
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AC adapter for digital camera. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
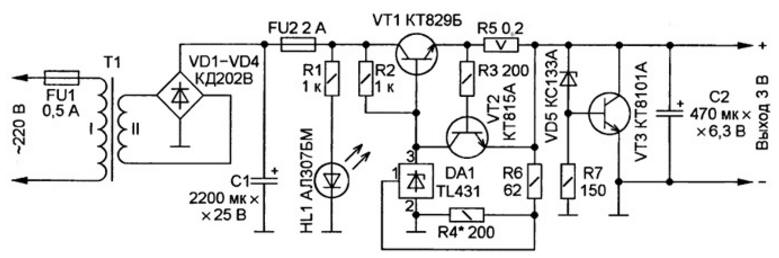
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies Batteries run out quickly in modern digital cameras. For example, the Canon A530 camera in picture playback mode consumes a current of no more than 0,2 A. But the photography mode without a flash requires a current of at least 0,4 A from the power source, and with a flash - no less than 0,7 A. In this camera two AA batteries are used, which can be quickly replaced. Most other cameras are powered by batteries only. This is another serious problem of most modern devices. Discharging a standard battery does not give any possibility of further operation of the camera. This is where quick battery replacement comes in handy. Having two spare fresh batteries in your pocket easily solves the problem of overcoming sudden battery discharge. When using a flash, it is no longer possible to stock up on galvanic cells - they are quickly discharged. High-quality elements last longer, but their prices have recently increased dramatically. It soon became clear that the operation of the camera from galvanic cells is very ruinous. The available energy-intensive small-sized batteries with a capacity of 2650 mAh, of course, help out. But they also wear out quickly. The main thing is that it happens unexpectedly. There is another serious drawback when operating the camera on 1,2-volt batteries. Long before the battery is completely discharged to 1 V, the camera will stop functioning. It simply "requires" to replace the batteries with the corresponding inscription on the display and then automatically turns off. The seized batteries have a voltage of 1,1 ... 1,15 V at a load current of 0,5 A, that is, there is an underutilization of the batteries. And very solid. We do not know how to charge these batteries, because we do not know what charge they should be told. And then there is nothing left but to forcefully discharge underused batteries to a voltage of 0,9 ... 1 V before charging. This takes several hours. As you can see, it is obvious that it is impossible to maximize the use of energy from both batteries and galvanic cells. Therefore, in stationary operating conditions, it is advisable to power the camera from the mains through the appropriate unit. The main requirement for it is reliability. Under no circumstances should it damage an expensive camera. Taking into account this requirement, a device has been developed, the circuit of which is shown in the figure. This is a linear compensating voltage stabilizer with output current limitation and protection unit against emergency increase of output voltage. The mains transformer T1, the diode bridge VD1 -VD4 and the smoothing capacitor C1 are used from an industrial power supply unit BP 12/10 (12 V, 10 W). The device uses a parallel stabilizer chip TL431 (DA1). Its control input receives voltage from the divider R6R4, the resistors of which are selected so that at the nominal output voltage, the resistor R4 will be 2,5 V. If the output voltage for some reason exceeds the nominal voltage, the current through the DA1 chip will increase sharply, which will lead to reducing the voltage on the basis of the regulating transistor VT1 and, accordingly, restoring the nominal output voltage of the stabilizer. In order to ensure reliability, the transistor VT1 is selected with a large margin for voltage, current and power. The output current limiting unit is assembled on a transistor VT2 and resistors R3, R5. Resistor R5 - load current sensor. At the moment when the voltage drop across it exceeds 0,6 V, the transistor VT2 opens and restrains the growth of the base current of the transistor VT1, as a result of which the output current is limited to 3 A. The transistor VT2 was also chosen powerful for reasons of reliability. There were cases of failure of low-power transistors (from the KT315 and KT503 series) in similar protective nodes. But there was no damage to powerful transistors. The advantages of the proposed voltage stabilizer are the inclusion of a current sensor in the gap of the positive, and not the negative (common) power wire, as well as the absence of a “drawdown” of the output voltage when the load current approaches the limit limit. Despite the high reliability of the voltage stabilizer, if it does fail, the camera may be damaged by the increased supply voltage. To prevent this, a protection unit was used on the transistor VT3, the zener diode VD5 and the resistor R7. With an emergency increase in the output voltage, the zener diode VD5 and the transistor VT3 open, the collector current of which blows the fuse FU2. Such nodes are well tested by the author to protect the filaments of TV kinescopes when they are powered by direct current. Since the proposed device is intended for home use, the task of minimizing its weight and size indicators was not set. Therefore, it is placed in a case from the above-mentioned BP 12/10 block, which in our time can be purchased very cheaply without much difficulty. The secondary winding of the network transformer is rewound: the number of its turns is reduced by about 30%, while the winding voltage drops to 7,7 V. You can also use any network transformer with a power of 5 ... 10 W with a winding of 6 ... 6,3 V , including incandescent for lamp technology. It is permissible to use modern small-sized transformers. But for many of them, the declared characteristics do not correspond to the real ones. Only such a transformer is suitable, the winding of which is capable of providing an output current of 2 A at a voltage of at least 6 V. Even a transformer with a winding of only 5 V is suitable if diodes with a lower voltage drop are used in the rectifier bridge VD1 - VD4, for example, germanium from the D302 series -D305 or Schottky diodes 1N5822, KD2998A-KD2998G. Oxide capacitors can be any, the capacitance of the capacitor C1 must be at least 1000 microfarads. Current sensor - resistor R5 - C5-16MV-5. If necessary, it can be homemade from nichrome wire. The remaining resistors are MLT-0,25. The power supply is mounted on a breadboard. Diodes of the rectifier bridge KD202V (VD1-VD4) can be replaced by others with a maximum forward current of at least 3 A, for example, from the KD213, D242, D243 series, or use ready-made bridges BR305 or BR605. The control transistor KT829B (VT1) is placed on a ribbed heat sink with a cooling surface area of about 150 cm2. This transistor is composite. It can be any of the KT829 or KT827 series, as well as foreign BDX53C. Transistor VT2. any of the KT815, KT817 series. Transistor VT3 - any powerful silicon low-frequency npn structure with a maximum direct collector current of at least 5 A, for example, from the KT803, KT808, KT819, BD911 series. This transistor is installed without a heat sink, since it does not have time to heat up during the blowing of the FU2 fuse. It follows that surrogate fuses cannot be used in this design. LED HL1 - any color of glow. Zener diode KS133A (VD5) can be replaced by KS139A or foreign BZX55C3V3, BZX55C3V6, BZX55C3V9. Establishing a power supply assembled from serviceable parts is easy. But given that an expensive load is connected to it, this process should be taken very responsibly. First, the protective node on the transistor VT3 is checked separately. At the time of adjustment, this transistor is installed on a heat sink with a cooling surface area of 200 cm2. The node is connected to a laboratory power supply with a continuously adjustable output voltage of 0 ... 15 V and output current limitation to ZA. In the absence of a laboratory power supply, you can use an adjustable voltage regulator, for which the constant resistor R4 is temporarily replaced by a variable connected as a rheostat. It is necessary to make sure that the transistor VT3 reliably opens and closes the output of the power supply at a voltage of no more than 4,5 V. Then check the output current protection. The required level of current limitation is set by selecting the resistance of the current sensor - resistor R5. After that, if necessary, select the resistance of the resistor R4 to set the output voltage within 3 ... 3,2 V. Finally, connecting and disconnecting a load with a resistance of 4 ohms to the output, check the stability of the output voltage. It should not change by more than 10 mV. The voltage was measured by the B7-38 device directly on the board. The proposed device can simultaneously power two cameras. During the operation (about two years) there were no comments on his work. For greater reliability of protecting the camera from an emergency increase in the output voltage, it is better to connect the collector of the VT3 transistor not to the output of the voltage stabilizer, but to its input - the connection point of the resistors R1, R2, upper according to the output diagram, the collector of the transistor VT1 and the fuse FU2, right according to the output circuit. Author: A. Zyzyuk
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Anesthesia works the same way on plants as it does on people. ▪ The main molecule of the Universe is determined ▪ New frost protection technology
▪ section of the site Radio - for beginners. Article selection ▪ article Pills will decorate the lamp. Tips for the home master ▪ article Which metal is the best conductor? Detailed answer ▪ article Measuring distances by travel time. Tourist tips ▪ article TV signal amplifier. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: