
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING A device for removing static charges from the surface of sheet polymeric materials. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Ham Radio Technologies Electrostatic charges on the surface of moving polymer sheet materials (for example, films) create a number of technological interferences, lead to defective products, adversely affect workers, worsen working conditions and create additional dangerous situations. The removal of static charges from the surface of moving polymeric materials is solved in several ways, one of which is the ionization of the air surrounding the polymeric material. One of the sources of air ionization are high-voltage ionizers based on corona discharge, which have a high ionization capacity. This article describes a device for removing static charges, which is designed for continuous non-contact neutralization of static electricity charges on the web of moving polymer sheet materials. A block diagram of a device for removing electrostatic electricity is shown in Fig.1.
Device Specifications:
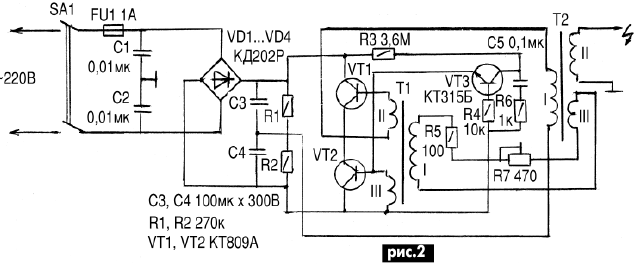
A high voltage of 10...12 kV with a frequency of 15...20 kHz is supplied from the transducer via a high-voltage cable to ionizers located on both sides of the neutralized film at a distance of 25...30 mm. Neutralizers are installed immediately before winding. The needle electrodes of the ionizer, together with the sharp edge of the body, create an electric field with a high density of field lines. The electric field accelerates the electrons in the air to a speed at which the energy of the latter is sufficient to split air molecules, especially oxygen. This produces both positive and negative ions. The spatial cloud of these ions recombines with the charge of the neutralized material. If the charge has a high potential (of the order of 1 kV and higher), then it can flow onto the grounded body of the ionizer through ionized air, which is a good conductor. The electrical circuit of a high-voltage converter with a frequency of 15 ... 20 kHz is shown in Fig. 2. The converter is assembled according to the scheme of a half-bridge inverter on transistors VT1 and VT2. It is loaded on the primary winding of the T2 transformer, which galvanically decouples the high voltage from the AC mains. The self-oscillating mode of operation is provided by a voltage feedback circuit, which is taken from the winding III of the transformer T2 and fed to the winding I of the auxiliary transformer T1 and the launch unit assembled on the transistor VT3. After switching on the switch SA1, the capacitor C5 is charged through the resistors R3, R6. When the voltage on it reaches approximately 50 ... 60 V, the VT3 transistor opens like an avalanche and the capacitor is discharged. The current pulse opens the transistor VT2 and starts the converter. After that, the negative half-cycles of the voltage from the base of the transistor VT2 periodically open the transistor VT3, keeping the capacitor C5 discharged. The launch node does not participate in the operation of the device. If, for any reason, the oscillations in the converter stop, then the capacitor C5 begins to charge and the trigger unit generates a pulse that starts the converter. Resistor R7 can change the frequency of the converter. The air ionizer (Fig. 3, where 1 is a high-voltage cable, 2 is a metal clip, 3 is an insulating sleeve, 4 is the metal case of the ionizer, 5 is a brass tube, 6 is metal needles) consists of a body, which is an aluminum or brass tube with a diameter of 30 mm with longitudinal holes. The edges of the holes are countersunk for sharp edges to create a high charge density.
Inside the case, a brass tube with soldered needles passes through the insulators, which are located exactly in the center of the annular holes in the case. A high-voltage cable passes through the inner tube, which together with the tube forms a small capacitor (about 15 pF). A small capacitance limits the amount of charge on the arresters. The ionizer needles are located at a distance of 1...2 mm from the surface of the ionizer body. The length of the ionizer is selected in each case depending on the width of the strip of the processed material. Setting. It is necessary to connect the ionizer to the converter with a high-voltage cable. Then, connect a frequency meter and an oscilloscope to the ends of the winding I of the transformer T1. The power is turned on and after the generation occurs, its frequency is estimated and, observing the shape and amplitude of the oscillations, the optimal frequency is set with resistor R7. Details. Transistors VT1 and VT2 type KT809A can be replaced by KT812A. They must be installed on radiators with an area of at least 50 cm2. Capacitors C1 and C2 type K73-17; C3 and C4 type K50-12; C5 type KM-6. Transformer T1 is wound on a 2000NN ferrite ring with dimensions K10Ch6Ch5. The primary winding contains 50 turns, the second and third windings - 8 turns each with PELSHO-0,25 wire. The T2 transformer is wound on an NMS2000 ferrite core from a TVS-110L line transformer. Windings I and III are wound with PELSHO-0,33 wire and contain 90 and 5 turns, respectively. The high-voltage coil of a horizontal transformer is used as a secondary high-voltage winding. Author: V.F. Yakovlev
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ Climate change causes bees to deform ▪ Cheap ICs - Signal Generators ▪ USB keys for accessing sites ▪ A new way to discover coral reefs ▪ Boat jet engine on outboard water
▪ section of the site Voltage stabilizers. Article selection ▪ article Don't Touch My Blueprints! Popular expression ▪ article What color is your brain? Detailed answer ▪ article Mint penny. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article The riddle of the torn poster. Focus Secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: