
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Pulse adjustable power supply for lamp equipment. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
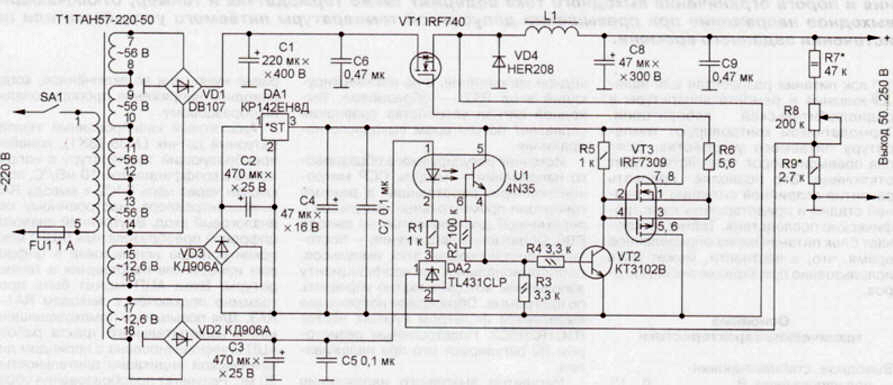
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies The proposed switching power supply for lamp equipment is assembled according to a simple scheme from common parts, it produces a stabilized voltage regulated within 50 ... 250 V. The maximum load current is 0,3 A. The ripple level does not exceed a few tenths of a volt. The figure shows a diagram of the proposed device. It contains a network transformer T1, an anode voltage rectifier bridge VD1, capacitors 01 and C6, a key transistor VT1, a storage inductor L1, a diode / 04, output capacitors C8 and C9, an output voltage regulator on a DA2 chip, an optocoupler U1, a transistor VT2 and an assembly of complementary key field effect transistors VT3. The device works as follows. When mains voltage is applied to transformer T1, capacitors C1-C7 are charged. The phototransistor of the optocoupler U1 is closed, and the transistor VT2 controlled by it is also closed. A voltage of 3 V is supplied to the gate of the top transistor of the VT5 assembly through the resistor R12, opening it. The same voltage is supplied to the gate of the transistor VT1 relative to its source, as a result of which VT1 opens, the current through the inductor L1 increases linearly, charging the output capacitors C8 and C9. The voltage on them increases, the current through the divider R7-R9 increases. When the voltage drop across the resistor R9 exceeds 2,5 V, the DA2 chip opens, a current limited by the resistor R1 flows through the emitting diode of the optocoupler U1. The phototransistor of the optocoupler U1 opens, the transistor VT2 also opens, closing the transistor of the VT3 assembly, which is upper in the circuit, and opening the transistor of this assembly, which is lower in the circuit, which shunts the gate-source of the transistor VT1, closing it. The use of the transistor assembly VT3 is due to the fact that the key transistor VT1 has a significant input capacitance - several thousand picofarads. For its fast recharging, the VT3 transistor assembly is used, the elements of which have a low channel resistance in the open state. Resistor R6 limits the surge current to a safe level, increasing the reliability of the device. When the transistor VT1 is closed, the energy accumulated in the magnetic field of the inductor L1 is transferred through the diode VD4 to the output capacitors C8 and C9. Capacitors are discharged to the load, the voltage across them decreases. When the voltage across the resistor R9 drops below 2,5 V, the DA2 chip closes, the emitting diode of the optocoupler U1 turns off, and the phototransistor of this optocoupler closes. The described process is then repeated. Transformers - TAN57-220-50. In its absence, you can use the TS160-TS200 network transformer on the PL magnetic circuit from a lamp black and white TV. The transformer is disassembled, the filament windings are wound from the coils (they are made with the thickest wire), counting the turns. Then the secondary windings are wound onto a separate spool. Usually they are made with a wire with a diameter of 0,7 ... 0,8 mm. Multiplying the number of turns of the filament winding by 20, we get the number of turns of the anode winding for each coil. After assembling the transformer, these windings must be connected in phase in series. The number of turns of the windings connected to the diode bridges VD2 and VD3 should be twice that of the filament winding. These windings are wound with an existing wire (PEL 0,31 can also be used) on different coils. The filament windings (not shown in the diagram) are wound with a previously removed wire. They are used to power the filament circuits of the lamps of the powered device. When assembling the transformer, it is necessary to apply ferrite paste to the ends of the magnetic circuit, made from crushed and sifted ferrite powder mixed with BF-2 glue. Transistor VT1 is a powerful field switching transistor with an internal diode, an insulated gate and an induced n-type channel, with a maximum allowable drain-source voltage of at least 400 V and a drain current of at least 2 A, for example, imported IRF710-IRF740, IRF810-IRF840, domestic KP707 with any letter index. Transistor VT2 - any low-power silicon with a base current transfer coefficient of more than 100, for example, KT342 or KT3102 with any letter index. Optocoupler U1 - imported 4N25-4N35, PC811-PC817, M008011, MOS8012 or domestic AOT128 with any letter index. Diode bridge VD1 - for a medium rectified current of at least 1 A and a reverse voltage of at least 400 V, for example, DB107, W10M, or assembled from separate KD226D diodes. Diode bridges VD2 and VD3 must be designed for a rectified current of at least 0,1 A and a reverse voltage of at least 30 V, they can be assembled from separate diodes with suitable parameters. Diode VD4 - pulsed with a permissible forward current of at least 1 A and a reverse voltage of at least 400 V, for example, FR30-7, FR207. The integral stabilizer DA1 can be any with an output voltage of 12 V and a current of at least 0,1 A, for example, 7812, 78M12, 78L12. Chip DA2 may be domestic K142EN19. Oxide capacitors are imported, with a rated voltage not less than that indicated on the diagram. Capacitors C6 and C9 - K73-17 with a rated voltage of 400 V. They greatly facilitate the operation of capacitors C1 and C8. Capacitors C5 and C7 - KM-5a or K10-17. Fixed resistors - MLT and S2-23. The variable resistor R8 is imported, it can be replaced with a domestic one that can withstand a voltage of at least 200 V. Inductor L1 is wound with PEL wire with a diameter of 0,46 mm until the frame size Sh6x6 is filled from M2000NM1 ferrite. The magnetic circuit is assembled with a gap of 0,2 mm, the finished inductor is impregnated with paraffin to eliminate whistling. The device is assembled on a universal breadboard by surface mounting and built into the radio editing table. Author: K. Moroz
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Phobos will be destroyed by Mars ▪ 32-bit microcontrollers with record low power consumption ▪ Accumulators of the third millennium
▪ site section Digital technology. Article selection ▪ article Was there a boy? Popular expression ▪ article Why are fly stickers placed in men's toilet urinals? Detailed answer ▪ article Buten tuberous. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Water varnishes. Simple recipes and tips ▪ article Soap in soft and hard water. Chemical experience
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: