Unijunction transistors of the KT133 series. Reference data

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Reference materials
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Silicon unijunction transistors with n-base KT133A and KT133B are designed to work in time delay units, voltage converters, generators of electrical oscillations, thyristor control devices and others where an element with relay characteristics is required.
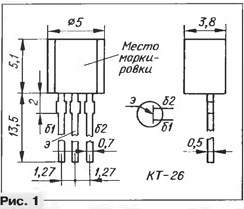
The devices are manufactured using epitaxial-planar technology. They are issued in a plastic case KT-26 (Fig. 1), the mass of the device is no more than 0,3 s. Foreign analogues of transistors KT133A, KT133B - 2N4870, 2N4871, respectively.
Main electrical characteristics at Tacr avg = 25°C
- Leakage current of the emitter junction, μA, no more, at reverse voltage emitter-base2 30 V and zero current base1......1
- Valley current, mA, not less than, at base1-base2 voltage of 20 V, resistor resistance in the emitter circuit of 100 Ohm, pulse duration of 6 µs or less with a duty cycle of 50 for
- KT133A......2
- KT133B......4
- Transfer coefficient at voltage base1-base2 10 V for KT133A ...... 0,56 ... 0,75
- KT133B......0,75...0,85
- The highest generated frequency, Hz......220
- Turn-on current*, µA, no more, at voltage base1-base2 25 V......5
- Modulation current*, mA, at voltage base1-base2 10 V and emitter current 50 mA......15...65
- Residual voltage*, V, at base1-base2 voltage 3 V and emitter current 50 mA......0,7...2,5
- Interbase resistance*, kOhm, at voltage base1-base2 3 V and zero emitter current .....4...9,1
- Temperature coefficient of interbase resistance*, %/°С, not more, at voltage base1-base2 3 V, zero emitter current and ambient temperature within -60...+125°С .0,1...0,9
- Impulse voltage of the base 1*, V, not more, with a resistance of resistors in the circuits baey1 20 Ohm, base2 - 100 Ohm, emitter - 10 kOhm, capacitor capacitance in the emitter circuit 0,2 μF and voltage base1-base2 20 V for KT133A .. ....3
- KT133B...........5
- Thermal resistance transition-environment, °С/W, no more......333
* Reference parameters.
Limit values
- The highest voltage base1-base2 (interbase voltage), V ...... 35
- Maximum reverse voltage emitter-base2, V......30
- The highest direct current of the emitter of an open transistor, mA......50
- The highest pulsed emitter current, A. with a pulse duration of not more than 10 μs and a duty cycle of at least 100 ...... 1,5
- The highest constant power dissipation, mW......300
- The highest transition temperature, ° С ...... 135
- Limits of ambient operating temperature, °С..... -60...+125
The input current-voltage characteristic of a unijunction transistor is shown in fig. 2. The turn-on current Ion of the device is usually called the value of the emitter current at which the transition from the closed state to the open occurs. The valley current Id is the value of the emitter current corresponding to the CVC point with the minimum voltage and zero differential resistance.
The leakage current of the emitter junction Iebo is the current through the emitter junction, reversely biased relative to the base2. Interbase resistance RB1B2 - resistance between the bases of the transistor at a given interbase voltage. The transfer coefficient r] is the ratio of the maximum possible emitter voltage minus the voltage drop at the p-n junction to the applied interbase voltage.
Residual voltage UBEnas - direct voltage on the emitter at a given emitter current and interbase voltage. The maximum allowable interbase voltage UB1B2max is the maximum voltage value of any form and frequency between the bases, at which the specified reliability is ensured.
The maximum allowable reverse voltage emitter-base2 UEB2 - the maximum value of the reverse voltage of the emitter junction relative to base2. Modulation current Imod - the minimum current in the base2 circuit for given interbase voltage and emitter current.
Since the KT133 series transistors are produced in the same package as the KT6113 series (see above), their mounting features are the same.

The main graphic typical dependences of the parameters of transistors KT133A, KT133B on the ambient temperature are shown in fig. 3-5
Author: V.Kiselev, Minsk, Belarus
 See other articles Section Reference materials.
See other articles Section Reference materials.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024
The modern world of science and technology is developing rapidly, and every day new methods and technologies appear that open up new prospects for us in various fields. One such innovation is the development by German scientists of a new way to control optical signals, which could lead to significant progress in the field of photonics. Recent research has allowed German scientists to create a tunable waveplate inside a fused silica waveguide. This method, based on the use of a liquid crystal layer, allows one to effectively change the polarization of light passing through a waveguide. This technological breakthrough opens up new prospects for the development of compact and efficient photonic devices capable of processing large volumes of data. The electro-optical control of polarization provided by the new method could provide the basis for a new class of integrated photonic devices. This opens up great opportunities for ... >>
Primium Seneca keyboard
05.05.2024
Keyboards are an integral part of our daily computer work. However, one of the main problems that users face is noise, especially in the case of premium models. But with the new Seneca keyboard from Norbauer & Co, that may change. Seneca is not just a keyboard, it is the result of five years of development work to create the ideal device. Every aspect of this keyboard, from acoustic properties to mechanical characteristics, has been carefully considered and balanced. One of the key features of Seneca is its silent stabilizers, which solve the noise problem common to many keyboards. In addition, the keyboard supports various key widths, making it convenient for any user. Although Seneca is not yet available for purchase, it is scheduled for release in late summer. Norbauer & Co's Seneca represents new standards in keyboard design. Her ... >>
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
Exploring space and its mysteries is a task that attracts the attention of astronomers from all over the world. In the fresh air of the high mountains, far from city light pollution, the stars and planets reveal their secrets with greater clarity. A new page is opening in the history of astronomy with the opening of the world's highest astronomical observatory - the Atacama Observatory of the University of Tokyo. The Atacama Observatory, located at an altitude of 5640 meters above sea level, opens up new opportunities for astronomers in the study of space. This site has become the highest location for a ground-based telescope, providing researchers with a unique tool for studying infrared waves in the Universe. Although the high altitude location provides clearer skies and less interference from the atmosphere, building an observatory on a high mountain poses enormous difficulties and challenges. However, despite the difficulties, the new observatory opens up broad research prospects for astronomers. ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Capacious and durable graphene ionistor
24.03.2013
Electrochemical capacitors, also called supercapacitors or supercapacitors, combine the advantages of capacitors and batteries. They differ from conventional capacitors of the same size in their ability to store much more energy, and can be charged and discharged much faster than batteries. Unfortunately, in terms of capacity, they are still noticeably inferior to the latter, so an increase in the energy density of ionistors could be an important breakthrough in energy storage technology. An approach to this breakthrough was found by specialists from the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA).
To increase the energy density, it is necessary to improve the electrodes by combining a large surface with good conductivity. Graphene is very well suited for the role of the material of such an electrode. Interestingly, to form the graphene electrode, scientists came up with the idea of using a regular DVD drive with LightScribe support. To do this, they coated the disk with a film of graphite oxide and processed it with a laser in an optical drive. As a result of irradiation, a graphene film with the properties of an "open network structure" was formed, which is characterized by the presence of short ion diffusion paths, which makes it possible to reduce the charging time.
An electrode made of a material called Laser Scribed Graphene (LSG) provides a significant improvement in energy density and power density (characterizing how much charge can be stored in the supercapacitor and how quickly). According to the researchers, the electrode retains its qualities in different electrolytes and withstands a large number of charge-discharge cycles. In addition, the properties of the graphene film make it possible to manufacture flexible power supplies for wearable electronics, overcoming the limitations inherent in traditional ionistors. It is important that the new ionistor turned out to be practically immune to mechanical influences.
The test results allowed scientists to declare that graphene ionistors can be comparable in capacity to modern batteries. At the same time, they can be charged 100-1000 times faster.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Electronics with Nickel Cause Rash
▪ Musical and mathematical gift are interconnected
▪ watermelon fuel
▪ External battery for Sanho HyperMac laptops
▪ PLM-40E - 40W Step Dimming LED Driver
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Reference materials. Article selection
▪ article Sociology. Crib
▪ article How did Bernard Shaw react to the Nobel Prize? Detailed answer
▪ article Tools and devices for equipment caches. Spy things
▪ article Dust - Kashcheeva computer needle. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Interiority of the coin. physical experiment
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: