
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Batteries for household equipment
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells In recent years, many different galvanic cells for powering household equipment have appeared on the Russian market. At the same time, there is a lack of information on the evaluation and selection of elements that are most suitable for specific equipment. The purpose of this article is to fill this gap and offer our readers additional information. In any galvanic cell, the electrochemical reaction consists of the process of oxidation at the negative electrode and reduction at the positive. The reactions are separated in space and the electrons formed at the negative terminal pass through the external circuit to the positive one and there participate in the reduction reaction. Depending on the materials of the electrodes and the composition of the electrolyte, the electromotive force (EMF) at the terminals of the element may be different. The EMF value is determined by the difference in the electrochemical potentials of the electrodes. In table. 1 shows some parameters of the most commonly used galvanic cells.
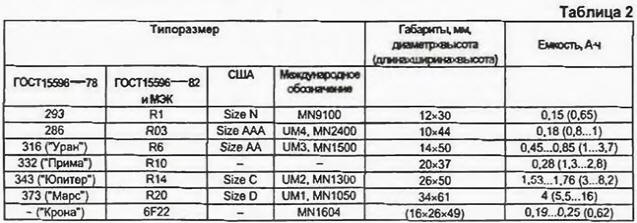
The copper-zinc element, despite the low voltage and other inconveniences (liquid acid electrolyte, the need for cleaning), works stably at low current for many years and has recently been widely used in railway automation systems. In practice, at present, we are faced with a limited number of elements. These are saline, alkaline, mercury, silver, air and lithium. Salt elements They are also called manganese-zinc or carbon-zinc elements. In them, the plus electrode is made of graphite, and the minus one is zinc (element body). The function of the electrolyte-depolarizer is performed by a mixture of manganese dioxide and ammonium chloride. The EMF of the salt cell is 1,6 V, and batteries with the required voltage are obtained by serial connection. Elements for such batteries are often not cylindrical, but rectangular in shape. The working temperature range of salt elements is from -20°С to +55°С. but at low temperatures, the current delivered to the load decreases. and at elevated temperatures, the destruction of the zinc electrode is accelerated and the electrolyte dries out faster. In the last decade, salt cells have been significantly improved: to reduce the destruction of the zinc case, mercury was added to the electrolyte, which was then replaced with environmentally friendly organic additives. These improvements extend the life of the cells to three years, although they are usually quoted as being between 9 and 12 months. Salt elements with improving additives are produced in a more reliable design - a protective steel (less often plastic) case is outside, and zinc is inside. These elements are safer to operate and. in addition, they have a higher energy intensity. The body of such an element is closed from above and below by shaped metal disks-electrodes with a seal in the form of polymer gaskets. Nevertheless, salt galvanic cells have the smallest electric capacity among chemical current sources, which is 450 ... 850 mAh (hereinafter, the values are given for an AA format element). They are designed for use in low to medium power devices such as watches, remote controls for household appliances, children's toys, alarm devices, pocket radios. To prolong the service life of salt cells, it is recommended, along with new sets, to use already used ones, but not bringing them to a completely discharged state. This is due to a very slow process of equalizing local inhomogeneities in a viscous electrolyte during discharge and in some restoration of the properties of the element during "rest". In particular, it is not recommended to use one set of salt elements for more than two hours in a row in an audio player. Alkaline elements Alkaline elements outwardly practically do not differ from salt ones, they contain carbon and zinc electrodes, manganese dioxide, but instead of ammonium chloride they use an alkaline electrolyte. Therefore, they are called alkaline or alkaline. The alkaline electrolyte eliminates gas evolution during the operation of the cells, so they are produced in a sealed version. The emf of such elements is slightly less than that of salt ones. But they have a greater specific capacity, discharge current and shelf life (up to five years). The capacity of alkaline cells is from 1000 to 3700 mAh. They remain operational at temperatures from -30°С to +55°С. However, the most significant difference between alkaline and salt cells is a slower decrease in voltage during discharge (but it decreases sharply at the end). Since the capacity of alkaline cells is much higher than that of salt ones, they are used in devices with medium and high energy consumption: flashlights, electric shavers, voice recorders, players, portable radios and radios, telephones and radio stations, powerful electric lights. mercury elements Mercury has long been successfully used to improve salt elements with zinc. As a result, elements with manganese dioxide and mercury oxides were created. The mercury element has a large capacity and a very long shelf life. The EMF of such an element is only 0.15 V less than that of an alkaline one, but due to the danger of environmental pollution with mercury, such elements of household formats are produced less and less (elements with the inscription "Merquri" cannot be thrown into garbage cans, and we have special containers for hazardous waste . Unfortunately, not yet). silver elements They are really silver - the positive electrode in them is made of silver oxides. The EMF of silver elements is 0.25 V greater than that of salt ones. They are expensive, rare, and can be distinguished by the inscription "Silver". Air-zinc elements These elements have zinc and air involved in the electrochemical reaction, so holes are provided in their body. Zinc air cells have high capacity and long shelf life. Their self-discharge at room temperature does not exceed 2% per year. But you need to store these elements in a hermetically sealed state, excluding air from entering. This feature, along with a very narrow range of operating parameters, has led to a limited release of consumer format elements. The EMF of air-zinc cells is 1.4 V with a capacity of 70 to 600 mAh. operating temperature range - from -18°С to +50°С. They are mainly used in hearing aids. Lithium cells Lithium batteries have appeared relatively recently. They use lithium negative electrodes and an electrolyte with manganese dioxide based on organic compounds. The cells are efficient in a wide temperature range (from -30°C to +65°C), have a high capacity and a very long shelf life with a very low self-discharge (up to 10 years). Lithium has the highest negative electrode potential of all other metals. The EMF of this element is 3,8 V. Lithium is an expensive metal, so lithium cells were used mainly where long-term reliable operation was required, for example, in backup power supplies for computer memory chips and in space technology. Previously, lithium cells were produced only in "button" ("push-button") versions for watches, calculators, cameras, and computers. Gradually, as their cost decreases, lithium cells appear not only for devices with high power consumption (modern cameras, camcorders - CR123, 2CR5 and CR2 cells). but also for other devices. Unfortunately, today there is no single designation of elements - there is an American system of dimensions, there is an international one - IEC, and leading companies often indicate several designations on their products at once (see Table 2, as well as "Radio", 2000, No. 2, p. 47).
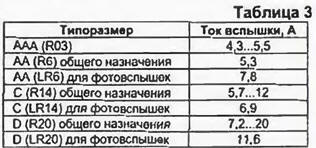
The letter "R" according to the IEC system denotes a cylindrical element, and "F" - rectangular. Adding the letter "L" before "R" or "F" means that this element is alkaline. In general, the full designation in the IEC system includes 14 characters, divided into five semantic groups, which, perhaps, has become a serious obstacle to its implementation. It is described in detail in the article by R. Varlamov "Foreign elements and batteries of the MC system" ("Radio", 1996, No. 3). The consumer is interested in the life of the battery and an affordable price, and the duration of the battery is primarily related to its electrical capacity. Manufacturers unanimously try not to indicate this parameter, and for this they have very good reasons. The fact is that the actual capacity depends on the discharge conditions. How quickly the cell voltage drops as it discharges depends on the load current and the type of electrolyte. It is impossible to discharge the element to zero - the device requires a certain voltage, and at low voltage it will not be able to work. The minimum allowable voltage during discharge is called the cut-off voltage. It is determined by the features of operation and usually ranges from 0,8 to 1 V. The lower the cut-off voltage, the more energy the element can give. The introduction of new technologies makes it possible to improve the characteristics of the elements - to increase the capacity, shelf life, discharge current. For example, Duracell has introduced Titanium technology - the addition of titanium dioxide to the electrolyte increases the life of the cells in devices with low current consumption. Panasonic introduced Power activator technology, TDK introduced X-treme technology. GP Batteries - Super alkaline, Energiser - High-Tech Formula. The use of some form of finely dispersed highly conductive granular graphite and a gelled organic electrolyte allowed these firms to significantly improve cell performance at medium and high power levels. On the one hand, manufacturers are persistently improving their household appliances, seeking to reduce energy consumption, and on the other hand, in the development of the production of batteries, there is a tendency to increase their energy intensity and discharge current. For example, Panasonic, which produces household appliances and batteries, advertising the RQ-SX20 player, emphasizes that branded LR6 alkaline cells (using Power activator technology) provide 45-hour recording playback. In advertising materials, companies usually report that new batteries they produce have significantly increased capacity (without indicating its value). Panasonic gives the following results of increasing the real capacity of the new LR6 Power Alkaline cells: when used in a CD player with a current consumption of 170 ... 300 mA, the operating time of the cells increased by 20%. in a flashlight with a halogen lamp (current consumption 600.. 800 mA) - by 20%. in the digital camera Casio QV-10 (power 315 mW) - by 28%. in an IBM ThinkPad 230 portable computer, by 30%, and in a Nikko toy car, by 45%. From one set of two Panasonic LR6 elements, you can get more than 500 flash units with a small interval between them. As you can see, again advertising: neither flash power nor the interval between them is indicated. Similarly, Energiser elements are advertised: the company indicates that its LR6 elements last 50% longer in a digital camera. in a pocket radio - by 45%. in a mobile phone - by 40%. in a portable flashlight - by 80%, in a radio-controlled car model - by 40% compared to conventional (salt) elements. In reality, the cost of salt and alkaline batteries of the same size differs by 4 ... 5 times, and the service life - by 6 ... 8 times. The actual electrical capacity of a particular battery is practically impossible to establish by marking. It can differ quite significantly even with the apparent identity of the elements. In table. 2 shows the capacity of salt, and in brackets - alkaline galvanic cells. In addition, the most important characteristic of the element is the maximum current. which this element can briefly but stably give to the consumer - the so-called flash current. In table. 3 shows the values of the flash current of some elements.
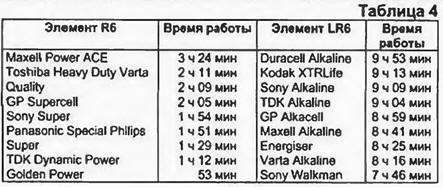
The flash current is different from the fault current at zero resistance of the external circuit. In the latter case, no useful work is done, and the duration of the fault current pulse is a fraction of a second. The flash current is measured at a certain, albeit very small, resistance of the external circuit, often even in comparison with the internal resistance of the source. This current does useful work, and its duration is several seconds (up to ten). The value of the flash current is very significant for consumers with short-term periodic intense load - cameras with automatic film advance, photo flashes. Cells and batteries with high flash current tend to have a significant amount of energy. For example, batteries in disposable sets of Polaroid cameras after using the photo set are still capable of delivering current up to 10 A for a long time. The lack of values for the parameters of the elements is made up for by test tests carried out under various conditions. In table. 4 shows the test results of AA elements (UM3, MN1500, R6, LR6) when working in an audio player. This use of elements is one of the most massive. The above information clearly illustrates the advantage of alkaline elements in comparison with salt ones. For the consumer, the presented parameters are of greater value than the promising advertising statements of firms.
How to distinguish between elements of different types and not run into a fake or simply low-quality products produced by no one knows who and no one knows where? The list of leading companies producing batteries and selling their products on the Russian market is very large. These are Duracell, Energiser, Panasonic, Varta, Kodak, TDK and others. Thus, their very name is already a kind of recommendation, especially if the element and the device for which you are going to purchase it are manufactured by the same company. However, it should be remembered that on alkaline, more advanced and energy-intensive cells, you will almost always find the designation - "Alkaline". Inscriptions indicating improved production technology - "Power Alcaline", "X-Treme". "Super Alkaline". "High-Tech", "Titanium", are also a solid recommendation. You should definitely pay attention to them when choosing a battery for a particular equipment. You can often hear that the all-metal stamped body of the element (especially with a non-smooth bottom surface) indicates that this is a salt element. This sign is not absolute - improved salt elements have a protective metal case with shaped metal washers at the ends, and therefore it is difficult to distinguish them from alkaline ones in appearance. You can distinguish between salt and alkaline elements by the designation of its brand and inscriptions. The letter "R" stands for salt elements (R1, R03, R6, R14, R20, etc.). Improved salt elements are additionally denoted by the letters "P" or "S" (less often HD, HE, EH, UP, UPS) - for example, R6P, SUMS, R20UPS. The letter "L" is entered into the designation of the alkaline element - LR1, LR03, LR6, LR14, LR20, 6LF22 - and the inscription "Alkaline", "Super Alkaline", etc. is almost always added. Mercury, silver and zinc-air elements are designated "Merqury", "Silver" (or "Silber") respectively. "Zn-Air", but for household equipment it is desirable to use elements with the inscriptions "0% Merqury", "0% Merqury & Cadmium". "0% Merqury and Cadmium Added". "0% Quecksilber Cadmium", "0% Hg Cd", "Merqury Free". Another reliable evidence of the high quality of batteries is their packaging. Serious companies pack their products in the so-called blister containers on a cardboard backing - transparent plastic shells that allow you to see the packed items and reliably protect them from moisture and mechanical damage. Usually several elements (two-four R6 elements or two R14 - R20 elements) in a transparent plastic case are glued to a colorful cardboard base, on which the name of the company, its trademark and other information about the company and the product are repeated, including the barcode of the country - manufacturer. Be sure to indicate the expiration date - this information is repeated on the packaging and on the element body in the form of stamped numbers: for example, 09.99. This is most characteristic of salt elements. On alkaline, the expiration date is most often indicated in the form of an inscription on the case: INSTALL BY JAN 2001, Best before MAR2003, or simply JAN2001 and MAR2003. Recently, some companies have begun to save on packaging and cardboard backing, do not protect their products with a polymer film. True, on the back of the cardboard packaging in several languages they provide information about the features of the operation of the goods and guarantees. A number of firms have already begun to print these inscriptions in Russian. In general, the information on the packaging of elements of leading companies is much more informative than the inscriptions on the element itself. Here are examples of inscriptions on salt elements in AA format. GP Batteries, Greencell Extra Heavy Duty 15G "SIZEAA" 1,5 V, 0% Merqury (Hong Kong) - salt cell (in the designation of which this is not mentioned), size AA. "heavy duty" (Heavy Duty), does not contain mercury. Varta company, element Varta Super MIGN0N'R6'AA'UM3'1.5 V 0% Merqury Cadmium. 0% Quecksilber Cadmium (manufactured in France) is a salt element of the same size, and this size is repeated four times in the marking (MIGNON'R6'AA'UM3). does not contain mercury and cadmium. Alkaline elements of the same format. Duracell, Duracell Alkaline element 1.5 V'SIZEAA'MN 1500 LR6, JAN2001 - AA alkaline element, size designation repeated three times, shelf life - until January 2001. No environmental notes. But on the packaging of this element you can read a more complete designation: Alkaline'ExtraPower'Titanium 'AA' MN1500'LR6'Mignon, environmental information - 0% Cd? 0% Hg, 0% Pb and place of production - Belgium. Recommendations are also given there: replace the entire set of elements, do not recharge, do not bring them to the fire and do not use elements of different types and systems at the same time (let's add, and of different degrees of discharge). Usually, warning labels are given on the element body in several languages: Do not throw in fire! Not rechargeable! (Do not throw into the fire! Do not reload!). The essence of these inscriptions is that modern alkaline, and even more so lithium galvanic cells, very often explode when heated or when trying to charge them, like a battery. And the contents of a galvanic cell, even if there are no mercury, lead and cadmium, are far from safe. You can find elements produced by a number of companies where these inscriptions are repeated in Russian (and on the packaging too). If the batteries are poorly packed, sloppy, do not have an indication of where they are made and what their expiration date is, then such products may not meet your expectations and it is dangerous to buy them. As a rule, they are among the cheapest. Therefore, the high price of elements is also indirect evidence of high consumer properties. Author: M.Mikhailov, Moscow
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Linguistic abilities of rats ▪ Seoul Semiconductor SunLike LED is the safest
▪ site section Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters. Article selection ▪ article Feeling of the elbow. Popular expression ▪ article What gesture did the ancient Romans order to kill a defeated gladiator? Detailed answer ▪ article Chief TV director. Job description ▪ article Electronic fishing rod-machine. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: