
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Radio transmitter with a fixed frequency master oscillator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
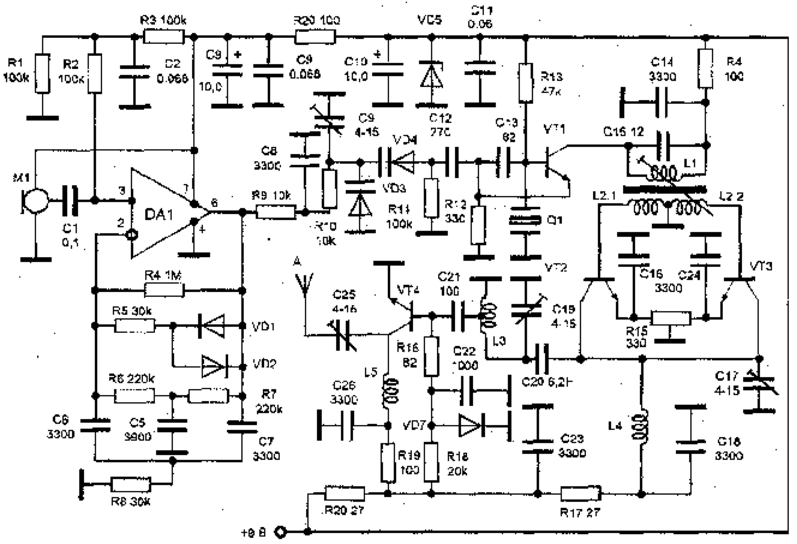
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Transmitters The transmitter operates at a fixed frequency, determined by the frequency of the quartz resonator in its master oscillator. Features transmitting path: - carrier transmission frequency ....... 145,68 MHz;
The schematic diagram of the transmitter is shown in Fig. 1. This circuit uses a modulating amplifier with an electret microphone with a built-in amplifier. In order to improve speech intelligibility, frequency and amplitude correction of the low-frequency signal is used. The signal from the microphone is fed to the non-inverting input of the operational amplifier DA1. This circuit uses unipolar power supply. In order for the operational amplifier to operate, a bias voltage equal to half the supply voltage is applied to this input, creating the midpoint of the bipolar source. The voltage is set by resistors R1, R2, R3. The feedback circuit of the operational amplifier includes a combined DC coupling circuit. When the signal from the microphone is weak and normal, the voltage at the output of the operational amplifier is small, and the diodes VD1 and VD2 are closed. When the output signal exceeds a certain level, the diodes open, which leads to the inclusion of an additional resistor R5 in the feedback. The OOS coefficient increases and the transfer coefficient of the op-amp decreases. This is how the compressor works, correcting the input signal in amplitude. In addition, the OOS circuit includes frequency-dependent circuits on elements R6-R8 and C5-C7, which turn the modulation amplifier into an active filter and select a frequency band from 450 Hz to 2500 Hz, filtering out unwanted interference at low and high frequencies. From the output of the operational amplifier, through a filter chain on resistors R9 and R10, audio frequency voltage is supplied to varicaps VD3 and VD4. The voltage across the varicaps changes in accordance with the audio frequency signal, changing their capacitance. Varicaps are connected in series to a capacitive divider in the feedback circuit of a quartz oscillator, and, therefore, when it is excited, the frequency of the oscillator will change in accordance with the change in the amplitude of the audio signal. The master oscillator is made on transistor VT1. A quartz resonator is connected to the base circuit of the transistor and is excited at the series resonance frequency.
In this case, a resonator with a main excitation frequency of 24 MHz is used. In the collector circuit of transistor VT28, a triple frequency value is allocated - 1 MHz. Circuit L72, C 84 is tuned to the third harmonic of the resonator. The input of a paraphase balanced frequency doubler operating on even harmonics is inductively coupled to the coil of this circuit. The doubler is made on transistors VT1 and VT15, the collectors of which are connected together, and the bases are connected to the out-of-phase coils L2 and L3. A bandpass filter on elements L2.1, C 2.2 and L4, C 17 at the output of the doubler produces a voltage with a frequency of 3 MHz, which from part of the turns of coil L19 is supplied to the input of the preliminary stage of the power amplifier on transistor VT145,68. It operates in A-B mode with a small bias voltage obtained from a parametric voltage stabilizer made on a VD3 silicon diode connected in the forward direction (according to a stabilist circuit). The amplified voltage is released in the collector circuit VT4 and enters the antenna through C7. The transmitter antenna is a quarter-wave vibrator with an equivalent resistance of 4 Ohms. Fixed capacitors can be of any type KM and KL, KT. Capacitors with a minimum TKE must be installed in the circuits. Electrolytic capacitors are type K53-14, but you can also use K50-35 and other small ones. The operational amplifier can be replaced with K140UD708, K140UD6, KR140UD2, K140UD7, K140UD8 or K140UD12. Instead of the KT315 transistor, you can use any one with a cutoff frequency of at least 300 MHz, for example, KT312, KT316 or KT368. The transistor of the output stage of the KT610 transmitter can be replaced with KT913, KT925. For the inductors L1 and L2 of the transmitter, plastic frames with a diameter of 5 mm are used, intended for vertical installation (at one end there is a rectangular area for five terminals). The frame has a tuning core made of 20HF ferrite. If such a core is not available, you can discard it and solder a tuning ceramic capacitor parallel to the C 15 capacitor on the installation side. Coil L1 has 10 turns, L2 - 6+6 turns. PEV-2 0,31 wire was used. The remaining transmitter coils are frameless; they are wound on mandrels, which are then removed. The diameter of all coils is 5 mm, L3 contains 1,5+3,5 turns, L4 - 5 turns. All coils are wound with PEV-2 1,0 mm wire. The winding length of coils L3 and L5 is 8 mm, L4 is 9 mm. More precisely, the dimensions of the coils are set during setup. After checking the correct installation, setting up the transmitter begins with tuning the circuits using a resonant wave meter. First, by moving the L1 core, the maximum voltage amplitude is achieved with a frequency of 72-73 MHz in circuit L1, C15. Then circuits L4, C17 and L3, C19 are sequentially adjusted to a maximum voltage of 144-146 MHz. Additionally, when setting up the circuits, you need to select the value of R12 so that there is a maximum output voltage of the transmitter. The tripler on VT2 and VT3 is balanced with a variable resistor R15 for maximum voltage suppression of 72-73 MHz at its output. Setting up the low-frequency path of the transmitter is reduced only to checking its functionality. Within small limits, the transmitter carrier frequency can be changed by adjusting C9.
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024 Primium Seneca keyboard
05.05.2024 The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
▪ A new method of observing the Sun ▪ Oukitel K10000 Pro smartphone with 10100 mAh battery ▪ Dell UltraSharp 40 Curved Monitor ▪ Global warming wakes up volcanoes
▪ section of the site Amateur Radio Technologies. Selection of articles ▪ article Devourers of emptiness, readers of newspapers. Popular expression ▪ article Who are trichologists? Detailed answer ▪ Triggers article. Radio - for beginners ▪ article Charge meter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article Micro HPP. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: