Digital power regulator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Regulators of current, voltage, power
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
This device is designed for phase power control in three-phase electrothermal installations. The permissible load power primarily depends on the power of the switching elements of the controller. With no less success, it can work in single-phase networks, as well as with a load of lower power. The peculiarity of the controller is that the value of the control angle can be set digitally; in other words, the microprocessor can control the load power.
The regulator uses a pulse method of regulation by switching elements - symmetrical thyristors. The phase regulation time determines the number of digits in the counter of the control unit and the period of the mains voltage. The block diagram of the three-phase version of the regulator is shown in Fig.1.
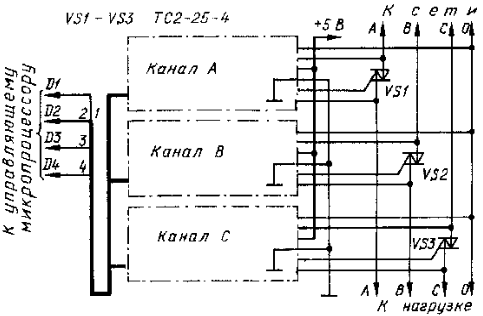
Ris.1
The digital control code from the control microprocessor is fed to the input of three identical control nodes - channels A, B and C. The phase information necessary for the operation of each channel comes from a three-phase load power supply network. Each channel generates a control signal for its triac. The channel circuits are powered by a separate stabilized voltage source of 5 V.
A schematic diagram of one of the channels is shown in Fig.2. The sinusoidal phase voltage through the resistor R1 is supplied to the synchronization node, made on the dual optocoupler U1.

Fig.2 (click to enlarge)
With a positive half-wave, the current flows through the LED of the optocoupler U1.1 and the transistor of this optocoupler is open, therefore, the signal level is low at the inputs of the logic element DD1.1. With a negative half-wave, the transistor of the optocoupler U1.2 is open and the inputs of the element DD1.1 are also low.
But at the moments when the mains voltage passes through zero, both LEDs are off, the transistors of the optocouplers are closed, and level 1.1 appears at the inputs of the DD1 element for short periods of time. Rectangular sync pulses are formed at the output of this element at the moments when the phase mains voltage is zero .
Synchronization pulses are fed simultaneously to the write enable input PE counter DD2, to one of the inputs of the RS-trigger, assembled on the elements DD3.1, DD3.2, and to the control input of the pulse generator (to one of the inputs of the element DD1.3). When a low-level voltage arrives at the PE input of the counter DD2, the code previously recorded via the parallel inputs D1-D4 of the counter is loaded into it regardless of the signals at the clock inputs, i.e., the parallel download operation is asynchronous.
initial position at the output >=15 counter high level. If the count has reached its maximum, then with the arrival of the next negative clock edge at the input +1 of the counter, a level of 0 will appear at its output. Thus, low-level pulses are received at the inputs of the RS-trigger DD3.1, DD3.2: a clock pulse from the logic element DD1.1. 2 and the output pulse of the counter DD1, shifted with respect to the clock pulse by a time determined by the digital code on the parallel inputs D4-DXNUMX of the counter.
At the output of the RS-flip-flop, a high-level signal appears, allowing the passage of the generator pulses to the output of the match element DD4.1. This element generates bursts of short pulses, which are fed through the pulse transformer T1 to the control transition of the channel triac and open it. The pulse transformer allows galvanically decoupling the channel circuits from the mains.
The current consumed by all three channels from a stabilized voltage source of 5 V is about 100 mA.
The pulse generator is made on the logic elements DD1.2-DD1.4. The frequency fg of the generator pulses is selected in accordance with the dependence fg=2Fc(2n-1), Hz, where Fc is the mains frequency, Hz; n is the number of digits of the counter. For the case under consideration, fg=2*50*(24-1)=1500 Hz.
Pulse transformer T1 - serial, MIT-4, having three identical windings of 100 turns.
Establishing a power regulator consists in setting the required frequency of the generator.
 See other articles Section Regulators of current, voltage, power.
See other articles Section Regulators of current, voltage, power.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Breakthrough in limb regeneration
09.03.2019
Scientists from Tufts University (USA) have uncovered the genetic mechanisms that explain why blocking electrical signals in the body of flatworms sometimes leads to the fact that they grow an extra head instead of a tail. Their study will help restore people's ability to regenerate limbs.
Three years ago, scientists found that the process of head regeneration in planarian worms is controlled not only by genes, but also by electrical signals exchanged between the cells of these invertebrates when growing a lost tail or front part of the body.
By studying this process, the team learned to make the worms grow alien heads with a completely different brain architecture, using electrical signals recorded from observing the head growth of other planarian species.
Subsequently, scientists tried to go further and decided to grow a worm with two heads and no tail. A year ago, they managed to solve this problem by cutting several dozen planarians into three parts, separating their heads and tails, and treating these “stumps” with octanol alcohol, which blocks the transmission of electrical signals between cells.
The successful completion of these experiments made us think about what plays the primary role in this process - electrical signals or genes. It is quite possible that the former may not orchestrate regeneration, but simply reflect changes in the activity of those DNA regions that are responsible for restoring a lost tail or head.
To answer this question, scientists conducted another series of similar experiments. They cut several planarians into pieces and watched how the activity level of certain genes associated with tail and head growth "programs" changed in the first hours after the operation. In parallel, they observed fluctuations in the electrical potential of cells located at the edge of the wound.
As it turned out, differences in the voltage on cell membranes in different parts of the wound appeared long before the level of activity of the Wnt, notum, and other DNA regions that are directly responsible for the formation of new organs and limbs changed. This suggests that it was the electrical signals that "conducted" the genes, and not vice versa.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Eating cheese can help you lose weight
▪ V2V technologies for road safety
▪ JUICE space probe
▪ Causes of senile smell
▪ Mornsun LD/R2 ultra-compact power supplies
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Car. Article selection
▪ article The sun rises and sets. Popular expression
▪ article How much wood do we currently consume? Detailed answer
▪ article Maintenance of workshop electrical equipment. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Chinese cement Chio-Liao. Simple recipes and tips
▪ article Small-sized three-element antenna. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: