauer & Co, that may change. Seneca is not just a keyboard, it is the result of five years of development work to create the ideal device. Every aspect of this keyboard, from acoustic properties to mechanical characteristics, has been carefully considered and balanced. One of the key features of Seneca is its silent stabilizers, which solve the noise problem common to many keyboards. In addition, the keyboard supports various key widths, making it convenient for any user. Although Seneca is not yet available for purchase, it is scheduled for release in late summer. Norbauer & Co's Seneca represents new standards in keyboard design. Her ... >>
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
Exploring space and its mysteries is a task that attracts the attention of astronomers from all over the world. In the fresh air of the high mountains, far from city light pollution, the stars and planets reveal their secrets with greater clarity. A new page is opening in the history of astronomy with the opening of the world's highest astronomical observatory - the Atacama Observatory of the University of Tokyo. The Atacama Observatory, located at an altitude of 5640 meters above sea level, opens up new opportunities for astronomers in the study of space. This site has become the highest location for a ground-based telescope, providing researchers with a unique tool for studying infrared waves in the Universe. Although the high altitude location provides clearer skies and less interference from the atmosphere, building an observatory on a high mountain poses enormous difficulties and challenges. However, despite the difficulties, the new observatory opens up broad research prospects for astronomers. ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Ultracold molecular quantum gas
04.12.2020
For the first time, American physicists have obtained a controlled state of an ultracold molecular quantum gas, which can have many practical applications - from ultraprecise measurement devices to quantum computing.
In the classical sense, a gas consists of a large number of randomly moving particles. When the gas is cooled to near absolute zero, the molecules stop behaving like particles and take on the properties of waves that overlap. This state is called a quantum gas, and the transition temperature of a molecular gas to a quantum state is called the degeneracy temperature.
The properties of a quantum gas depend on the degree of its degeneracy, when the gas molecules, like particles, repel each other, but interact at large distances due to their overlapping waves, electric dipole moments, and other characteristics.
Researchers at JILA - a joint venture between the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Colorado Boulder - have developed tools to "turn on" the state of an ultracold molecular quantum gas and control intermolecular interactions over long distances.
Ultracold quantum gases can potentially find application in ultraprecise measurement devices, for modeling extreme states of matter, creating quantum many-particle systems, and in quantum computing.
According to the authors, a new scheme for pushing a molecular gas to its lowest energy state, called quantum degeneracy, which suppresses chemical reactions that destroy molecules, will allow us to explore exotic quantum states in which all molecules interact with each other.
At a temperature of 250 nanokelvins - just above absolute zero - the researchers created a dense gas of about twenty thousand dipole potassium-rubidium molecules, which behave like tiny magnets in an electric field, due to the fact that rubidium atoms have a positive charge, and potassium atoms - negative.
Turning on the horizontal electric field slowly over hundreds of milliseconds reduced the strength of the trap in one direction long enough for the hot molecules to escape and the remaining molecules to cool. At the end of this process, the molecules returned to their most stable state, but now in a denser gas.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Reconstructed the navel of the earth
▪ Causes of senile smell
▪ New Bluetooth 5.0 modules from STMicroelectronics
▪ Android devices last longer
▪ Sharks are less likely to attack people
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Batteries, chargers. Article selection
▪ article Solomon's decision. Popular expression
▪ What was the essence of the crusades (goals, participants, results)? Detailed answer
▪ article Asparagus officinalis. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Photomechanical sensor. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Charging the battery from Peltier elements. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: