
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Voltage converter 12/220 volts 100 watts. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
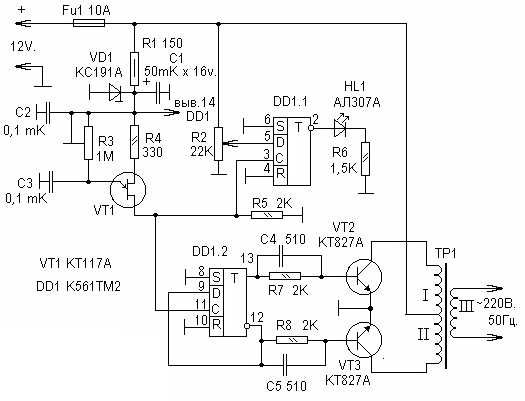
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters The device is relevant for owners of yet non-electrified garden houses, garages, where the only source of electricity can be a car battery. To solve this problem, a converter was developed (see diagram), which makes it possible to power many household electrical appliances with a power of up to 100 watts from a battery.
The master oscillator of the converter is assembled on a unijunction transistor VT1, resistors R3-R5 and capacitor C3. The frequency of the pulses generated by it, equal to 100 Hz, is divided by the D-trigger DD1.2 by 2. In this case, mutually inverse pulses are formed at the outputs of the trigger, following with a frequency of 50 Hz. They control the key transistors VT2 and VT3, connected according to the push-pull power amplifier circuit. The load of the transistors of this cascade is the transformer T1, which increases the pulse voltage of the stabilizer to 220V. The supply voltage is supplied to the collectors of the transistors of the output stage of the converter through the corresponding halves of the primary winding of the transformer T1, and to the master oscillator and the DD1 microcircuit through the parametric voltage regulator R1VD1. Together with capacitor C1, the stabilizer eliminates the influence of key transistors on the operation of other elements of the device. Capacitors C4 and C5 speed up the process of switching key transistors, thereby facilitating their operation. Trigger DD1.1, input D of which is connected (through resistor R2) to the positive conductor of the power source, and input C to the output of the master oscillator, serves to monitor the battery voltage and signal its discharge to the level set by resistor R2. The essence of the operation of this node of the device is as follows. With a fully charged battery at the D-input of the trigger DD1.1, the voltage is above the switching threshold, the inverse output is logic 0, so the HL1 LED is off. As soon as the battery voltage is less than the allowable one, this trigger will switch to the zero state along the edge of the master oscillator pulse at input C and the HL1 LED will light up, signaling an unacceptable battery operation mode. Mounting of the transducer is arbitrary. Resistor R1 - MLT-0,5, other fixed resistors - MLT-0,125. Variable resistor R2 - SP-1, trimmer R3 - SPZ-16 or any other similar. Capacitor C1 - oxide K53-1; capacitors C2 - C5 - KM-5. Capacitor C2 should be installed directly on the power pins of the microcircuit. We will replace the KS191A (VD1) zener diode with any other one with a stabilization voltage of 8 ... 9 V. Transistors VT2 and VT3 - any of the KT827 series, with the highest possible static current transfer coefficient of the base, they are installed on heat sinks with a surface area of at least 300 cm1 . Transformer T27 is made on the PLM 40-58-15 magnetic circuit. Windings I and II contain 2 turns of wire PBD-2 or PSD-704, winding III - 2 turns of wire PEV-0,64 XNUMX. Starting to establish the device, the positive conductor of the power source is disconnected from the connection point of the windings I and II of the transformer T1 and, using an oscilloscope, check the frequency and amplitude of the pulses at the bases of transistors VT2, VT3. The amplitude of the pulses should be about 2 V, and their repetition rate, equal to 50 Hz, is set by resistor R3. Then set up the voltage control node, assembled on the trigger DD1.1. To do this, the power supply voltage is reduced to 10 ... 10,5 V and the resistor R2 achieves a continuous glow of the HL1 LED. Next, the connection of the positive conductor of the power source with the midpoint of the primary winding of the output transformer is restored and the operation of the converter is checked with a fully charged battery. The described converter was tested in conjunction with various loads with a power of 80 ... 100 V. In particular, it was used to power a small-sized drilling machine, a submersible water pump in a garden plot. At the same time, the voltage at the output of the converter did not decrease to more than 210 V, and the current consumed by it did not exceed 10 A. The consumed current at idle is no more than 1 A. The converter is also suitable for powering household sound-reproducing equipment, if it is supplemented with a filter that smoothes the squareness of the output voltage pulses. Author: V. Shangareev; Publication: cxem.net
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Link between climate and crime found ▪ Floating wind farm Hywind Tampen
▪ section of the website Basics of First Medical Aid (BFA). Selection of articles ▪ Aesop article. Famous aphorisms ▪ article When was the cow domesticated? Detailed answer ▪ article Loudspeaker impedance meter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article Water turns into... blood. Focus secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: