Two-level neon signaling device. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Indicators, sensors, detectors
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
In network devices, a light signaling device is often used, consisting of a neon lamp and a current-limiting resistor. Such a signaling device is usually turned on at the input of the device or after the switch. But in the first case, the lamp indicates the presence of mains voltage, regardless of the position of the power switch, in the second case, when it is closed.
A signaling device with two gradations of brightness of the lamp glow is more informative (the lower glow of the lamp corresponds to the open position of the switch, the larger glow corresponds to the closed position). This allows not only to determine the operating position of the switch, but also to find the device connected to the network in the dark. One of these schemes is shown in Fig.1.
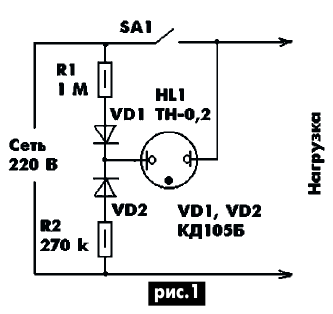
When the SA1 power switch is open, the mains voltage is supplied to the HL1 lamp through the resistor R1, the VD1 diode and the load. The R2VD2 circuit practically does not shunt a neon lamp. When the power switch is closed, the HL1 lamp is powered through the elements R2, VD2, and the R1VD1 circuit, being connected in parallel to the neon lamp, does not shunt it. Since the value of the resistor R2 is several times less than that of R1, the neon lamp in the second mode shines brighter.
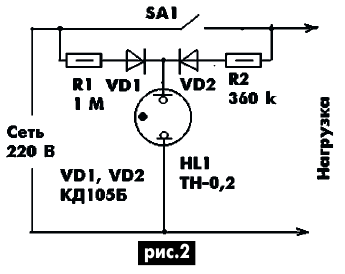
A feature of the circuit shown in Fig. 2 is that when the SA1 switch is open, the neon lamp is powered by a half-wave voltage through the R1VD1 circuit, and when the switch is on, it is fed by a full-wave voltage through both circuits (R1VD1 and R2VD2), so the neon lamp flashes brighter. The circuit can be simplified by removing the diodes and slightly changing the resistance of the resistors.
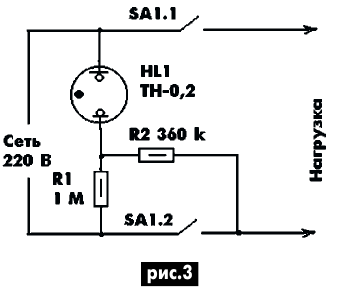
If the device has a paired mains switch that opens both power wires, then the circuit becomes simpler (Fig. 3). Here, the different brightness of the glow of a neon lamp is provided by turning it on through resistors of different ratings.
Very convenient indicator with two neon lamps. The device, the circuit of which is shown in Fig. 4, is intended for use with a single-pole switch. When the switch is open, the neon lamp HL1 shines, the circuit of which is closed through the resistor R1 and the load. When SA1 is closed, the neon lamp HL1 goes out, and HL2 lights up.

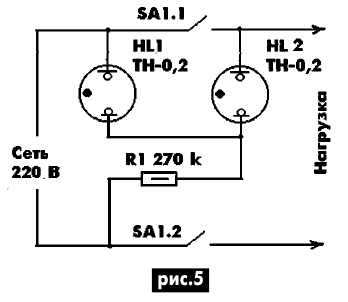
In devices with two-pole switches (Fig. 5), such a signaling device can be assembled differently. When the switch is open, the neon lamp HL1 shines, which is powered through the resistor R1. When the switch is turned on, a parallel connection of neon lamps is formed, while one of them goes out. It is necessary to choose the lamps so that HL1 goes out.
Details. Any diodes with a reverse voltage of at least 300 V (D226B, KD102B, etc.). Resistors type MLT-0,25. In the case of using neon lamps from starters and other devices, the resistor values \uXNUMXb\uXNUMXbmay be different.
Author: R. Kushchik
 See other articles Section Indicators, sensors, detectors.
See other articles Section Indicators, sensors, detectors.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Microwaves for drugs
11.06.2013
It turns out that microwave radiation, familiar to us from home microwave ovens and used to heat food, can be useful for the pharmaceutical industry. Researchers from the University of Bradford (UK) have found that the use of microwaves can provide a fast and environmentally friendly way to produce medicines.
Microwave radiation, as first proven by scientists in the UK, can be effectively used for co-crystallization, a process that creates single crystals built from two compounds. Drugs obtained in this way can outperform their competitors in terms of shelf life, water solubility and, importantly, absorption into the blood, that is, fewer doses will be needed to achieve the desired effect.
As an example, scientists used caffeine and maleic acid. These substances were not taken by chance - they have different degrees of solubility, and this often creates problems in the manufacture of drugs, forcing the use of a large amount of not always safe solvents.
During an experiment using microwaves, the researchers were able to achieve 100% crystallization in just one minute. At the same time, as a special achievement, it is noted that the amount of solvents used was minimal, which is safe for the environment, in contrast to traditional methods for the production of pharmaceutical products.
Best of all during the experiment, such solvents as water and methanol showed themselves - they transfer heat from microwave radiation most efficiently, and acetone, ethyl acetate and toluene did not show themselves in the best way.
So far, the experiment on cocrystallization using microwaves has been carried out only in laboratory conditions, but the curators of the study are confident that the procedure can be repeated on an industrial scale and completely change the pharmaceutical production process. It is microwave radiation that should be considered as one of the promising ways to create cocrystals with minimal use of unsafe solvents.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ see the wind
▪ Water found on distant planets
▪ Pocket Ultrasound
▪ Discovery made in a pharmacy
▪ New switching regulator
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Electrician's Handbook. Article selection
▪ Apollo article. Popular expression
▪ article Are all monkeys equally smart? Detailed answer
▪ article car painter. Job description
▪ article Doorbell. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article How to make an electromagnet rotate. physical experiment
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese





 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: