
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Single-cycle converters with high efficiency, 12/220 volts. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
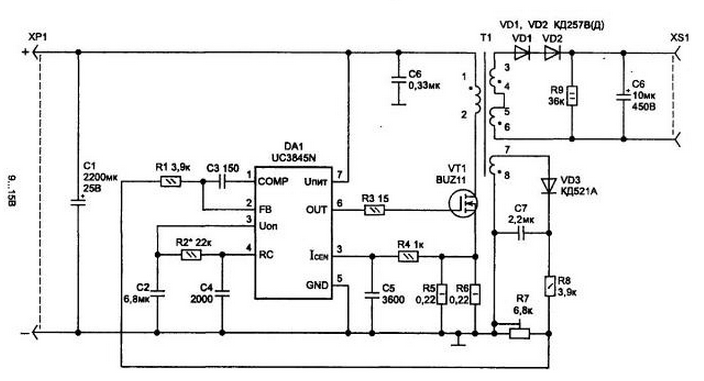
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters Some familiar household electrical appliances, such as a fluorescent lamp, a photo flash, and a number of others, can sometimes be conveniently used in a car. Since most devices are powered by a mains voltage of 220 V, a step-up converter is needed. An electric shaver or a small fluorescent lamp consumes no more than 6 ... 25 watts of power. In this case, such a converter often does not require an alternating voltage at the output. The above household electrical appliances normally operate when powered by direct or unipolar pulsating current. The first version of a single-cycle (flyback) pulse DC voltage converter 12 V / 220 V is made on an imported UC3845N PWM controller chip and a powerful N-channel BUZ11 field-effect transistor (Fig. 4.10). These elements are more affordable than domestic counterparts, and allow you to achieve high efficiency from the device, including due to a small source-drain voltage drop across an open field-effect transistor (the efficiency of the converter also depends on the ratio of the width of the pulses that transfer energy to the transformer to the pause). The specified microcircuit is specially designed for single-cycle converters and has all the necessary nodes inside, which makes it possible to reduce the number of external elements. It has a high-current quasi-complementary output stage specifically designed for direct driving a high-powered one. M-channel field-effect transistor with an insulated gate. The operating frequency of the pulses at the output of the microcircuit can reach 500 kHz. The frequency is determined by the values of the elements R4-C4 and in the above circuit is about 33 kHz (T = 50 μs).
The chip also contains a protection circuit to disable the operation of the converter when the supply voltage drops below 7,6 V, which is useful when powering devices from a battery. Let us consider in more detail the operation of the converter. On fig. 4.11 shows voltage diagrams that explain the ongoing processes. When positive pulses appear at the gate of the field-effect transistor (Fig. 4.11, a), it opens and the resistors R7-R8 will have the pulses shown in Fig. 4.11, c. The slope of the peak of the pulse depends on the inductance of the transformer winding, and if there is a sharp increase in the voltage amplitude at the top, as shown by the dotted line, this indicates saturation of the magnetic circuit. In this case, the conversion losses sharply increase, which leads to heating of the elements and degrades the operation of the device. To eliminate saturation, it will be necessary to reduce the pulse width or increase the gap in the center of the magnetic circuit. Usually a gap of 0,1 ... 0,5 mm is sufficient. At the moment of turning off the power transistor, the inductance of the transformer windings causes voltage surges, as shown in the figures.
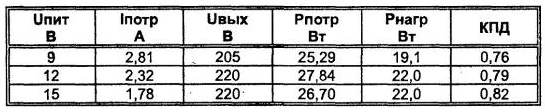
With the correct manufacture of the transformer T1 (sectioning the secondary winding) and low-voltage power supply, the surge amplitude does not reach a dangerous value for the transistor, and therefore, in this circuit, special measures, in the form of damping circuits in the primary winding T1, are not used. And in order to suppress surges in the current feedback signal coming to the input of the DA1.3 microcircuit, a simple RC filter is installed from elements R6-C5. The voltage at the input of the converter, depending on the condition of the battery, can vary from 9 to 15 V (which is 40%). To limit the change in the output voltage, the input feedback is removed from the divider of resistors R1-R2. In this case, the output voltage at the load will be maintained in the range of 210 ... 230 V (Rload = 2200 Ohm), see table. 4.2, that is, it changes by no more than 10%, which is quite acceptable. Table 4.2. Circuit parameters when the supply voltage changes
Stabilization of the output voltage is carried out by automatically changing the width of the opening transistor VT1 pulse from 20 µs at Upit=9 V to 15 µs (Upit=15 V). All elements of the circuit, except for capacitor C6, are placed on a single-sided printed circuit board made of fiberglass 90x55 mm in size (Fig. 4.12).
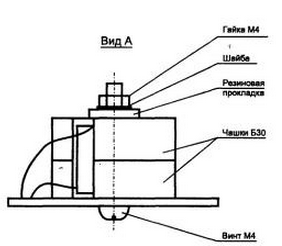
Transformer T1 is mounted on the board with an M4x30 screw through a rubber gasket, as shown in fig. 4.13.
Transistor VT1 is mounted on a radiator. Plug design. XP1 must exclude erroneous voltage supply to the circuit. The pulse transformer T1 is made using the widely used BZO armor cups from the M2000NM1 magnetic circuit. At the same time, a gap of 0,1 ... 0,5 mm should be provided for them in the central part. The magnetic circuit can be purchased with an existing gap, or you can make it with coarse sandpaper. It is better to choose the gap value experimentally when setting up so that the magnetic circuit does not enter saturation mode - it is convenient to control it by the shape of the voltage at the source VT1 (see Fig. 4.11, c). For transformer T1, winding 1-2 contains 9 turns of wire with a diameter of 0,5.0,6 mm, windings 3-4 and 5-6 each with 180 turns of wire with a diameter of 0,15 ... 0,23 mm (PEL or PEV wire). In this case, the primary winding (1-2) is located between the two secondary, i.e. first winding 3-4 is wound, and then 1-2 and 5-6. When connecting the transformer windings, it is important to observe the phasing shown in the diagram. Improper phasing will not damage the circuit, but it will not work properly. When assembling, the following parts were used: a tuned resistor R2 - SDR-19a, fixed resistors R7 and R8 of the C5-16M type for 1 W, the rest can be of any type; electrolytic capacitors C1 - K50-35 for 25 V, C2 - K53-1A for 16 V, C6 - K50-29V for 450 V, and the rest of the K10-17 type. Transistor VT1 is mounted on a small (by the size of the board) radiator made of duralumin profile. Setting up the circuit consists in checking the correct phrasing of the connection of the secondary winding using an oscilloscope, as well as setting the desired frequency with resistor R4. Resistor R2 sets the output voltage at the sockets XS1 when the load is on. The above converter circuit is designed to work with a known load power (6 ... 30 W - permanently connected). At idle, the voltage at the output of the circuit can reach 400 V, which is not acceptable for all devices, as it can damage them due to insulation breakdown. If the converter is supposed to be used in operation with a load of different power, which is also switched on during the operation of the converter, then it is necessary to remove the voltage feedback signal from the output. A variant of such a scheme is shown in Fig. 4.14. This not only allows you to limit the output voltage of the circuit at idle to 245 V, but also reduces the power consumption in this mode by about 10 times (Ipotr=0,19 A; P=2,28 W; Uh=245 V).
Transformer T1 has the same magnetic circuit and winding data as in the circuit (Fig. 4.10), but contains an additional winding (7-4) - 14 turns of PELSHO wire with a diameter of 0.12.0.18 mm (it is wound last). The remaining windings are made in the same way as in the transformer described above. For the manufacture of a pulse transformer, you can also use square cores of the series. KV12 from M2500NM ferrite - the number of turns in the windings in this case will not change. To replace armored magnetic cores (B) with more modern square ones (KB), you can use Table. 4.3. Table 4.3. Recommended options for replacing the magnetic circuit
The voltage feedback signal from the winding 7-8 through the diode is fed to the input (2) of the microcircuit, which allows you to more accurately maintain the output voltage in a given range, as well as provide galvanic isolation between the primary and output circuits. The parameters of such a converter, depending on the supply voltage, are given in Table. 4.4. Table 4.4. Circuit parameters when the supply voltage changes
It is possible to increase the efficiency of the described converters a little more if the pulse transformers are fixed on the board with a dielectric screw or heat-resistant glue. A variant of the printed circuit board topology for assembling the circuit is shown in fig. 4.15.
With the help of such a converter, it is possible to power electric shavers "Agidel", "Kharkov" and a number of other devices from the on-board network of the car. Author: Shelestov I.P.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Renewable energy sources will become more popular than natural gas ▪ The deadly danger of ordinary dust
▪ site section Welding equipment. Article selection ▪ article Victory has a thousand fathers, but defeat is always an orphan. Popular expression ▪ article How long has weaving existed? Detailed answer ▪ article Senior Research Fellow. Job description ▪ article Stabilizer for table lamp. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese






 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: