We turn on household appliances at low mains voltage. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Protection of equipment from emergency operation of the network, uninterruptible power supplies
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Unfortunately, often in rural areas, and often in cities, the mains voltage in houses is less than the nominal voltage, and in the evenings it drops so much that refrigerators, pumps, washing machines, etc. refuse to work. And if the problem of TV power supply can be solved by purchasing AC voltage stabilizer, then with asynchronous electric motors used in household appliances, everything is much more complicated: their launch is accompanied by significant current overloads, and buying a powerful stabilizer is unreasonably expensive.
On the other hand, for electric motors, the increased voltage is not so “painful” as its disadvantage: with a reduced voltage, they lose the ability to start, and as a result, the stator winding burns out. In other words, one can simply increase the voltage without much fear of further fluctuations in the network.
However, the step-up transformer is bulky and expensive. Therefore, to solve the problem, I propose a non-standard use of a conventional small-sized step-down transformer. You just need to add the necessary "volts" by summing the mains and voltage from the secondary winding of the transformer to the required output value. The principle of operation is easily explained by the diagram shown in the figure.
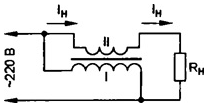
The figure shows that the current in the secondary winding and in the load is the same, respectively, the criteria for choosing a transformer are the required voltage and current in the secondary winding. There is no need to achieve an exact value of 220 V, already at 210 V everything will work.
You will need a transformer with a primary winding of 220 V, a secondary winding for the required "missing" voltage, and the maximum current of the secondary winding is sufficient even for low-power step-down transformers! It is easy to pick it up from the standard range for industrial transformers.
An approximate calculation (and this is more than enough for the task at hand) can be done using the following formulas.
First, we calculate the current of the secondary winding of the transformer - the load current:
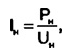
where In - rated load current, A; Рн - nominal (passport) load power, W; UH - rated load supply voltage (220...230), V.
Then, knowing what voltage needs to be added, we determine the required power of the transformer
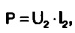
where P is the power of the transformer, W; I - rated current of the secondary winding, A; U2 - voltage of the secondary winding, V.
We select a ready-made transformer with suitable parameters for nameplate power and output voltage.
Now you can calculate the final result - the new voltage on the load:
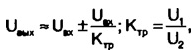
where Ktr - transformation ratio; U - rated voltage of the primary winding (220), V.
From the last formula it can be seen that the voltage on the load can be both increased and decreased! To correctly phase a transformer, it is enough to swap the conclusions of one of its windings. The desired result can be achieved even by assembling a "garland" of several transformers: their primary windings should be connected in parallel, and the secondary windings in series and do not forget about phasing.
Let me give you a few practical examples.
- To increase the voltage by 30 ... 35 V for a pump with a power of 0,5 kW, it is enough to use a transformer with a voltage on the secondary winding of 42 V and a power of only 100 W.
- Lighting lamps in the entrance will last much longer if the voltage on them is slightly reduced - a 220/24 V transformer with a power of 160 W will easily "serve" the entire entrance of a multi-storey building with a total lighting power of 1,5 kW.
- A 1/6 V transformer with a power of 220 W will cope with the start of the electric motor of the refrigerator compressor (IN = 42, ZA, at startup - up to 63 A) with a voltage reduced by 45 V in the network.
Similarly, you can very effectively increase or decrease the voltage in a three-phase network - this will require, respectively, three transformers.
Author: Yu.Arkhipov, St. Petersburg
 See other articles Section Protection of equipment from emergency operation of the network, uninterruptible power supplies.
See other articles Section Protection of equipment from emergency operation of the network, uninterruptible power supplies.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Improvement of clean methanol fuel cells
12.12.2020
Due to the many environmental problems caused by the use of fossil fuels, many scientists around the world are focused on finding effective alternatives. While there are high hopes for hydrogen fuel cells, the reality is that transporting, storing, and using pure hydrogen comes with huge additional costs, making it difficult for today's technologies. In contrast, methanol (CH3O3), a type of alcohol, does not require refrigeration, has a higher energy density, and is easier and safer to transport. Thus, a transition to a methanol-based economy is a more realistic goal.
However, generating electricity from methanol at room temperature requires a direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC), a device that has so far offered poor performance. One of the major problems with DMFCs is the undesired "methanol oxidation" reaction that occurs during the transition of methanol, "that is, as it passes from the anode to the cathode. This reaction results in the destruction of the platinum (Pt) catalyst, which is essential to the operation of the cell. While certain strategies have been proposed to mitigate this problem, none have been good enough so far due to cost or stability issues.
A group of scientists from Korea came up with a creative and effective solution. They made - using a relatively simple procedure - a catalyst consisting of Pt nanoparticles enclosed in a carbon shell. This shell forms an almost impermeable carbon network with small holes caused by nitrogen defects. Although oxygen, one of the main reactants in DMFC, can reach the Pt catalyst through these "holes", the methanol molecules are too large to pass through.
"The carbon shell acts like a molecular sieve and provides selectivity for the desired reactants that can actually reach the sites of the catalyst. This prevents unwanted reaction of the Pt nuclei," explains Prof. Oh Jung Kwon from Incheon National University (Korea), who led the study.
The scientists conducted various experiments to characterize the general structure and composition of the prepared catalyst, and proved that oxygen can pass through the carbon shell, but methanol cannot. They also found an easy way to control the number of defects in the casing by simply changing the temperature during the heat treatment step. In subsequent experimental comparisons, their new purified catalyst outperformed commercial Pt catalysts and also showed much higher stability.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Solar panels from cheap raw materials
▪ Powerful 40V N-Channel MOSFETs
▪ Mathematicians have developed the perfect espresso coffee
▪ Crime Prediction Algorithm
▪ A robot's sense of touch is 100 times more sensitive than a human's.
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Color and music installations. Selection of articles
▪ article The land of the native long-suffering, the land of the Russian people! Popular expression
▪ article Why are we fooling everyone on April 1st? Detailed answer
▪ article Rassevny worker. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Infrared port for a computer on COM. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Magic powder. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

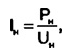
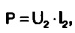
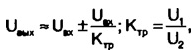
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: