Light control of the exhaust fan. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Miscellaneous electrical devices
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
In order for the exhaust fan in the toilet to turn on when the light is turned on, and turn off after the light is turned off, you can redo the wiring and connect the fan in parallel with the lamp. But, if this is undesirable (for structural and aesthetic reasons), you can install an optical sensor in the fan that will turn it on after turning on the light in the toilet, and turn it off after turning off the light in the toilet.
The circuit is shown in the figure. FT1 is a phototransistor from an old ball computer mouse.
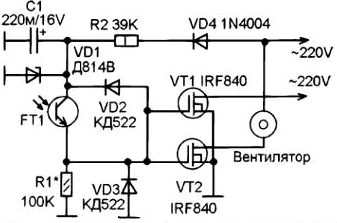
The sensitivity is set by selecting the resistance R1.
When it is dark, FT1 is closed and there is no voltage on the gates VT1 and VT2, they are closed, and the fan is turned off. When the light is turned on, FT1 opens abruptly and supplies voltage to the gates VT1 and VT2. They open and turn on the fan.
Literature
- Radioconstructor 2011 №7
 See other articles Section Miscellaneous electrical devices.
See other articles Section Miscellaneous electrical devices.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Photosynthesis battery
25.01.2023
Plants are often considered sources of food, oxygen, and decoration, but not a source of electricity. However, scientists have found that by using the natural transport of electrons in plant cells, it is possible to produce electricity as part of a biological ecological solar cell.
Scientists have used a succulent plant for the first time to create a living "bio-solar battery" powered by photosynthesis.
Electrons are naturally transported as part of biological processes in all living cells, from microbes and fungi to plants and animals. Through the introduction of electrodes, the cells can be used to generate electricity that can be used outside. Previous research has created fuel cells using bacteria, but they need a constant supply of food. This new approach uses photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, to generate electricity.
During this process, light triggers the flow of electrons from the water, which leads to the formation of oxygen and sugar. This means that living photosynthetic cells are constantly producing a stream of electrons that can be pulled off like photographs and used to power an external circuit, like a solar cell.
Some plants, such as succulents in dry environments, have thick cuticles that hold water and nutrients in the leaves. Janov Schlosberg, Gadi Schuster and Adir wanted to test for the first time whether photosynthesis in succulents could create energy for living solar cells by using their internal water and nutrients as an electrochemical cell electrolyte solution.
Researchers have created a living solar array using the succulent Corpuscularia lehmannii, also known as the "ice plant". They inserted an iron anode and a platinum cathode into one of the plant's leaves and found that its voltage was 0,28 volts. When connected to a circuit, it produced a photocurrent density of up to 20 μA/cm 2 under the action of light and could continue to produce current for more than a day. Although these numbers are less than those of a traditional alkaline battery, they only display one flap.
Previous research on similar organic devices suggests that daisy-chaining multiple leaflets can increase voltage. The team specifically designed the living solar cell so that the protons in the internal leaf solution could combine to form hydrogen gas at the cathode, and that hydrogen could be harvested and used for other purposes.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ artificial shrimp
▪ Flying car
▪ Life without passwords
▪ Ultrasonic dry cleaning at home
▪ Charging cable Phoenix Contact 375 kW
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Microcontrollers. Article selection
▪ article by Herve Bazin. Famous aphorisms
▪ article What tributaries of the Don flow side by side and have the same name? Detailed answer
▪ Vesuvius Volcano article. Nature miracle
▪ article Bicycle speedometer. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article What is Wi-Fi? Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: