
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Two power supplies for portable equipment. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
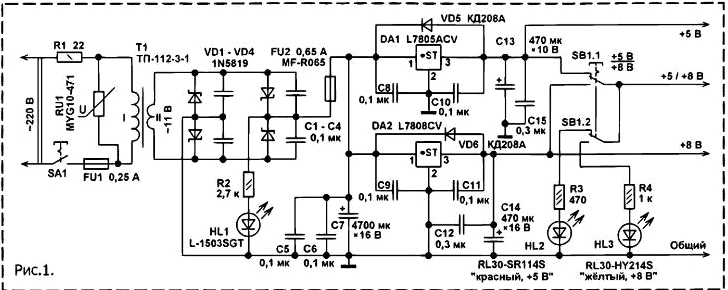
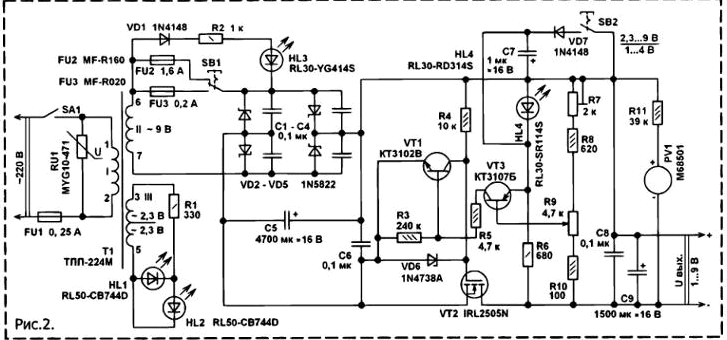
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies On the basis of a network adapter from an unnecessary outdated telephone set with an automatic caller ID function, assembled on a Z80A microprocessor, you can make a simple power supply with a linear stabilizer that provides two stabilized voltages of +5 V and +8 V at the output with a total load current of up to 500 ma. It can be used to power digital and analog devices, to recharge the batteries of mobile devices, to power children's toys. A schematic diagram of such a PSU is shown in fig. 1. The AC mains voltage 220 V through the closed contacts of the switch SA1 and the protective resistor R1 and the fuse enters the primary winding of the network transformer T1. From the secondary winding of this transformer, an alternating current voltage reduced to 11 V is removed, which is rectified by a bridge rectifier assembled on Schottky diodes VD1 - VD4. The use of such diodes reduces the power losses in the diode rectifier and increases the voltage across the filter capacitor C1 by about 7 V. Resettable fuse FU2 protects the step-down transformer from overload. Since the power supply was mounted in a compact package, the maximum load current for this transformer was reduced from 0,8 A to 0,5 A in order to increase reliability. Diodes VD5, VD6 protect microcircuits from damage by reverse voltage, which can be at the outputs of microcircuits if the voltage on the plates of the capacitor C7 will decrease faster than the voltage at the output of the stabilizer, for example, due to a short circuit at the output of the rectifier or loss of capacitance of the capacitor C7. Varistor RU1 protects the transformer and Schottky diodes from mains voltage surges. Power supply according to the scheme of fig. 1 contains two linear stabilizers assembled on integrated circuits DA1 and DA2. The first provides a stabilized output voltage of +5 V, the second - a stabilized voltage of +8 V. The total current of the connected loads can reach 0,5 A. At higher current, the FU1 polymer self-resetting fuse heats up and goes into a high resistance state. With switch SB1, you can select the voltage supplied to the load: +5 V or + 8 V. In this case, if SB1 is in the "+5 V" position, the HL2 LED lights up, if in the "+8 V" position, then HL3 will light up. Also, in addition to the maximum allowable total current of the connected loads, there are no restrictions on the simultaneous use of two stabilizers. For example, you can install a USB socket on the output of the "+5 V" channel and charge a pocket Flash player, a mobile phone battery, a camera from it, and the "+8 V" channel can be used at this time to power the radio. This PSU has a resettable fuse with a rated operating current slightly greater than the stated maximum 0,5A. The fact is that in a small case at such a current, the step-down transformer heats up noticeably, the temperature in the compact case rises, which leads to the fact that the self-resetting fuse operates at a lower current. When the fuse is blown, the HL1 LED remains on, which indicates the presence of the mains supply voltage. Power supply with adjustable DC output voltage from 1 to 9 V, assembled according to the scheme of fig. 2, allows you to connect a load that consumes up to 1,6 A. The unit has protection against overload and short circuit in the load circuit, as well as protection against overvoltage of the AC mains. This power supply works as follows. The AC mains voltage through the fuse FU1 is supplied to the primary winding of the step-down transformer T1. The AC voltage, reduced to 9 V, is removed from one of the secondary windings of the transformer and, through one of the polymer self-healing fuses FU2 or FU3, is fed to a bridge rectifier assembled on Schottky diodes VD2 - VD5. The ripple of the rectified voltage is smoothed out by a high-capacity oxide capacitor C5, after which the voltage is supplied to a compensation voltage regulator, implemented entirely on discrete components. The adjustable compensation stabilizer is implemented using a hybrid technology - on field-effect and bipolar transistors [1]. Its distinguishing feature is a very low saturation voltage (the minimum voltage between input and output), which, when tested with a load current of 2 A, did not exceed 60 mV. This is dozens of times less than that of traditional type compensation stabilizers, for example, the popular KR142ENxx, **78xx series, and significantly less (10...30 times) than that of linear voltage stabilizer microcircuits with a low minimum voltage between input and output. The rectified voltage is supplied to the source of a powerful field-effect MIS transistor VT2. Since it is much easier to purchase an n-channel powerful field-effect transistor with a low gate-source opening threshold voltage than a p-channel one, this transistor had to be installed in the negative power circuit. The opening voltage is supplied to the gate of this VT2 through R4, connected to the common plus of the power circuit. This method of controlling a field-effect transistor in a compensation stabilizer does not require special measures for starting, which greatly simplifies the design. The compensation stabilizer works as follows. When the input voltage increases or the load current decreases, the output voltage also tends to increase. This leads to the fact that VT3 opens more strongly, therefore, VT1 will also open more strongly, which, by shunting the gate-source circuit of VT2, lowers the opening voltage of VT2, the resistance of the drain-source channel of VT2 increases, the output voltage of the stabilizer decreases. The output voltage is adjusted with a variable resistor R.9. A VD6 zener diode with a stabilization voltage of about 8,2 V protects the field-effect transistor from damage. With the switch SB2, you can select the output voltage range of 1 ... 4 V or 2,3 ... 9 V. When the contacts SB2 are open, the red HL4 LED works as a reference voltage source, the output voltage can be set within 2,3 ... 9 V. When the SB2 contacts are closed, the silicon diode VD7 will become the reference voltage source, and the output voltage can be set from 1 to 4 V. It should be noted that there are relatively few designs of laboratory power supplies with a minimum output voltage of 1 V. On the pointer microammeter PV1, an output voltage voltmeter is made. Switch SB1 can select the protection operation current. LED HL3 green indicates the operation of a self-resetting fuse. Varistor RU1 protects the step-down transformer and diode rectifier from mains voltage surges. Super-bright blue LEDs HL1 and HL2 indicate that the power supply is connected to the network, and also illuminate the voltmeter scale. the voltage regulator used in the power supply (Fig. 2) with minor modification can be used in power supplies designed for a load of 10 ... 15 A. To do this, it is necessary to install two more of the same capacitors in parallel with C5, use Schottky diodes for the appropriate current, for example, 16-amp MBR1645, mounted on heat sinks. Of course, all high-current connections must be made with "thick" wires, and the step-down transformer must be of the appropriate overall power with a high-current secondary winding. On the details of structures. Fixed resistors can be used for small-sized general applications of any type, for example, C1-4, MLT, C2-23 of the appropriate power. Trimmer resistor R7 (Fig. 2) - any small-sized, preferably closed design. In place of the variable resistor R9, a tuning SP4-1 was used in a semi-hermetic case. Good stability of the output voltage can also be obtained with other similar resistors, for example, SPZ-96, SP4-2M, SGTO-1 or small-sized wire ones. PPB-1A, PPB-ZA. Varistors MYG10-471 can be replaced by FNR-10K471, FNR-14K471, FNR-20K431, TNR10G471. Oxide capacitors - imported analogues of K50-35, K50-68. The rest are ceramic for an operating voltage of at least 16 V, type K10-17, K10-50 or in SMD version for surface mounting. Capacitors C8 - SP (Fig. 1) are installed directly on the pins of the microcircuits. Instead of 1N5819 Schottky barrier diodes, you can install similar SM5819, MBRS140TR, MBRS140TRPBF, SR360, 1N5822. Powerful 1N5822 Schottky diodes (Fig. 2) can be replaced with three-ampere SB360, MBRS360T3, MBRD350, MBR340 and other similar ones. The mentioned types of Schottky diodes are made in different packages. Diodes KD208A can be replaced by any of the series KD209, KD243, KD247, 1N4001 - 1N4007. Diodes 1N4148 can be replaced with 1N914, 1SS176S or any of the KD510, KD521, KD522 series. LEDs can be applied to any type of general application, such as series. KIPD1, KIPD4738, KIPD55, L-8. Instead of the L2ACV chip, you can install KR8EN2 A, B, MC2, MC182, LM1T-2, LM182T-2, LM182 and others similar [21]. Instead of the L40CV chip, integrated stabilizers MC66, UVI1503-7805, and others similar for an output voltage of +142 V and a load current of at least 5 A are suitable. Both microcircuits are mounted on a common heat sink made of a duralumin plate 80x50x2 mm. The heat sink flanges of the microcircuits are isolated from the heat sink by mica gaskets. This is done to prevent accidental unwanted short circuits. In addition, the heat sink, which is part of the housing wall, is covered with black insulating varnish on the outside. Before painting, the metal plate is treated with sandpaper and cleaned with acetone. As a varnish, you can use black nail polish or car enamel. Instead of the KT3102V transistor, you can install any of the KT3102, KT6111, SS9014, VS547 series. Instead of KT3107B, any of the KT3107, KT6112, SS9015, VS556 will do. Transistors of different series have differences in the pinout. In place of the transistor VT2, a powerful n-channel field effect transistor with an insulated gate of the IRL2505N type was used. This type of transistor is controlled by a logic level voltage, has an open channel resistance of 0,008 Ohm, a maximum direct current at a temperature of 25 ° C 104 A (it should be understood as a direct current in for no more than 1 ms), the maximum drain-source voltage is 55 V, it is made in a metal-plastic case. TO-220 In this design, it can be replaced, for example, with such as IRL3705N, IRLZ44, or you can choose the appropriate one according to the table [3]. The field effect transistor is installed on the heat sink. When installing it, it is necessary to take appropriate measures to protect it from breakdown of the gate insulator by static electricity. The pinout of the mentioned types of field-effect transistors is standard - gate-drain-source. The microammeter used is miniature from the recording / playback level indicator of an old domestic tape recorder. Switches - P2K, with position fixing, free groups of contacts are connected in parallel. step-down transformer type. TP112-3-1 with an open circuit voltage on the secondary winding of about 11 V can be replaced with. TP114-2, TP121-17. CCI112-6. step-down transformer type. TPP-224M - from an old switching power supply from the Soviet computer "Electronics MS". The transformer has two secondary windings designed for different currents. Less low-current winding with an open-circuit output voltage of about 5,5 V used to power the backlight LEDs. The rectifier is connected to the secondary winding with terminals 6, 7. With such a transformer, the power supply (Fig. 2) is capable of delivering voltage up to 6,5 V at a load current of 1,6 A and up to 9.10 V at a load current of 0,5 A. Instead of such a transformer, you can use a unified type TPP115-6 or TPP114-6. Literature 1. Butov A.L. Backup power supply for Pocket Flash Player. - Radio constructor, 2009, No. 10, pp. 17 -18.
Author: Butov A.L.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ 5G Network Performance Optimization ▪ Makeup helps women build a career ▪ The tablet will be able to control an unmanned truck ▪ Smartphone Microsoft Lumia 430
▪ section of the site Aphorisms of famous people. Article selection ▪ Mammon article. Popular expression ▪ article What does the Dow Jones index show? Detailed answer ▪ article What gases does air consist of. Children's Science Lab ▪ article LCD from Nokia 3310 on LPT. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article The magic wand is a faithful watchman. Focus Secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: