
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Battery maintenance device. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
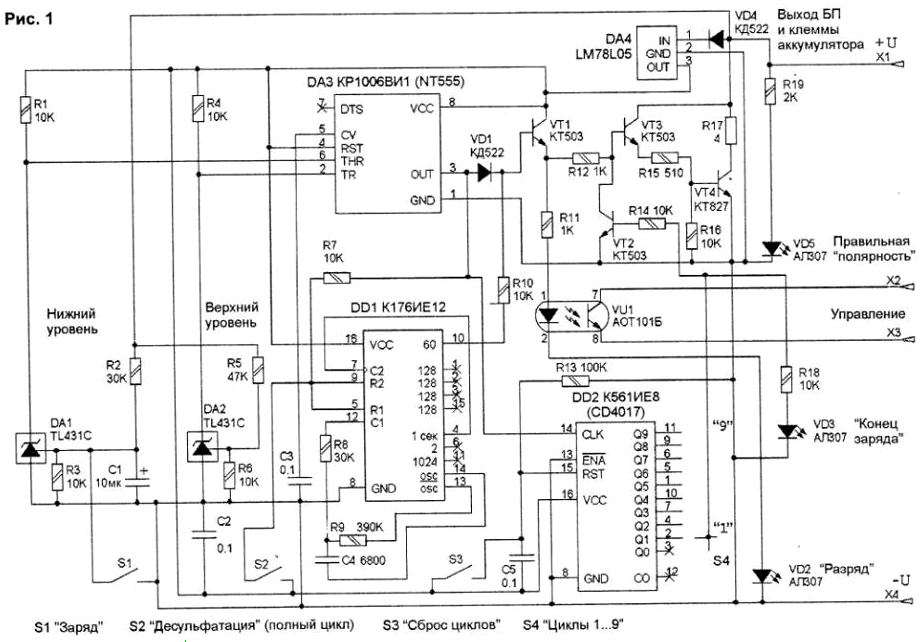
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells The proposed device (Fig. 1) is designed to control the charge and discharge of 12-volt acid batteries (for cars and motorcycles) in order to eliminate their sulfation and achieve maximum capacity.
It is easy to convert it to other batteries (with a nominal voltage of 3,6; 4,8; 6,0; 7,2; 18 and 24 V) by changing the resistances of the resistors R2 and R5 in the voltage level dividers R2-R3 and R5-R6 . True, with a low battery voltage, the device itself needs additional power (12 ... 15 V / 50 ... 70 mA). The charger operating in conjunction with this control unit can be anything: both complex with electronic control, and thyristor, or even the simplest, consisting only of a transformer and a diode bridge. The output of the optocoupler (terminals "Control" - X2 and X3) works as a key, which, when the battery is discharged, should block the charger. The battery is discharged by the control unit. The magnitude of the discharge current is determined by the resistance R17 (you can turn on a car incandescent lamp instead) and for the specified rating it is about 3 A. The allowable power dissipation R17 (at least 50 W) should provide a long-term operation. Diode VD4 protects the control unit from connecting the battery in the wrong polarity (it does not protect the charger!) In the case of an electronically controlled charger (charger), it is connected to the control unit according to the diagram in Fig. 2, i.e. The optocoupler is connected in parallel with the upper resistor of the voltage divider of the voltage control unit (the resistances of the resistors R* and R** are indicated conditionally).
In simple thyristor chargers (Fig. 3), a little modification is needed (in addition, node A1 is installed). The output of the optosimistor VU1 is included in the open circuit of the current regulator. In the simplest memory (Fig. 4), node A1 is also added, but with a powerful triac VS1, which is controlled by an optotriac VU1. The triac is included in the break of the network wire of the memory. When charging, the control unit prevents the battery from being recharged by turning off the charger. When you select a mode consisting of several cycles, the unit automatically monitors the full charge and discharge of the battery. When the mains voltage is turned off, the device goes into standby mode. If there was a charge, it will resume when the supply voltage appears, if there is a discharge, no changes will occur. The control unit can operate in several modes: 1. Selecting the 1st cycle will only fully charge the battery. 2. When choosing the 2.9th cycle, the modes "full charge - full discharge" alternate. 3. If the fixed button S2 (Fig. 1) is in the depressed state, the desulfation function is activated: the charge / discharge occurs in faster cycles (partial charge - 40 minutes and partial discharge - 20 minutes) until the battery is fully charged. The control unit circuit contains two voltage comparators on "controlled zener diodes" DA1 and DA2. They define two thresholds (lower - start of charging - DA1, upper - end of charging - DA2). Resistors R2 and R5 determine specific threshold values (10.5 and 14,4 V on the battery). Instead of constants, you can put tuning resistors and adjust the thresholds for existing batteries. The first comparator (DA1), when the voltage at its control input drops below a predetermined threshold, closes and a high level is set on it, i.e. at the input 6 of the DA3 timer, a voltage appears close to the supply voltage. At input 2 DA3 - a similar level, since the second comparator (DA2) is designed for a voltage of 14,4 V and is also closed at this time. The timer switches and its output (pin 3) goes low. The same state of DA3 will be when the power is turned on due to a discharged capacitor C1 or when the S1 button is pressed (forced charging). A low (close to zero) level from the output of DA3 through the diode VD1 enters the base of the transistor VT1 and closes it. As a result, no current flows through the LED of the VU1 optocoupler, the optocoupler is closed, and the charger is unlocked, the battery is charged with a current determined by the charger connected to it. When the voltage at the control input of the comparator DA2 exceeds the upper threshold (14,4 V), it opens, and the voltage on it (and at input 2 of DA3) decreases to 2,5 V. The DA3 timer switches, a high level appears at its output, which opens VT1, which in turn turns on the VU1 optocoupler and lights up the VD2 LED. The optocoupler blocks the memory. At the same time, a high level from the emitter VT1 opens the composite transistor VT3-VT4, which connects the discharge resistor R17 to the battery. Discharge mode starts. In addition: a high level from output 3 of DA3 disables the counter DD1 and increases the state of the counter DD2 by 1. The "charge - discharge" cycles continue until a high level appears at the output of the counter DD2, connected by switch S4 to the base of the transistor VT2. The transistor opens and blocks the composite transistor VT3-VT4. This terminates the discharge mode. The number of discharge cycles is always one less than the number of charge cycles. If you select 1 cycle, there will be only a charge cycle. The counter of the number of cycles DD2 is reset when the power is turned on or using the S3 button. The control unit is assembled on a printed circuit board, the drawing of which is shown in Fig. 5, and the location of the elements is in Fig. 6.
Setting up a properly assembled device comes down mainly to setting the threshold levels for comparator operation by selecting resistors R2 and R5. By connecting terminals X1 and X4 to an adjustable power supply, connect a voltmeter to pin 6 of DA3 and achieve a voltage close to 9 V when the voltage drops below 10,5 V. Then the voltmeter is connected to pin 2 of DA3 and a sharp drop in voltage is achieved at this pin after increasing the supply voltage above 14,4 V. The time of the desulfation cycle can be adjusted by selecting the resistance R9 or capacitance C4.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Link found between food intake and body clock ▪ 27-inch ASUS VA278Q monitor with a resolution of 2560x1440 pixels ▪ Hydrogen-electric aircraft Odonata ▪ SONY camcorders burn DVD on the fly
▪ section of the Antenna website. Article selection ▪ article Go to the light. Popular expression ▪ article Does gravity act on the moon? Detailed answer ▪ article Forester forestry. Job description
Comments on the article: a guest Someone did? No mistakes
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese






 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: