Programmable frequency synthesizer. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Application of microcircuits
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Readers are offered a description of a frequency synthesizer up to 950 MHz, which can be used as fixed or swept frequency generators in measuring technology, as well as in receiving and receiving-transmitting equipment. The use of specialized microcircuits greatly simplifies the manufacture of the device and makes it easier to work with it.
The frequency synthesizer is built on the basis of two specialized microcircuits - the KR1830BE751 controller and a single-chip frequency synthesizer.
KF1015PL2. The device, together with a voltage controlled generator (VCO), can be used as:
- frequency generator in the range of 50...950 MHz;
- swept frequency generator;
- generator in radio receiving and receiving-transmitting devices.
The programmable controller allows you to:
- direct dialing of the frequency 50...950 MHz and its indication with the formation of a code on the synthesizer;
- frequency grid step selection -100 Hz... 1 MHz;
- selection of the division factor of the reference oscillator of the KF1015PL2 microcircuit 10, 20, 40, 100, 200, 400, 800, 1000;
- intermediate frequency (IF) set higher or lower relative to the indicated frequency and multiple of the frequency grid - 100 Hz ... 900 MHz;
- a set of transmitter frequency detuning above or below the reception frequency in multiples of the frequency grid - 100 Hz ... 900 MHz;
- selection of initial and final frequencies for frequency scanning mode - 50...950 MHz;
- selection of the initial and final "lines" of memory for the scanning mode using the built-in frequency memory - 0...9 (0...99 with external memory).
Memory capacity of frequency values (number of "lines" in memory) - 10 (with external memory - 100).
The time for generating a new frequency code is 28 ms.
With a stabilized supply voltage of 5 V, the device consumes a current of 12 mA, with external memory - 14 mA. In standby mode (micro consumption mode), the current consumption is reduced to 15 μA.
The device consists of a synthesizer controller, a keyboard, an indication unit, a frequency synthesizer, and a voltage regulator of the power supply.
The purpose of the pins of the KR1830BE751 chip is given in Table. one.
| N output |
designation |
appointment |
| 1-8 |
P1.0-P1.7 |
Keyboard polling lines |
| 9 |
RESET |
Reset |
| 10 |
RZ.0 |
Synthesizer and ILC data |
| 11 |
RZ.1 |
Synchronization of data to the synthesizer and ILC |
| 12 |
RZ.2 |
Synthesizer recording strobe |
| 13 |
RZ.3 |
External memory management |
| 14 |
RZ.4 |
HML management |
| 15 |
RZ.5 |
Transmitter activation control |
| 16 |
RZ.6 |
External memory write strobe |
| 17 |
RZ.7 |
External memory read strobe |
| 18 |
XTAL1 |
Quartz resonator circuit |
| 19 |
XTAL2 |
Quartz resonator circuit |
| 20 |
OB |
General conclusion |
| 21-23 |
P2.0-P2.2 |
Address outputs (to external memory) |
| 24 |
R2.3 |
Enabling External Memory |
| 25-27 |
P2.4-P2.6 |
Keyboard scan lines |
| 30 |
SALE |
External memory address write strobe |
| 31 |
EA |
Connect to Up1 |
| 32-39 |
P0.7-RO.O |
Input/Output address and data of external memory |
| 40 |
Up |
Supply voltage +5 V |
The electrical circuit for switching on the controller is shown in fig. 1. Its main purpose is to generate a code for a frequency synthesizer chip.

Fig.1 (click to enlarge)
The output of the code to the synthesizer is carried out each time after changing the following parameters:
- current frequency;
- grid step (Grid); - division ratio of the reference divider (CD);
- intermediate frequency (IF);
- frequency detuning (Funset).
For the case of using extended memory, the output РЗ.3 of the DD1 chip (polled by the controller once when the power is turned on for the first time) is connected to a common wire and contains an additional register DD2 and a memory chip DD3. Without external memory, the controller can memorize 10 numerical frequency settings (10 "lines"). In this case, microchips
DD2, DD3 are excluded, and the output RZ.3 DD1 must be disconnected from the common bus. The register is powered and the memory chip is selected only for the time of accessing the external memory (according to a signal from the P2.3 output of the controller).
To control the controller, a keyboard is used, the keys of which are assigned according to Table. 2.
| Tires |
R2.6 |
R2.5 |
R2.4 |
| R1.0 |
"2" |
"N.SK." |
"Ex./Trans." |
| R1.1 |
"3" |
"K.SK." |
"Scan." |
| R1.2 |
"4" |
Tek |
"Bl. Frustration." |
| R1.3 |
"5" |
"Memory" |
"Dir. Trans." |
| R1.4 |
"6" |
"+/-" |
"Upset" |
| R1.5 |
"7" |
"Slaughter" |
"PC" |
| R1.6 |
"8" |
"0" |
"KD" |
| R1.7 |
"9" |
"1" |
"Grid" |
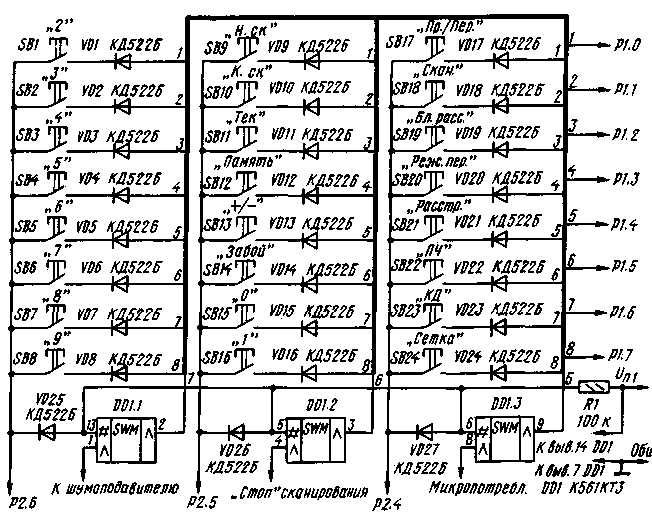
Fig.2 (click to enlarge)
The electrical circuit of the keyboard is shown in fig. 2, and the diagram of its operation is shown in Fig. 3a. Time of protection against a bounce of contacts - 3 ms. The DD1 chip is used to input information from several nodes of the synthesizer: from the power source - about the transition to the micro-consumption mode; from a frequency synthesizer microcircuit - about switching to a new frequency with a guaranteed installation of the old frequency; from the receiver noise suppressor - about a temporary stop of scanning for 5 s. All active levels are low. The duration of the "micro-consumption" signal pulse must be at least 50 ms.
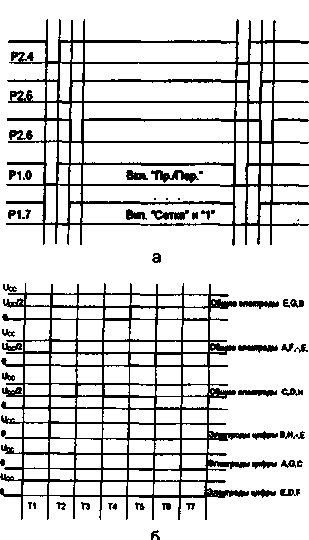
Ris.3
Visualization of the state of the controller is carried out using a liquid crystal indicator (LCI), which has eight familiarity and two special characters, for example, "E" and "M".
The display panel contains:
- frequency indicator (six familiarity) - to display various information;
- memory "line" number indicator (two familiarity) - to visualize the number of the working "line" of memory;
- "direction" indicator (sign "-")
- to visualize the scanning direction, the sign of the intermediate frequency and the sign of the transmitter detuning;
- "error" indicator ("E" sign) - to visualize an error when calculating the frequency synthesizer code;
- indicator "block detuning" (sign "M") - to visualize the inclusion or deactivation of detuning.
The electrical circuit of the indicator on the ILC is shown in fig. 4, and the diagram of indicator control signals - in fig. 3b.

Fig.4 (click to enlarge)
The operation of the indicator is controlled by the phase method with the formation of a voltage value equal to half the supply voltage for common electrodes: A, F, -, M; E, G, B; C, D, H. Any segment is activated when the common electrode and the electrode of the corresponding digit are switched inversely switching voltage levels and is not activated when acting in phase. In the time intervals T1, T2, T3, voltage is applied to the segments of one polarity, and in the intervals T4, T5, T6 - the other. During the T7 interval, all electrodes are at a low level and the indication is turned off. The segments of all eight digits are controlled in parallel. Registers DD1 - DD4 convert the controller's serial signal code into a three-level one. The operating frequency of the indicator switching is 50 Hz, the duty cycle is 3. The use of precise resistors (with a tolerance of ±1%) practically eliminates the flow of the direct current component from the unbalance of the control voltage.
Current consumption - 60 uA.
Authors: V. Semenov, V. Shlektarev, Pushchino, Moscow Region; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Application of microcircuits.
See other articles Section Application of microcircuits.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive The oceans are losing oxygen
10.12.2019
The International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) has published a report according to which the level of oxygen in the world's oceans is declining at an unprecedented rate. Climate change is dangerously exacerbating the situation.
The new study involved 67 scientists from 17 countries. It turned out that since 1950, the level of oxygen in the oceans has decreased by 2%, and the volume of water completely deprived of oxygen has quadrupled since the 1960s.
60 years ago, only 45 regions of the ocean suffered from low oxygen concentrations, in 2011 their number reached 700. According to research, about 50% of oxygen loss in the upper layers of the ocean is caused by global warming.
According to scientists, if the current state of affairs is maintained, an increase in global temperature and an increase in nutrient consumption will lead to the fact that by 2100 the level of oxygen in the ocean will decrease by 3-4%. As a result, giant dead zones will grow, where, under conditions of severe hypoxia, able to survive marine organisms.
The researchers note that deoxygenation threatens large species, including tuna, marlin, swordfish and sharks. Their decline could affect the lives of hundreds of millions of people dependent on fisheries.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Women's brains age more slowly
▪ Opioid pain reliever without side effects
▪ Connecting chips at unthinkable angles
▪ By 2025, HDD capacity will grow to 100 TB
▪ Male and female perception of colors
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Amateur Radio Technologies. Selection of articles
▪ article by Eric Berne (Leonard Bernstein). Famous aphorisms
▪ article Which animal lives the longest? Detailed answer
▪ article Alpine strawberry. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Universal security device for a car, apartment, garage. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Two modem options, Hamcomm and Hamcomm+. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese




 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: