 Free technical library
Free technical library
Some Applications of the Type 741 Operational Amplifier. Encyclopedia of Radio Electronics and Electrical Engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Radio amateur designer
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The widely used operational amplifier (op-amp) of the 741(140UD7) type has a large common-mode noise suppression ratio, which makes it possible to implement a variable-gain amplifier and even an analog switch on its basis at low cost. The gain of the op-amp can be easily adjusted by changing the ratio between the signals arriving at its inputs. In the case of equal signals at the inputs, they are suppressed as common mode noise, and the output voltage is zero. When the signal at one input is greater than at the other, it is amplified.
In the variable gain amplifier circuit (a), the resistors R1 and R2 are chosen as usual, based on the given input resistance (in this case f1/2) and the gain (-R2/R1). By changing the resistance of the feedback resistor R2, you can achieve maximum attenuation of the signal at the maximum resistance of the resistor R3 (R3 = R2), which regulates the gain. In practice, when adjusting the control resistor from maximum to zero, the gain changes from zero to -R2/R1 without shifting the DC output level.
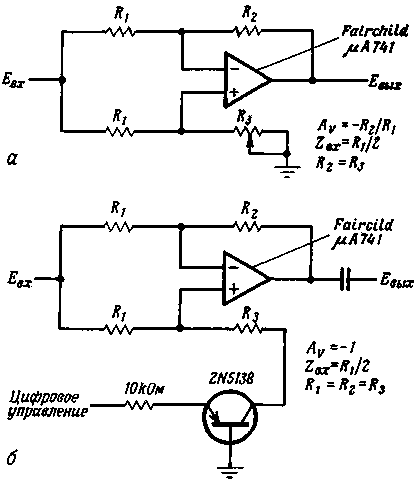
This circuit can also be used as an analog switch (b). In this case, however, there are the following restrictions: mandatory capacitive coupling at the output, input signal swing no more than 1,2, and unity op amp gain (R1=R2=R3). Under these conditions, the circuit works like an ideal analog switch.
When a logic 1 level (2,4-4 V) is applied to the input of the digital control circuit, the transistor saturates and grounds the resistor R3, as a result of which the signal is attenuated by 70-90 dB. When the transistor is turned on, the potential at the non-inverting input of the op-amp becomes 0,6 V, causing a corresponding voltage of 0,6 V DC at the output, and therefore a transition capacitor is required.
When a logic zero (ground level) is received, the transistor turns off, as a result of which the non-inverting input of the op-amp is ungrounded, and the signal passes through the amplifier. If the positive voltage of the control signal is sufficient to open the base-collector junction, then positive spikes seep into the output signal.
Author: Beach McGraw-Hill Center of Excellence (Washington, DC); Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Radio amateur designer.
See other articles Section Radio amateur designer.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive 12W net power wireless power IC
10.01.2015
Toshiba introduced the TC7765WBG and TB6865AFG Enhanced Version chips, which perform the functions of a receiver and transmitter in wireless power systems that comply with the Qi LP 1.1 specification. The feature of this chipset is high power - about 10W. Evaluation samples of the TC7765WBG and TB6865AFG Enhanced Version should appear at the end of this month, and the manufacturer expects to start serial deliveries in June this year.
The TC7765WBG implements control functions in hardware, which Toshiba says eliminates the need for software implementation for wireless charging system developers. The TB6865AFG Enhanced Version transmitter is controlled by an integrated ARM Cortex-M3 core.
The transmitter is designed for an input voltage of 19 V. The receiver output voltage is 7-12 V, the maximum output power is 12 W. Applications for the chipset include smartphones, tablets and mobile device accessories.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Profits from the sale of World of Warcraft servers will go to charity
▪ New switching regulator
▪ Super Yielding Rice
▪ New electronics will withstand radiation and heat
▪ Reality alteration and false memory
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Power supplies. Article selection
▪ Quanta article. History and essence of scientific discovery
▪ article How are infrared and ultraviolet radiations detected that are inaccessible to the eye? Detailed answer
▪ article Linden small-leaved. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Spiral antenna. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Flying with a mirror. physical experiment
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: