
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Push-pull-parallel bass amplifier. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Tube Power Amplifiers When a push-pull cascade operates in modes with cutoff of the anode current in the frequency range above 2...3 kHz, specific non-linear distortions occur, which increase with increasing frequency. The reason for this is the non-ideal magnetic coupling (flux linkage) between the halves of the primary winding and between each half of the primary winding and the entire secondary winding of the output transformer. Transient processes distort the shape of the anode current of the lamps, and a characteristic dip appears on the oscillogram of the anode current. Under the same conditions, non-linear distortions in the region of lower audio frequencies are due to the inductance of the primary winding of the transformer and are successfully compensated by deep feedback. Distortions at higher frequencies are not compensated by feedback. Therefore, when designing amplifiers operating in AB or B mode, they often compromise on distortion at lower and higher frequencies, or use mode A. The described amplifier when operating in class AB mode gives, without compromise, minimal distortion at lower frequencies due to very good frequency and phase characteristics with deep feedback, and also at higher frequencies due to the minimization of leakage inductance. A schematic diagram of a push-pull parallel cascade is shown in fig. 1. A distinctive feature of this amplifier is the parallel connection of lamps relative to the total load. The output transformer has two primary windings, each of which consists of two sections - cathode and anode, and the cathode and anode windings of the lamps of opposite arms are wound together in two wires, which practically eliminates leakage inductance. The directions of the alternating current in the anode and cathode sections of different lamps are the same, and the alternating voltage between them is zero.
This circumstance makes it possible to replace the circuit diagram with the equivalent circuit shown in Fig. 2. It can be seen from it that an amplifier with a push-pull-parallel connection of lamps is covered by deep voltage feedback at a feedback coefficient The total reduced resistance of both lamps operating on a common load is Ri / (2+ and the condition that the equivalent load resistance is much greater than the reduced resistance of the lamps, i.e. Za>>Ri/(2+ The depth of feedback in such a stage can be estimated by comparing the gain of a push-pull-parallel and an ordinary push-pull stage. Taking the load factor for the pentode K0=SRa=Sa Hence the depth of feedback of the push-pull-parallel stage Aos=1+ A push-pull-parallel stage used in a three- or four-stage amplifier can also be covered by a total OOS with a depth of 10 ... 12 dB. Thus, the OOS in the final stage increases to 35 ... 37 dB in a wide frequency band, significantly improving all the electro-acoustic characteristics of the amplifier. When the last three stages of the amplifier are covered by a common OOS circuit, the reduced resistance of the lamps of the final stage becomes equal with two lamps in the final stage: Ri oe=Ri/[(2+ where K0 is the overall initial gain of the cascades covered by the common feedback. The most suitable lamps for a push-pull-parallel stage are 6PZS lamps (similar to 6L6G), as they make it possible to obtain the lowest output impedance and do not require a very high anode voltage. An amplifier with such an end stage, assembled on two 6PZS lamps, in AB mode delivers power up to 25 W to the load, and up to 35 W on four lamps. For 6PZS lamps, the voltage anode - cathode and screen grid - cathode - 350 ... 380 V, control grid - cathode - -38 ... -40 V can be recommended. Here, the voltage on the screen grid exceeds that specified in the reference books UС2 max = 300 V However, in practice, 6PZS lamps in this mode can operate much longer than the warranty period, since the power dissipated in this case on the screen grid does not exceed the allowable one. It is better to make the offset in the grid chain fixed. The screen grids are connected to the anodes of the lamps of the opposite arm. Thus, they receive in relation to their cathode a constant voltage equal to the anode one. For alternating current, connecting, for example, a screen grid VL1 to the anode VL2 is equivalent to connecting it to the cathode. Resistors R1, R2, R4, R5, mounted on lamp panels, prevent the excitation of the RF cascade. For the output push-pull-parallel stage, the input voltage between the control grids should be about 270 V. The transition from the preliminary stage to the final stage (when both stages are powered from a common source) must be transformer-based, because with a rheostat-capacitive coupling, a change in the anode voltage will manifest itself as a change in bias and will greatly disrupt the mode of the terminal lamps. The value of the required inductance of the primary winding of the output transformer L1, depending on the given distortion at the lowest frequency, can be approximately determined by the formula (for a pentode)
where RH' is the load resistance converted to the primary winding in ohms, FH is the specified lower frequency in hertz, MH is the signal attenuation at the FH frequency, as the ratio of the gain factors at the middle and lower frequencies (KCP / KH), is selected within 1,05 ... 1,25 (0,5 ... 2 dB). <It is also necessary to check the value of the allowable magnetic induction Bmax. The low ohmic resistance of the windings is very important, since if it turns out to be greater than the reduced resistance of the lamps (for two 6PZS lamps - 90 Ohm, for four 6PZS lamps - 45 Ohm), then there will be a big loss in output resistance. The transformation ratio is chosen so that the load resistance converted into the primary winding is 15 ... 20 times greater than the output resistance of the lamps. In this case, the cascade gives maximum power with low distortion. So, for a cascade on two 6PZS lamps (without covering the entire amplifier with a common feedback circuit), the optimal transformation ratio
where RH is the load resistance, w1 is the number of turns of the entire primary winding, w2 is the number of turns of the secondary winding. For an amplifier also covered by a common feedback circuit,
The intertube transformer has a ratio of turns of the primary and secondary windings of 1: 1 (the windings for each arm are wound in two wires). Due to the very large depth of the OOS, a push-pull amplifier with a final stage according to this scheme, when supplying the filament of all lamps with alternating current and with a gain of about 40 dB, provides an interference level of -75 dB at the amplifier output even without selecting lamps. A feature of the push-pull-parallel cascade is the presence of an alternating LF voltage between the cathode of the lamps. If the filament lamps of both arms are powered from a common winding, then this voltage is applied between the cathode and the heater of each lamp. In practice, the peak signal voltage never exceeds the maximum allowable voltage between the cathode and the heater for 6P3S, which is 180 V. However, for many lamps this voltage should not exceed 100 V, and this problem is solved by separating the filament windings of the power transformer. The design of the output transformer is relatively simple. As usual for push-pull cascades, the frame is made of two sections with a partition in the middle. Both sections are wound in the same direction, but with the frame turned over after filling one of the sections. The primary anode and cathode windings are wound with two wires folded together (they are wound simultaneously from two coils), turn to turn. The most suitable brand of wire is PELSHD, and to reduce the leakage inductance, the secondary winding is placed between the two halves of the primary winding section and a crossover scheme is used (Fig. 3, a). On fig. 3b shows the connection diagram of the transformer windings. In the absence of a wire of a suitable brand with a high breakdown voltage of insulation, you can use a wire of the PEL-1 brand and perform the winding in the usual way (with separate anode and cathode windings).
Screen winding - an open coil of thin copper foil connected to a common wire. With the usual winding of transformer windings, it is advisable to supplement the inductive coupling between the windings with capacitive coupling. To do this, the ends of the windings of the same name are interconnected through capacitors with a capacity of 2000 ... 3000 pF (for a voltage of at least 400 V), with which resistors with a small resistance (100 ... 300 Ohms) are connected in series. The quality indicators of the UMZCH with conventional transformers are not much inferior to the quality indicators of the described amplifier, but in the region of higher frequencies the former gives less undistorted power. The windings of the output transformer can also be made with PEL-2, PEV-2 and other similar wires. With a wire diameter of more than 0,15 mm, the minimum breakdown voltage of their insulation is at least 800 V, which is quite enough to ensure reliable operation of a transformer with twin windings (winding in two wires). Regarding the problem of using a simpler rheostat-capacitive coupling between the phase-inverted and output stages, it should be noted that the elimination of bias instability is quite achievable by using an effective voltage stabilizer. Recommendations for total feedback coverage of three or more stages in similar amplifiers of those years often discredit its effectiveness at the present time. It is advisable to form such feedback only for two stages of the amplifier. However, these recommendations were known in the fifties. But with regard to lamps, we recall that later a number of output pentodes and beam tetrodes appeared - 6P14P, 6P36S, 6P42S, 6P45S ... Russian enterprises also mastered the production of new analogues of foreign radio tubes recommended for use in UMZCH. Author: B.Mints
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ The best gift is for yourself ▪ Xbox One with overheating protection
▪ section of the site Children's scientific laboratory. Article selection ▪ article by Henry Mencken. Famous aphorisms ▪ article What is the largest mammal on the planet? Detailed answer ▪ article Work on the HDTV installation. Standard instruction on labor protection
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

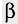 \u0,5d 2, since half of the output voltage U1 at the load Zа is supplied in antiphase to the excitation voltage of the lamp of one arm U2 / XNUMX.
\u0,5d 2, since half of the output voltage U1 at the load Zа is supplied in antiphase to the excitation voltage of the lamp of one arm U2 / XNUMX. ), Where
), Where  \u0,25d 6, for a cascade on two 22PZS lamps with an output resistance Ri \u6d XNUMX kOhm and an average slope S \uXNUMXd XNUMX mA / V, we determine the gain.
\u0,25d 6, for a cascade on two 22PZS lamps with an output resistance Ri \u6d XNUMX kOhm and an average slope S \uXNUMXd XNUMX mA / V, we determine the gain. Ri=6.10-3.0,25.22 .103=33
Ri=6.10-3.0,25.22 .103=33




 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: