A simple radio wave detector. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Transmitters
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The device is a simple radio wave detector with sound indication. With it, you can find a working microtransmitter in the room. The radio wave detector is sensitive to frequencies up to 500 MHz. You can adjust the detector when searching for working transmitters by changing the length of the telescopic receiving antenna.
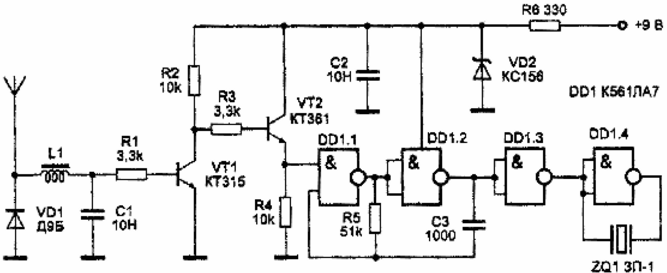
Fig.1 Simple radio wave detector
The telescopic receiving antenna perceives high-frequency electromagnetic oscillations in the range up to 500 MHz, which are then detected by a VD1 diode of the D9B type. The high-frequency component of the signal is filtered out by the inductor L1 and capacitor C1. The low-frequency signal enters through the resistor R1 to the base of the transistor VT1 type KT315, which leads to the opening of the latter and, as a result, to the opening of the transistor VT2 type KT361. At the same time, a positive voltage appears on the resistor R4, close to the supply voltage, which is perceived by the logic element DD1.1 of the DD1 microcircuit of the K561LA7 type as the level of a logical unit. This turns on the pulse generator on the elements DD1.1, DD1.2, R5 and C3. From its output, pulses with a frequency of 2 kHz are fed to the input of the buffer stage on the elements DD1.3, DD1.4. The load of this cascade is a sound piezoceramic transducer ZQ1 type ZP-1, which converts electrical vibrations with a frequency of 2 kHz into acoustic ones. In order to increase the sound volume, the ZQ1 converter is connected between the input and output of the DD1.4 element of the DD1 chip. The detector is powered by a 9 V current source through a parametric stabilizer on the elements VD2, R6.
The detector uses MLT-0,125 type resistors. Diode VD1 can be replaced with GD507 or any high-frequency germanium. Transistors VT1 and VT2 can be replaced by KT3102 and KT3107, respectively. The VD2 zener diode can be any with a stabilization voltage of 4,7-7,0 V. The ZQ1 piezoceramic converter can be replaced with ZP-22.
It is best to tune the detector using a high-frequency generator. Connect an insulated wire - antenna to the output of the generator, and place the detector antenna parallel to it. This way you loosely couple the detector to the generator. Explore the entire radio band from 500 kHz up to the point where the detector stops receiving radio waves. Notice how the sensitivity of the detector changes with frequency.
 See other articles Section Transmitters.
See other articles Section Transmitters.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024
The modern world of science and technology is developing rapidly, and every day new methods and technologies appear that open up new prospects for us in various fields. One such innovation is the development by German scientists of a new way to control optical signals, which could lead to significant progress in the field of photonics. Recent research has allowed German scientists to create a tunable waveplate inside a fused silica waveguide. This method, based on the use of a liquid crystal layer, allows one to effectively change the polarization of light passing through a waveguide. This technological breakthrough opens up new prospects for the development of compact and efficient photonic devices capable of processing large volumes of data. The electro-optical control of polarization provided by the new method could provide the basis for a new class of integrated photonic devices. This opens up great opportunities for ... >>
Primium Seneca keyboard
05.05.2024
Keyboards are an integral part of our daily computer work. However, one of the main problems that users face is noise, especially in the case of premium models. But with the new Seneca keyboard from Norbauer & Co, that may change. Seneca is not just a keyboard, it is the result of five years of development work to create the ideal device. Every aspect of this keyboard, from acoustic properties to mechanical characteristics, has been carefully considered and balanced. One of the key features of Seneca is its silent stabilizers, which solve the noise problem common to many keyboards. In addition, the keyboard supports various key widths, making it convenient for any user. Although Seneca is not yet available for purchase, it is scheduled for release in late summer. Norbauer & Co's Seneca represents new standards in keyboard design. Her ... >>
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
Exploring space and its mysteries is a task that attracts the attention of astronomers from all over the world. In the fresh air of the high mountains, far from city light pollution, the stars and planets reveal their secrets with greater clarity. A new page is opening in the history of astronomy with the opening of the world's highest astronomical observatory - the Atacama Observatory of the University of Tokyo. The Atacama Observatory, located at an altitude of 5640 meters above sea level, opens up new opportunities for astronomers in the study of space. This site has become the highest location for a ground-based telescope, providing researchers with a unique tool for studying infrared waves in the Universe. Although the high altitude location provides clearer skies and less interference from the atmosphere, building an observatory on a high mountain poses enormous difficulties and challenges. However, despite the difficulties, the new observatory opens up broad research prospects for astronomers. ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Medicines for old age
16.03.2013
Renowned Harvard scientist David Sinclair has announced a breakthrough in the development of drugs that can block the aging process. According to the scientist, in 5 years there will be drugs that can extend life up to 150 years. Sinclair's article, published in Science, explains that interaction with a single amino acid in the SIRT1 enzyme is critical to the development of life-extending drugs.
SIRT1 controls DNA repair, apoptosis (cell death), circadian rhythms, inflammatory pathways, insulin secretion, and mitochondrial biogenesis at the cellular level. SIRT1 is an enzyme in a class of molecules called sirtuins. Recent studies show that sirtuin activation reduces the rate of cell aging through interaction with other cellular "switches" such as FOXO3a and PGC-1a.
Resveratrol, a polyphenol found in red wine and grapes, is a weak natural sirtuin activator and has been shown to prolong life in mice in some studies. However, data on sirtuin activators are conflicting, and direct activation of SIRT1 is considered incredibly difficult, since there has never been a drug in the history of pharmaceuticals that could harmlessly speed up the enzyme. However, the search for a cure for senile diseases led to the fact that in 117 experiments, scientists were able to confirm the ability of individual substances to activate SIRT1. Now Harvard scientists know exactly how to activate the enzyme and have a good understanding of the molecular mechanism of activation.
Thus, the mechanism of allosteric activation (as in the case of resveratol) allows the development of drugs for the treatment of many diseases associated with aging. A "side effect" of this therapy will be life extension up to approximately 150 years. According to David Sinclair, the "longevity pill" will be on sale in the coming decades. At the same time, "drugs for old age" will be ready within 5 years, but it will take a long time to test them and confirm their effectiveness.
"In fact, the new drugs will treat one disease, but unlike current drugs, prevent 20 other diseases," says Sinclair. "In essence, we will be able to slow down aging. Some of us could live up to 150 years."
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Quantum dot photosensors outperform CMOS sensors
▪ Pocket infrared thermometers
▪ RackStation RS3617xs NAS
▪ Smart ring from Samsung
▪ Engine made of molecules
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Batteries, chargers. Article selection
▪ article Alexandre Dumas (son). Famous aphorisms
▪ article Where American Transport Aircraft Are Worshiped? Detailed answer
▪ article Economical sanding pad. home workshop
▪ article Starting relay for an asynchronous electric motor. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Scheme of a universal frequency radio modem. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: