
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Microphone with recording-playback device. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Civil radio communications When working on the air, you often have to repeat your callsign many times. A digital tape recorder, which is available in some transceivers, can "automate" this process. Often a computer is also used for this purpose. However, the latter option is not always convenient or possible. The device described below can help in this situation. The recording-playback device allows you to record transmitted or received information and reproduce it repeatedly. Its basis is the ISD1416 (ISD1420) chip. It is an electronic device for recording and playing sound information. The duration of the recording depends on the type of microcircuit used. To record information, an electret microphone must be connected to the microcircuit, and for playback, a dynamic head. Here you can use a computer multimedia microphone headset, for example, MHS101, MHS111, which includes headphones and an electret microphone. The circuit of a microphone headset with a recording-playback device (Fig. 1) is designed for wearable transceivers of types "ALINK0-191" STAN-DARD-C510" and similar. A microphone headset is connected to the XS1, XS2 jacks, and kXS4 - connecting cables connected to the telephone and microphone jacks of the transceiver. Without power supply, the device provides the output signal of the receiver to the headphones and the microphone signal to the input of the transceiver, as well as remote activation of the "TX" mode. It happens like this. When the SB2 button is closed, the power supply from the transceiver is supplied to the microphone and due to the current flowing through it, the transceiver switches to the "TX" mode, and the microphone signal goes to it.
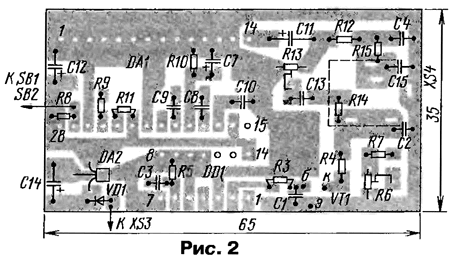
When power supply voltage (3...9 V) is applied to socket XS24, the device can record received and transmitted messages, as well as playback recorded information on headphones or transmit it on the air in automatic mode. Each of the modes is activated by the corresponding button. The supply voltage is stabilized by a microcircuit voltage regulator DA2. LED HL1 indicates the presence of supply voltage, and HL2 - recording mode. An RS flip-flop is assembled on the DD1 element, and an electronic key is assembled on the transistor. The device works like this. The mode of recording transmitted information. In this mode, press the SB2 "PTT" button, the transceiver switches to the "TX" mode and the microphone signal is fed to it, as well as to the input of the DA1 chip. To record information, you must also press the SB4 "REC TX" button. In this case, low the logic level will go to pin 27 of the DA1 chip (recording mode), and the signal from the microphone amplifier of the microcircuit through the contacts SB4.2 will go to the final amplifier and will be written to the memory device.The duration of the recording is determined by the duration of pressing the SB4 button, but will not exceed 16 s for ISD1416 and 20 s for ISD1420.In this mode, the HL2 LED will be on. Recording mode of received information. To do this, when receiving, press the SB3 button and hold it. In this case, a low logic level will go to pin 27 of the microcircuit, and the signal from the output of the UHF transceiver through resistors R7, R6 and contacts SB3.2 will go to the input of the final amplifier and will also be recorded. The maximum recording duration will be the same, and the HL2 LED will be lit in this mode. Playback mode on headphones. To do this, briefly press the button SB5 "PLAY". A low logic level will appear at pin 24 of the microcircuit, and it will go into playback mode. At the same time, a powerful signal will appear at the output of the ultrasonic microcircuit (pin 14), which will go through the resistor R12 to the head phones. At the end of playback, the HL2 LED will flash briefly. Playback in "TX" mode. In this mode, the recorded information is played back on the headphones and at the same time the transceiver is turned on and transmitted over the air. To enable this mode, briefly press the button SB1 "TX PLAY". In this case, a high logic level will go to the input of the R-flip-flop, and a low level will appear at its direct output, which will go through the capacitor C6 to pin 24 of the microcircuit and it will switch to playback mode. The signal from the output of the ultrasonic microcircuit through the elements R13, C13, P14 will go to the microphone input of the transceiver. At the same time, a high logic level at the inverted output of the trigger will open the transistor, current will flow through the microphone input of the transceiver and it will switch to transmit mode. At the end of playback, a low logic level will briefly appear at pin 25 and the HL2 LED will flash. A positive voltage drop through the capacitor C3 will go to the input S of the trigger, and a low logic level will appear on the inverted output, the transistor will close and the transceiver will switch from the "TX" mode to the "RX" mode. Surface mount parts should be used in the device to reduce its dimensions. Possible replacements for DA2 elements - KR1157EN502, VD1 - any small-sized rectifier, LEDs - small-sized with an operating current of 5 ... 10 mA, polar capacitors - tantalum chip, non-polar - K10-17, tuning resistors - SPZ-19, constant - P1- 12. Buttons - any small-sized self-returning, sockets XS1-XS4 - two-channel (stereo 2,5 and 3,5 mm) from household radio equipment. All external connecting wires must be shielded. Most of the parts are placed on a printed circuit board made of double-sided foil fiberglass (Fig. 2). The second side is left metallized and is used as a common wire. The workpiece holes on this side are countersunk. The board is placed in a case made of insulating material with suitable dimensions, for example, a case from a computer mouse is suitable. Sockets, buttons and LEDs are placed on the case. If desired, the circuit can be simplified by excluding the LEDs from it, installing a jumper instead of HL2 and increasing the resistance of the resistor R9 to 10 kOhm.
The adjustment comes down to setting the necessary signal levels with trimmer resistors, while you must first set the output signal level of the 3H transceiver and then maintain it approximately constant. To adapt the device to transceivers with a separate transmission control bus, the resistor R4 must be disconnected from the microphone bus and connected to the control bus. Author: I. Nechaev (UA3WIA), Kursk
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Superconductor without limits ▪ Viruses are 10 times stronger in the morning than in the evening ▪ Orbital connection of qubits improves quantum computing
▪ section of the site Car. Article selection ▪ article Sing, swallow, sing! Popular expression ▪ article Adjuster equipment. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ article Electric starter for a car. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: