
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Automatic device for charging and restoring batteries. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
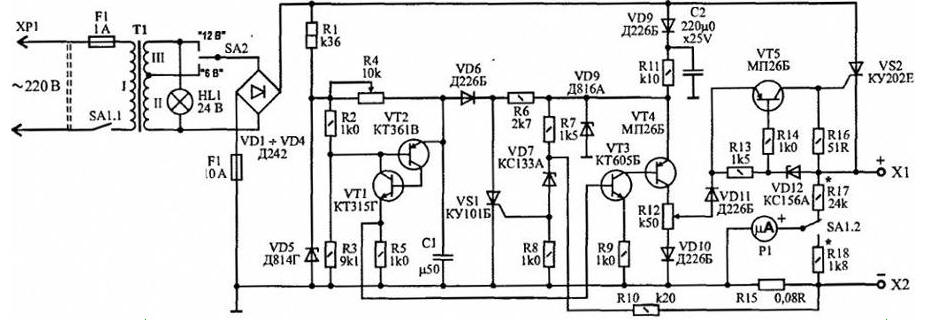
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells The described charger allows you to restore sulfated batteries in automatic mode, or to carry out the formation and preventive processing of serviceable ones. The charging current is switched off automatically when the voltage at the battery terminals reaches 14,1...14,2 V. The comparison of the battery voltage with the reference voltage occurs in the absence of the charging current, which allows the battery to be charged to full capacity. The charging current is continuously adjustable from 0 to 10 A. The device has protection against accidental short circuits of output jacks X1 and X2. The device consists of the following main components:
Operation of the device When the network is turned on with the SA1 toggle switch, the voltage from the rectifier output is supplied to the phase-pulse generator (VT1, VT2), the pulses of which are fed to the pulse shaper (VT3, VT4). At the same time, pulses with a stable amplitude are formed at its output, independent of the phase of the generator pulse. The amplitude of the pulses is set when setting the variable resistor R12. The comparison unit (VT5, VD12) is designed for stable operation of the VS2 thyristor regardless of the ambient temperature, as well as for narrowing the limits of the automatic shutdown operation voltage. When the voltage of the rechargeable battery reaches 14,1 ... 14,2 V, the Zener diode VD12 closes and the thyristor VS2 stops passing the charging current. In the event of a short circuit of the output sockets or incorrect connection of the poles of the battery being charged, the voltage across the resistor RI5 increases, which causes the opening of the zener diode VD7 and the thyristor VS1. The thyristor, in turn, shunts the capacitor C1 of the phase-pulse generator. In this case, the supply of control pulses to the thyristor VS2 stops and the charging current drops to zero. To restore the charging current, it is necessary to open and close the contacts of the SA1 toggle switch again. The VD10 diode protects the device from incorrect connection of the battery poles, and the VD11 diode protects it from spontaneous discharge. In the event of a mains failure, the measuring device P1 indicates the voltage value of the connected battery. The six-volt batteries are charged when the SA2 switch is set to the "6 V" position. The desulfation mode is set as follows. A rechargeable battery with a voltage Ua of at least 12,2 V and an appropriate specific gravity of the electrolyte is connected to the output terminals of the device. The charging current I is set at the position of the variable resistor knob R4 at the first third of the scale. Charging pulses with a duration of 1/3 half-cycle of the mains voltage are best set using an oscilloscope. Next, the resistance of the discharge resistor Rp is determined; which is connected to the output of the device in parallel with the battery: Rp=10Ua/I3, where Ua is the battery voltage (V), h is the charging current (A). Resistor Rp must be at least 15 watts. The battery is charged until the charging current is automatically turned off. Do this after eliminating the cause of plate sulfation. Device setup Establishing a short-circuit protection unit is reduced to installing a voltage of 7 V on the cathode of the Zener diode VD2,5 by selecting a resistor R10. The charging current is set to about 3 A. Setting the voltage value at which the charging current is automatically turned off is carried out as follows. From the control thyristor VS2, a wire is soldered to it from the connection point of the transistor VT5 and resistor R16. Then, a stabilized voltage source of 14,2 V is connected to the output terminals of the device and a sharp decrease in the voltage at the collector of the transistor VT12 is achieved with a variable resistor R5, after which the connection with the control electrode of the thyristor VS2 is restored. Resistors R17, R18 are selected depending on the microammeter used and the selected scale for measuring voltage and current. Starting to test the device, a load resistor with a resistance of 25 - 50 Ohm with a power of 10 ... 20 W is connected to the output terminals. Turn on the power with the SA1 toggle switch and measure the voltage at the load at different positions of the variable resistor R4 slider. A smooth change in voltage indicates the normal operation of the device. Details Resistor R15 is made of four 0,8 mm manganin wires twisted together, the length of which, with a resistance of 0,08 ohms, is about 200 mm. The twisted wire is wound on a porcelain sleeve with a diameter of 20 mm from an unusable wire resistor, with a small gap between the turns. The magnetic circuit of the network transformer T1 - type PL 27x40x58. The transformer windings contain: I - 674 turns of PEV-2 wire 0,7; II - 48 turns of wire PEV-2 1,8; III - 20 turns of PEV-2 1,8. Resistors R4 and R12 type. SP2-1, R1 -MLT-1, the rest - MLT-0,25. Capacitors: C1 - K73P-3; C2 - K50-29. Measuring device P1 - microammeter type M-592 for a current of 50 μA. Signal lamp HL1-KM24-105. Author: Shelestov I.P.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Music server on ARM processor ▪ Noctua Cooling Systems with Active Noise Canceling Technology ▪ New chipset for high-definition color television ▪ Gut bacteria can affect mood ▪ Home appliances controlled via the Internet
▪ site section Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers. Article selection ▪ article The spilled sea. Popular expression ▪ article Ship electrician. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ article Useful thread. Focus secret
Comments on the article: Tahir The comparison node on the VD12 zener diode and the VT5 transistor did not work for me. Is there an error in the circuit? Andrei In reality, the comparison node on VT5 and VD12 does not work at all. On an active load, everything is regulated, but no current goes to the battery. This node is not working!!! Viktor Has anyone set up automatic shutdown? maybe the zener diode is not connected right? Boris I have the same! Can use another scheme to disable? Alexander I can’t start the t1 t2 generator (I’m doing it for the second time), about twenty years ago. at random, replaced d11 with a conder, from P10 and d12 to + out d226 and p5k, cathode to +, WORKED! stabilitron) I can’t set up a new board. To help the radio amateur release 4 page 5 M GAZIZOV Peter I assembled this device but it does not work, the parts are all working. I would like to know how the resistor R12 will affect the voltage on the collector of the transistor VT5 if there is a D11 diode in front of the resistor that will not let the positive potential to the resistor pass? Gennady When T4 opens, resistor R12 starts to get very hot. Maybe he should be in someone, and not in ohm? Gennady Does anyone have a resistor R12? Maybe there should be com and not om? Node T5 is down. a guest Who has earned a comparison unit share information.
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: