
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Electronic fishing rod-machine. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Home, household, hobby Even the most timid attempts to transfer to electronic equipment some functions that a person is accustomed to consider "their own", and, accordingly, irreplaceable, arouse a wary attitude towards themselves. Last but not least, this applies to amateur fishing - one of the most conservative forms of human hobbies. Although it is difficult to imagine a more interesting activity for a radio amateur designer. Starting from the very formulation of the problems that arise here, from the "algorithmization of intuition" to testing the invented. And not in the virtual space, where we have been so urgently called lately, but in the very present: under the blue sky, among forests and meadows, with splashing water and fish without a barcode.
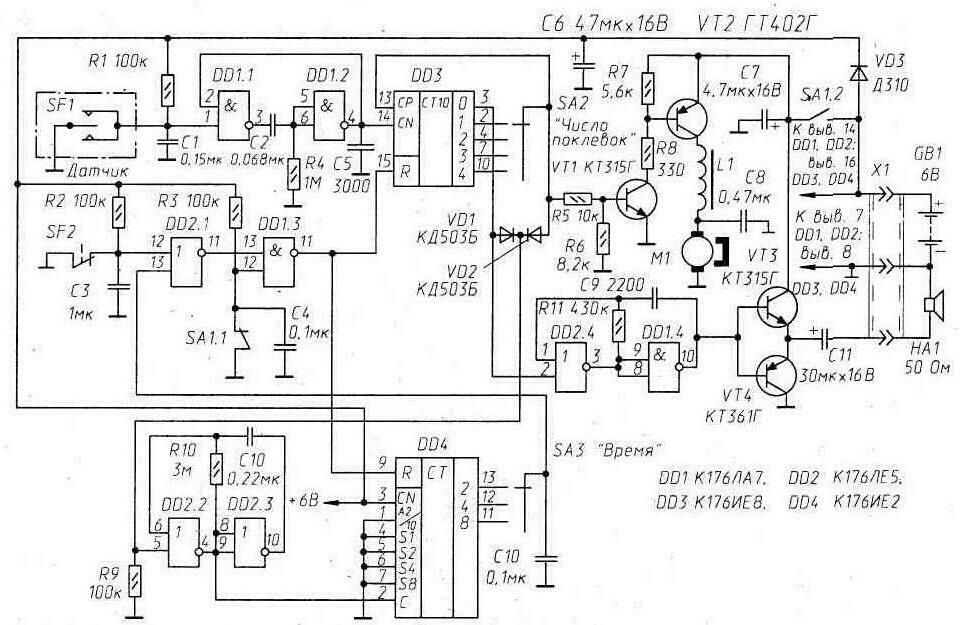
The kinematic diagram of a device designed for automatic hooking of fish in difficult fishing conditions is shown in Fig.1. Here: 1 - housing, which houses the entire electronic-mechanical "stuffing" of the machine; 2 - flat spring, the main mover of the machine; b - spring-loaded rocker with a clip 7 of the fishing line 11, forming with a bracket 4, mounted on an insulating plate 3, a contact pair; 8 - thrust with a hook earring 9; 10 - gearbox shaft with MZ thread at the end; 12 - clamp for fastening the machine on board or the stern transom of the boat. In the cocked state, the machine is held by the coupling of the shaft 10 of the gearbox with the earring 9. The turned on engine is able to instantly, in a few revolutions of the rotor, disconnect this coupling. But at what point this will happen - the electronics of the machine will decide. The algorithm of its work is simple. The very first electrical signal of the sensor, which occurs at the moment the rocker 6 touches the bracket 4, switches the machine to the active state: the countdown begins and the counting of these touches, which are still unclear in origin. If their total number - both interference and bites - in this active state of the automaton (its duration is set) does not reach a certain number N (also set), then the automaton again takes the initial state - the waiting state. If this number is reached, then the electric motor is turned on and - hooking. This algorithm is implemented by the electronic "stuffing" of the machine, the schematic diagram of which is shown in fig. 2. Here: SF1 - contact pair "rocker-bracket" - system sensor; SF2 - contact pair "shaft of the reducer-earring" (the reducer and the electric motor are placed on the base-insulator); SA1 - toggle switch, the contacts SA1.2 of which, when opened, de-energize the power part of the machine when it is set up, the bait is changed, etc .; SA2 - switch that sets the number of "bites" - N О{l,2,3,4}; SA3 - switch for the duration of active time intervals (in seconds) - T О{2, 4, 8}.
Elements DD1.1, DD1.2, C2, R4 constitute a single vibrator that eliminates a false count in DD3 - in the "bite" counter - from the "bounce" of the SF1 sensor contacts. On the elements DD2.2, DD2.3, a clock pulse generator is assembled, following at a frequency of 1 Hz. The counter DD4, summing up these pulses, sets the time of the active state of the machine. Resetting the counters, returning the machine to its original state - the waiting state - is carried out by pulses of a "single" amplitude, generated by elements DD2.1 and DD1.3. This happens either at the end of the active time (when a high-level voltage appears on the SA3 switch engine), or at the beginning of the cutting (when the SF2 contacts are broken), or when the machine is manually turned off with the SA1 toggle switch - closing the SA1.1 contact pair. On the elements DD2.4, DD1.4 and transistors VT3, VT4, a controlled (by input 2 element DD2.4) tone generator is assembled, which, by exciting the dynamic head HA1, signals the angler about the transition of the machine to the active state. Transistors VT1 and VT2 - an electronic key to control the electric motor M1. The inductor L1 in the LC filter is wound on an annular magnetic circuit (outer diameter - 10 ... 12 mm) made of ferrite with m=1000...2000. Its winding contains 50...100 turns of wire PEV-2 0.2...0.3. A flat power spring (2 in Fig. 1) - the main mover of the machine - is made from a strip of phosphor bronze 0,8 mm thick. Its width is 78 and its length (without embedded ends) is 220 mm. The initial force created by the spring during cutting is 1,3 kg, "max" - up to 750 mm. Knot 7 - a regular terminal with a hole for passing fishing line. The dimensions of the contact bracket are not critical, it is only important that the necessary gaps can be set between its contact pads and the end of the rocker arm moving between them: minimum - 1, maximum - 10 mm. The position of the rocker in relation to the contacts of the bracket can be changed by tensioning or loosening the springs in nodes 5. The overall mechanical strength of all these elements must be sufficiently high, since they "hold" the fish. In any case, they must endure 10 ... 15-kilogram jerks and blows without consequences. The screw-axis on which the rocker swings must provide it with minimal resistance. The trigger device of the machine and the placement of its parts in a case glued from sufficiently thick (8 ... 10 mm) sheet organic glass or high-impact polystyrene in the form of a box with a patch lid is shown in fig. 3, a. Electric motor 1 - any small-sized low-power, for example, from an electrified toy, having a small gear 7 on the axis with a diameter of 5 ... 6 and a length of at least 5 mm (large gear 4 should move freely along it, unscrewing from the earring). Before installing the electric motor, it is necessary to check the quality of the insulation of its rotor winding - the leakage resistance must be at least 1 MΩ. A suitable large gear gear that provides four to five times slowdown can be found in the same toy. Other details of the trigger: 6 - gearbox shaft (steel); 2nd internal support (it is attached to the "bottom" of the body); 3- soft flat spring on the shaft, pushing it out; 5 - bronze or brass bearing pressed into the housing wall. The gear shaft coupling earring with spring tension can be made according to the variant shown in fig. 3b. In this case, a hole with a diameter of about 25 mm should be made in the housing cover (its place in Fig. 1 is marked by arrow A), through which, by rotating the large gear of the gearbox with a finger, the end of its shaft is screwed into the earring. This is a hitch of very high reliability, it is not subject to almost any extraneous influences. According to another option (Fig. 3, c), the earring, the thread in which is preserved only in the lower part of its elliptical hole, is simply thrown onto the end of the gearbox shaft protruding from the housing.
Undercutting begins with the appearance of "1" - a voltage close to the supply voltage - on the SA2 switch engine. This voltage blocks the counting input of the counter DD3 (according to CP; the signals from the SF1 sensor can no longer change its state) and, opening the electronic key, made on transistors VT1, VT2, turns on the electric motor M1. For 8 ... 10 revolutions of its rotor, the "gear shaft-thrust link" assembly is disengaged and the power spring, sharply straightening, strikes. But already at the moment of disconnection of this node (contact pair SF2) at the input 12 of the element DD2.1 there is a "single" voltage, which leads to the appearance of "1" and at the input R of the counter DD3. As a result, the counter returns to its original, “zero” state, “2” is restored on the SA0 switch engine (voltage close to the potential of the zero bus), transistors VT1, VT2 close and the electric motor, having made only the necessary revolutions, turns off. Reloading of the machine is carried out with the SA1 toggle switch turned off: its SA1.1 contact pair, shorted in this position, "holds" the machine's electronics in the pre-launch state. The delay of the automaton, i.e. the time between the appearance of signal 1 on the switch engine SA2 and the actual hooking depends on the speed and power of the electric motor (it can be strongly forced), the deceleration of the gearbox, the number of shaft threads inserted into the earring, the lubrication of rotating parts and, of course, the state of the power source. In the manufactured copy, it did not exceed 0,2 s. The sensitivity of the SF1 sensor is 10 g / mm (force - on the fishing line, movement - at the contact bracket). It depends on the softness of the rocker springs. The power source of the machine equipped with a 4-volt electric motor (from an uninstalled toy) can be a battery of four galvanic cells or batteries capable of delivering a current of 0,5 ... 1 A during short-term discharge (a few tenths of a second). nutrition may be higher. But, of course, not higher than the maximum allowable for machine microcircuits. The described electronic machine was tested for a long time at the marine experimental station of the Institute of Marine Biology of the Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (the water area of the islands of Popov, Reinike, Rikord, etc.). Fishing was carried out mainly for bottom fish at depths of up to 20...25 meters. And although the peculiarities of sea fishing - pitching, displacement of the boat under the wind, uneven bottom, other obstacles - set rather difficult tasks for the machine, it was practically not inferior to experienced fishermen in anything. And often he demonstrated his superiority ... The machine gun was also distinguished by a neat, almost never damaging vital tissues. This turned out to be a pleasant surprise, as the fish were also caught for transplanting into the aquarium.
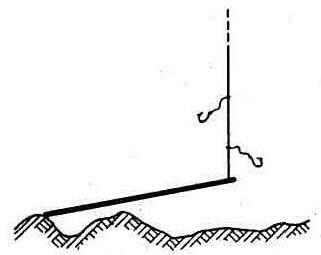
The figure shows the usual equipment of the machine, close to that adopted in Primorye: main fishing line 0,7 ... 1 mm, leashes - 0,5 ... 0,6 mm 3 ... 5 cm long, single hooks No. 10. ..12. But the sinker is different: a steel rod with a diameter of 6 ... 8 and a length of 250 mm or more. Such a sinker and such a position at the bottom allow you to keep the tension of the fishing line almost unchanged even with noticeable excitement. But this is in addition to the electronic "thinking" of the machine itself. Catching fish "at half water" was not a problem for him at all. The real sensitivity of the machine could be judged by the minimum weight of the caught specimens - 50 ... 100 g. The maximum weight of the fish was limited only by the strength of the leads. Publication: cxem.net
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Robotic materials with the properties of living beings ▪ IQ is not related to a person's level of intelligence ▪ Memory 1000 times faster than flash ▪ Unique double asteroid discovered
▪ section of the site Microcontrollers. Article selection ▪ Article Dreaming Dreams. Popular expression ▪ article How do tornadoes start? Detailed answer ▪ article Zopnik tuberous. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Water cooling system. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: