
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Minimizing harmonic distortion in a tube amplifier. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
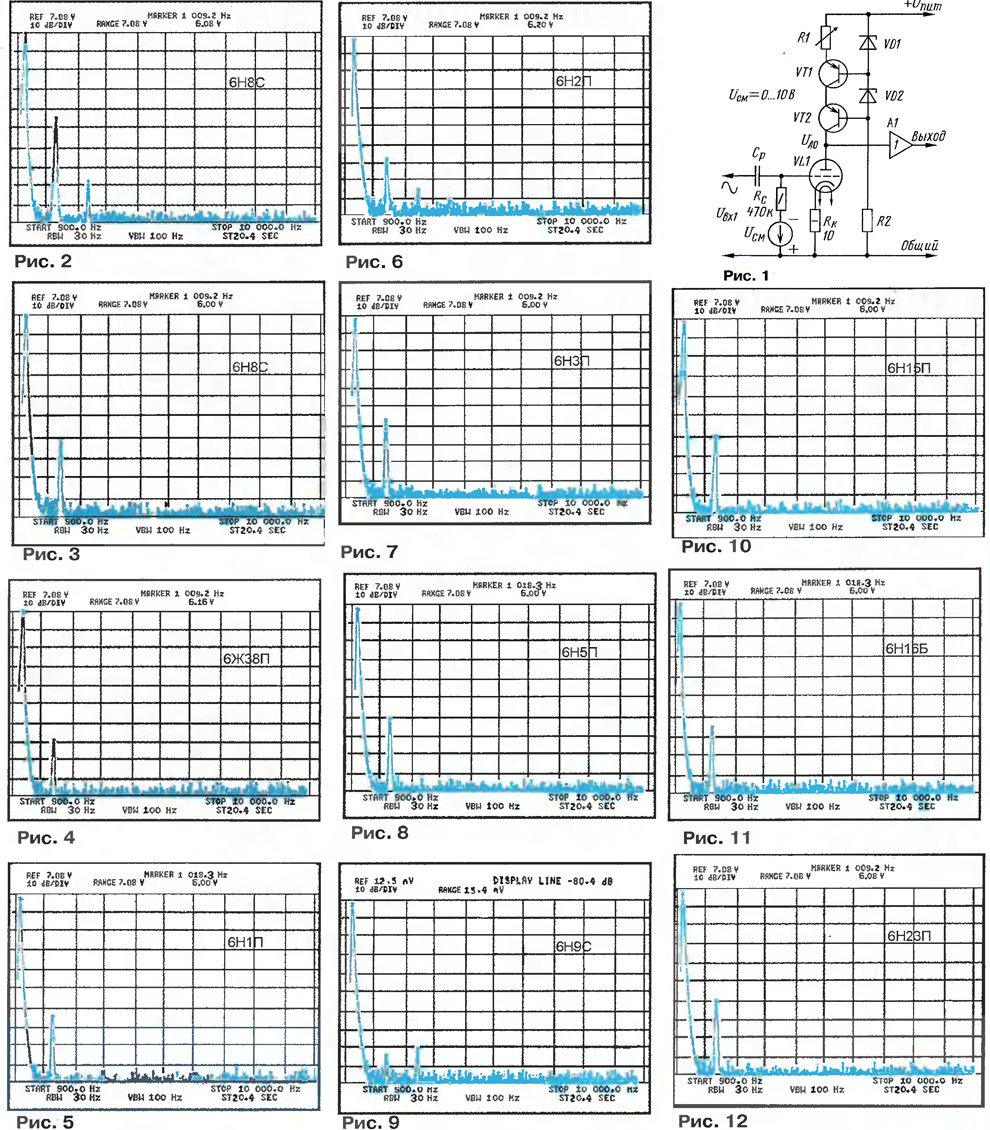
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Tube Power Amplifiers The article discusses the results of studies of the linearity of the lamp cascade with a current source in the anode circuit. The parameters of electrical regimes for a number of amplifying triodes, which provide the highest linearity, are given, and the characteristic spectra of signal distortions in these operating modes are shown. Recommendations on the use of the studied lamps are given. The study of the potential linearity of the tube cascade pursued several goals. It was supposed to objectively confirm the feasibility of using current sources as the anode load of the lamp and, thus, shake the confidence of the opponents of this approach and strengthen the faith of its supporters. I wanted to once again check the correctness of a number of recommendations on the choice of the operating mode of the preliminary cascades given in [1], where a cascade with a current source is described in detail and a method for calculating the cascade itself and the current source is given. I hope that the results of my work will make it easier for all radio amateurs and audiophiles to choose the type of lamp and its operating mode. Unlike the previous article [2], where tests of many lamps were carried out in modes that differed from real ones, the results obtained can be immediately used in practice. During operation, the operating modes of the lamp in a cascade with a current source in the anode circuit were optimized to ensure maximum linearity. The presumed purpose of the cascade is to work in the pre-amplification circuits of power amplifiers; this determined the list of tested lamps and the magnitude of the output voltage at which measurements were made. The parameters were measured in a cascade according to the scheme shown in Fig. 1. In fact, the circuit has already been described [3, 4], the cascade is supplemented with elements for regulating the lamp current and bias voltage. To eliminate the influence of the input resistance of the measuring equipment, a measuring buffer amplifier was used, which has a very high input resistance and linearity. I draw attention to this condition: in real devices, the best results are achieved when using a cathode follower as a subsequent stage. A GZ-118 generator was used as a signal source, and a non-linear distortion meter (INI) C1-6 and an HP-9A spectrum analyzer were connected to the output of the buffer amplifier (A3585). The range of changes in the operating currents of the lamp is limited from below by the necessary frequency properties of the cascade, and from above by the allowable dissipation power at the anode. In the general case, the upper cutoff frequency of the cascade (according to the 3 dB drop) can be determined by the formula fgr =1/(2πC∑R'). where Su is the total capacitance connected in parallel with the load (including the output capacitance of the lamp), R' is the total equivalent resistance connected in parallel with the anode circuit of the lamp for alternating current. The frequency properties of the cascade were determined for a load in the form of a cathode follower. In this case, the load capacitance is very small, and the total equivalent resistance R' is practically equal to the output resistance of the lamp at the quiescent point, which depends on the quiescent current. The measurements were carried out as follows: the minimum (preliminarily calculated) operating current of the lamp was set, the voltage at the anode of the lamp was selected in the range of 100 ... 150 V at an effective value of the output voltage of the cascade of 6 V. Further, by changing the bias voltage UCM, the harmonic coefficient of the output voltage was minimized. The procedure for finding the minimum of harmonics was repeated for large values of the operating current of the lamp, and as a result, several operating points were obtained that claim to be optimal; at these points, the behavior of the cascade was studied in more detail. For lamps with PSpise models, the search range for the optimal mode was smaller due to the preliminary simulation of the operating modes on the computer. The optimum operating point is considered to provide the highest linearity of the cascade at the lowest quiescent current. This means the following: if the minimum level of harmonics was recorded at several values of the quiescent current, then the smallest of them was considered optimal. The rest mode of the lamp, corresponding to the optimal point, is determined by two parameters: the voltage at the anode of the lamp (UA0) and the current of the cathode of the lamp (Ik0 - it was measured by the voltage drop across the precision resistor RK) in the absence of a signal. In the process of studying different types of lamps, one curious effect was discovered, which, it seems to me, has not been described anywhere else. It turned out that for different types of lamps, the nature of the change in the distortion spectrum of the output signal, depending on small changes in the DC mode, differs significantly. Moreover, we are not talking about entering the region of low currents and voltages, where the lamp is essentially non-linear and such differences are quite expected, but in the working region, where nothing foreshadows such anomalies. The effect is stable and depends little on a particular lamp instance. Eighteen types of lamps were studied (not all material was included in this article), and if the lamp behaved in a certain way, then testing another specimen taken at random gave approximately the same picture. Therefore, I decided to add one more subjective parameter to the characteristics of the lamp, which characterizes the stability of the harmonic spectrum of the output signal depending on the lamp mode for direct current (hereinafter, simply stability). Conditionally, three gradations of stability were introduced - "low", "medium", "high". Lamps with high stability are characterized by a small change in the spectrum of the output signal when changing modes for direct current over a wide range. A striking representative of this group of lamps is the 6N8S lamp: changing its DC mode leads only to a slight (by 1,5 ... 2,5 dB) change in the level of the second harmonic, and higher harmonics do not appear. Perhaps this is one of the reasons audiophiles love this tube so much; it forgives all conceivable and unthinkable design errors. Lamps with medium stability respond to a change in DC mode more sharply, but predictably. For example, when the anode voltage is lowered, changes in the output signal spectrum become noticeable very soon: the level of the second harmonic increases, higher harmonics appear. The further the deviation of the regime from the optimal point, the higher the levels of harmonics and the greater their number. Lamps with low stability change the output spectrum dramatically with relatively small changes in DC mode and sometimes have multiple operating areas with a sharp transition between them. A typical example is the 6C3P lamp. When the anode voltage changes by only 6%, the lamp dramatically changes the nature of the spectrum: the higher harmonics disappear, the level of the second harmonic increases, and with a further increase in the anode voltage, it changes little. When the lamp is in the low stability zone, as a rule, the minimum harmonic distortion is reached and the lamp is extremely sensitive to the DC mode, a slight change in the mode can effectively control the level and ratio of the harmonic amplitudes. For some types of lamps, the characteristics of both modes of operation are given. Separately, the possibilities of lamp operation at low anode voltage were studied. Periodically appearing recommendations on the use of conventional lamps in a resistive cascade at low anode voltage, to put it mildly, are not justified in any way. The use of a current source in the anode circuit is one of the possibilities to implement such a mode of operation of the cascade with sufficient amplification and satisfactory frequency properties, without entering the "microcurrent" mode. For lamps that are acceptable, in my opinion, worked in such modes, the corresponding parameters are indicated. On fig. Figure 2 shows the output signal spectrum of a resistive stage on a 6H8C lamp (I specifically give an example of changing the parameters of the stage with this lamp, since it is considered one of the most linear). The lamp operates approximately in the same mode (the same instance) as in the cascade with a current source (UA0=187 V, lK0-4,7 mA), the resistance of the anode resistor is 20 kOhm. This value was chosen in accordance with frequently encountered recommendations: take its resistance 2 ... 3 times the internal resistance of the lamp at rest. For this lamp, the internal resistance at a current of 4,7 mA is 9150 ohms. Let's compare the spectrograms: the use of a current source (Fig. 3) led to a decrease in the level of the second harmonic by almost ten times, the third harmonic disappeared altogether! Accordingly, the harmonic coefficient of the stage has decreased from 0,608% to 0,078%, and the output signal has a more favorable spectrum. As the output level increases, the advantages of the current source stage become even stronger. The summary table shows the average parameters of the optimal operating modes for all lamps, and the spectrograms (Fig. 4-12) show the harmonic spectra of the output signal characteristic of some of them.
It should be taken into account that the lamps have a significant scatter of parameters, and there will be no complete coincidence of the cascade parameters when using different lamps, but the differences are small - 15 ... 25%. Therefore, the voltage on the grid of the lamp is characterized as indicative and serves as the initial value for design. For combined lamps, the parameters of the triode part are given; the 6Zh38P pentode is switched on in the triode mode (pay attention to this lamp!). As a result of the studies and measurements of the nonlinearity of amplifying triodes used with a current source in the power circuit and a buffer stage, the author made the following conclusions. 1. Comparison of the obtained results with the parameters of resistive cascades on the same lamps proves that the use of a current source (even on transistors!) significantly increases the linearity of the cascade and improves the spectral composition of the output voltage. 2. The high linearity of the cascade with a current source in the power circuit and the improvement of the output signal spectrum significantly expand the range of tubes suitable for use in high-quality audio frequency amplifiers. Traditionally criticized lamps 6N2P, 6NZP, 6N23P show excellent results in terms of linearity and sound quality! 3. The gain of the cascade with a current source tends to a value equal to the value of μ of the lamp (with a sufficiently large input resistance of the next cascade). In the general case, this makes it possible to reduce the required number of stages while maintaining the given sensitivity. 4. Reducing the anode voltage of the lamp leads to a deterioration in the linearity of the cascade. Although the current source stage allows this mode of operation for most tubes, it is not recommended to use such modes in high quality amplifiers. This conclusion is true not only for conventional radio tubes, but also for those designed to operate at low voltage. The study of lamps 6S63N [1] and 6N27P (typical anode voltage - 28 V) showed that the best linearity of the cascade is achieved at a much higher anode voltage. 5. In the case of powering the amplifier with unstabilized voltage, lamps with high spectral stability of harmonics should be used. The use of stabilized power supplies removes this limitation and makes it possible to use all the lamps listed here with a stable result. 6. If the lamp has a pronounced zone with low spectrum stability, then, apparently, it should be avoided, since there is no information on the temporal stability of such a regime (in any case, from the author). When tuning the amplifier using only the INI, there is a danger of falling into just such a working area, since it is in this mode that the lowest total harmonic distortion in the output voltage of the cascade is achieved. Literature
Author: E.Karpov, Odessa, Ukraine
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ The internet is bad for trees ▪ Signal transmitters up to 1,5 Gbps ▪ Creating the Perfect Chocolate Texture ▪ Jupiter diverts comets and sends asteroids to Earth ▪ Vacuum cleaner for cameras with interchangeable lenses
▪ section of the site Household electrical appliances. Selection of articles ▪ article Oh, how deadly we love! Popular expression ▪ article Which of the living organisms is the largest? Detailed answer ▪ Aconite article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ Article Various compositions for removing stains. Simple recipes and tips
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: