
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Switching power supply of a powerful UMZCH
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies Switching power supplies are widely used in modern electronic equipment. Radio amateurs also began to use them more often, as evidenced by the increased number of publications in radio engineering literature, in particular in the journal Radio. However, in most cases, relatively low-power designs are described. The author of the published article brings to the attention of readers a switching power supply with a power of 800 W. It differs from those described earlier by the use of field-effect transistors and a transformer with a primary winding with an average output in the converter. The first provides higher efficiency and reduced high-frequency interference, and the second - half the current through the key transistors and eliminates the need for an isolation transformer in their gate circuits. The disadvantage of such a circuit solution is the high voltage on the halves of the primary winding, which requires the use of transistors with the appropriate allowable voltage. True, unlike a bridge converter, in this case two transistors are enough instead of four, which simplifies the design and increases the efficiency of the device. Switching power supplies (UPS) use one- and two-stroke high-frequency converters. The efficiency of the former is lower than the latter, so it is not advisable to design single-cycle UPSs with a power of more than 40 ... 60 W. Push-pull converters allow you to get much more output power with high efficiency. They are divided into several groups, characterized by the method of excitation of the output key transistors and the circuit for including them in the circuit of the primary winding of the converter transformer. If we talk about the method of excitation, then two groups can be distinguished: with self-excitation and external excitation. The former are less popular due to difficulties in establishing. When designing powerful (more than 200 W) UPSs, the complexity of their manufacture unreasonably increases, so they are of little use for such power supplies. Externally excited converters are well suited for high power UPS applications and sometimes require little or no maintenance. As for connecting the key transistors to the transformer, there are three schemes: the so-called half-bridge (Fig. 1, a), bridge (Fig. 1, b) and with a primary winding having a tap from the middle (Fig. 1, c). To date, the most widely used half-bridge converter [1]. It requires two transistors with a relatively low voltage Uke max. As can be seen from fig. 1, a. capacitors C1 and C2 form a voltage divider to which the primary (I) winding of transformer T2 is connected. When opening the key transistor, the amplitude of the voltage pulse on the winding reaches the value Upit / 2 - Uke max.
The bridge converter [2] is similar to the half-bridge one, but in it the capacitors are replaced by transistors VT3 and VT4 (Fig. 1. b), which open diagonally in pairs. This converter has a slightly higher efficiency due to an increase in the voltage supplied to the primary winding of the transformer, and therefore, a decrease in the current flowing through the transistors VT1 - VT4. The voltage amplitude on the primary winding of the transformer in this case reaches the value Upit - 2Uke max. Standing apart is the converter according to the scheme in Fig. 1. c. with the highest efficiency. This is achieved by reducing the current of the primary winding and. as a result, a decrease in power dissipation in key transistors, which is extremely important for powerful UPSs. The amplitude of the voltage pulses in half of the primary winding increases to the value Upit - Uke max. It should also be noted that, unlike the other converters (1,2), it does not need an input isolation transformer. In the device according to the scheme in Fig. 1. it is necessary to use transistors with a high value of Uke max. Since the end of the upper (according to the scheme) half of the primary winding is connected to the beginning of the lower one, when current flows in the first of them (VT1 is open), a voltage is created in the second that is equal (in absolute value) to the amplitude of the voltage on the first, but opposite in sign relative to Upit. In other words, the voltage at the collector of the closed transistor VT2 reaches 2Upit. therefore, its Uke max must be more than 2Upit. In the proposed UPS, a push-pull converter with a transformer is used, the primary winding of which has an average output. It has high efficiency. low level of ripples and weakly radiates interference into the surrounding space. The author uses it to power a two-channel powered version of the UMZCH. described in [3]. UPS input voltage - 180...240 V. nominal output voltage (with input 220 V) - 2x50 V. maximum load power - 800 W. the operating frequency of the converter is 90 kHz. The schematic diagram of the UPS is shown in fig. 2. As you can see, this is a converter with external excitation without output voltage stabilization. At the input of the device, a high-frequency filter C1L1C2 is included, which prevents interference from entering the network. After passing it, the mains voltage is rectified by the diode bridge VD1 - VD4. ripples are smoothed out by capacitor C3. Rectified DC voltage (about 310 V) is used to power the high-frequency converter. The converter control device is made on DD1-DD3 microcircuits. It is powered by a separate stabilized source, consisting of a step-down transformer T1. rectifier VD5 and voltage regulator on transistors VT1, VT2 and zener diode VD6. On DDI elements. 1. DD1.2 assembled a master oscillator that generates pulses with a repetition rate of about 360 kHz. This is followed by a frequency divider by 4, made on the triggers of the DD2 chip. With the help of elements DD3.1, DD3.2 additional pauses are created between pulses. A pause is nothing more than a logic 0 level at the outputs of these elements, which appears when there is a level 1 at the outputs of the DDI.2 element and triggers DD2.1 and DD2.2 (Fig. 3). The low level voltage at the output of DD3.1 (DD3.2) blocks DD1.3 (DD1.4) in the "closed" state (at the output - logic level 1).
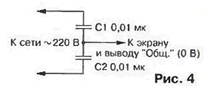
The pause duration is equal to 1/3 of the pulse duration (Fig. 3, voltage diagrams at pins 1 DD3.1 and 13 DD3.2), which is quite enough to close the switching transistor. From the outputs of the elements DD1.3 and DD1, the finally generated pulses are fed to transistor switches (VT4. VT5), which, through resistors R6, R10, control the gates of powerful field-effect transistors VT11, VT9. Pulses from the direct and inverse outputs of the trigger DD2.2 are fed to the inputs of the device, made on transistors VT3. VT4. VT7. VT8. Opening alternately, VT3 and VT7. VT4 and VT8 create the conditions for rapid discharge of the input capacitances of the key transistors VT9, VT10. i.e. their fast closing. Moreover, as can be seen from Fig. 3 (diagrams of voltages at pins 12 and 13 of DD2.2). VT7 and VT8 open immediately after the end of the pulse, therefore, at any output power, each of the transistors VT9, VT10 always has time to close securely before the second one opens. If this condition were not met, through them, and therefore through the primary winding of the transformer T2, a through current would flow. which not only reduces the reliability and efficiency of the UPS. but also creates voltage surges, the amplitude of which sometimes exceeds the converter supply voltage. Resistors of relatively high resistance R9 and R10 are included in the gate circuit of transistors VT10 and VT11. Together with the capacitance of the gates, they form low-frequency filters that reduce the level of harmonics when opening the keys. For the same purpose, elements VD9-VD12 were introduced. P16, R17, S12.S13 In the stock circuits of transistors VT9. VT10 included the primary winding of the transformer T2. Output voltage rectifiers are made according to the bridge circuit on diodes VD13 - VD20, which somewhat reduces the efficiency of the device, but significantly (more than five times) reduces the level of ripple at the output of the UPS. It is important to note that the shape of the oscillations, almost rectangular at maximum load, smoothly turns into close to sinusoidal when the power decreases to 10...20 W. which has a positive effect on the noise level of the UMZCH at low volume. The rectified voltage of the winding IV of the transformer T2 is used to power the fans (see below). The device uses capacitors K73-17 (C1. C2. C4). K50-17 (C3), MBM (C12. C13). K73-16 (C14-C21. C24. C25). K50-35 (C5-C7). KM (others). Instead of those indicated in the diagram, it is permissible to use K176 series microcircuits. K564. Diodes D246 (VD1-VD4) are interchangeable with any other diodes designed for direct current of at least 5 A and reverse voltage of at least 350 V (KD202K. KD202M. KD202R, KD206B. D247B). or a diode rectifier bridge with the same parameters, diodes KD2997A (VD13-VD20) - on KD2997B. KD2999B. zener diode D810 (VD6) - on D814V. As VT1, you can use any transistors of the KT817, KT819 series. as VT2-VT4 and VT5, VT6 - respectively, any of the series KT315, KT503, KTZ102 and KT36K KT502. KT3107. in place of VT9, VT10 - KP707V1, KP707E1. Transistors KT3102ZH (VT7. VT8) are not recommended to be replaced. Transformer T1 - TS-10-1 or any other with a secondary winding voltage of 11 ... 13 V at a load current of at least 150 mA. The mains filter coil L1 is wound on a ferrite (M2000NM1) ring of size K31M8,5u7 with PZV-1 1,0 wire (2x25 turns), transformer T2 is wound on three ferrite rings glued together of the same brand, but size K45x28x12. Winding I contains 2x42 turns of wire PEV-2 1,0 (slightly winding wires), windings II and III - 7 turns each (in five wires PEV-2 0,8), winding IV - 2 turns PEV-2 0.8. Three layers of insulation made of PTFE tape are laid between the windings. The magnetic circuits of the chokes L2, L3 are ferrite (1500NMZ) rods with a diameter of 6 and a length of 25 mm (trimmers from B48 armor cores). The windings contain 12 turns of wire PEV-1 1.5. Transistors VT9. The VT10 is installed on fan heatsinks used to cool Pentium microprocessors (similar nodes from 486 processors are also suitable). Diodes VD13-VD20 are fixed on heat sinks with a surface area of about 200 cm2. To cool the transistors of the UMZCH output stage, a fan is installed on the back wall from a computer power supply or any other with a supply voltage of 12 V. When installing the UPS, you should strive to ensure that all connections are as short as possible, and in the power section use a wire of the largest possible cross-section. It is desirable to enclose the UPS in a metal shield and connect it to the 0 V terminal of the source output, as shown in fig. 4. The common wire of the power unit must not be connected to the screen. Since the UPS is not equipped with a short circuit and overload protection device, 10 A fuses must be included in the UMZCH power circuit.
The described UPS practically does not need to be adjusted. It is only important to correctly phase the halves of the primary winding of the transformer T2. If the parts are in good condition and there are no errors in the installation, the unit starts working immediately after being connected to the network. If necessary, the frequency of the converter is adjusted by selecting the resistor R3. To increase the reliability of the UPS, it is desirable to operate it with a UMZCH, which provides through blowing by a fan. Literature
Author: D.Kolganov, Kaluga
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Transcend 2GB M.512 Solid State Drives ▪ Ear plugs in the nose for those who want to lose weight ▪ Gut microflora affects our health and mood ▪ Taipei street lights to be equipped with smart LED bulbs ▪ Piezoelectric MEMS Microphones for Smartphones
▪ section of the site for the Builder, home craftsman. Selection of articles ▪ White Crow article. Popular expression ▪ article How do you get a tan? Detailed answer ▪ article Turmeric cultural. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: