
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING SHI motor power regulator
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers In recent years, the amateur assembly of electrified vehicles and the conversion of cars to convert them to electric traction has become popular. On this path, enthusiasts expect a lot of difficulties. So, for example, one of the complex and expensive components of such vehicles - an electric motor control device - will most likely have to be developed and manufactured independently. It remains to add that there is very little practical literature on the topic of high current control. The article below should help in solving a number of issues in this area of design. In the development of the device described below, the experience of one of the pioneers of the electric vehicle industry [1] was used. The device will help electrify toys, scooters, powerful fans, create electric drives up to 5 kW with voltage up to 150 V. The power of the SHI regulator presented to the attention of readers allows you to drive the electric motor of a vehicle of the Zhiguli weight category -classic. The device scheme allows an increase in the power of controlled devices by replacing radio elements with more powerful ones in compliance with the recommendations outlined in the article.
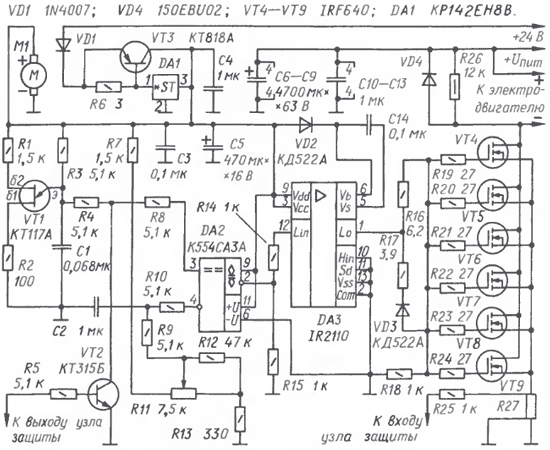
The regulator, the circuit of which is shown in fig. 1, consists of four nodes: a master oscillator based on a VT1 transistor, a control pulse shaper assembled on DA2, DA3 microcircuits, a powerful current switch based on VT4-VT9 transistors, a power supply unit VD1, R6, VT3, DA1. The regulator is powered by two sources: one - with a voltage of 20 to 30 V to power the low-current part of the device, the second - up to 150 V to power the load. The device has a signal input for blocking the regulator and an output to an external protection unit that generates this signal. The traction motor is connected in series with the current switch. The frequency-setting element of the regulator is a sawtooth pulse generator on a transistor VT1. The frequency of 3 ... 4 kHz is determined by the R3C1 circuit. The pulses are fed to the non-inverting input of the comparator DA2, and the inverting input is energized from the engine of the resistor R11, which controls the speed of the rotor of the electric motor. As this resistor, a throttle position sensor from VAZ cars of the tenth series was used. The sensor resistance varies from 0 to 7,5 kOhm. The sensor has a built-in 1,5 kΩ resistor in the slider circuit. In addition to it, resistor R9 and capacitor C2 are added to this circuit in the SHI regulator to reduce the influence of the "bounce" of the engine contact and increase the smoothness of regulation. During operation on a particular equipment, it may be necessary to select the elements of this chain to obtain the desired process dynamics. The criterion for satisfactory dynamics in the case of an electric vehicle is smooth acceleration (when the resistor R11 slider moves to the left according to the scheme) and braking (the same to the right) of the car, as well as the value of the maximum current through the electric motor.
On fig. 2 at the top shows in a simplified way the pulses Ug of the generator and the voltage URd taken from the engine of the resistor R11. As the practical experience of using the regulator shows, to speed up the process of braking the electric motor, it is advisable to shunt the resistor R9 with a KD522A diode, connecting it with an anode to the connection point of the resistor R9 and capacitor C2 to accelerate the discharge of this capacitor. Resistor R12 serves to prevent an emergency in case of accidental disconnection of resistor R11 or breakage of wires connecting it to the regulator. At the output of the comparator DA2, we obtain a sequence of pulses Uynp (Fig. 2) with a duration set by the resistor R11. Then the signal is fed to the amplifier-shaper DA3, which generates pulses with a front and a recession with a duration of no more than 120 ns, and then to the gate circuit of a block of powerful field-effect switching transistors VT4-VT9. Resistors R19-R24 equalize the charging current values of the gate capacitance of the transistors. The charging current pulse can reach hundreds of milliamps. When the transistors are closed, the discharge current flows through the resistors R19-R24, the resistor R16, the VD3R17 circuit and the output of the DA3 amplifier. The closing speed of transistors is important no less than the opening speed - the degree of their heating depends on this. When setting up the device, it is necessary to control the voltage of the control pulses at the gate of powerful transistors - it should not be less than 10 V - to prevent their transition to a linear mode. The load supply voltage depends on the characteristics of the electric motor used, but should not exceed the nominal drain-source voltage of the transistors. For the IRF640 transistor block, the maximum voltage is 150 V with a total load current of up to 80 A. The nature of the change in power Red of the electric motor from a change in voltage on the engine of the control resistor R11 is shown in a simplified way in fig. 2. The initial position of the engine of this resistor is the extreme right according to the scheme. In this case, there are no control pulses, field-effect transistors VT4-VT9 are closed, the load is de-energized. To power the low-current part of the device, it is convenient to use part of the load supply voltage, especially if the electric motor is powered by a battery. But this method requires careful testing of the regulator before installation on the machine, since the resistance of the common power wire can adversely affect the quality of the regulator as a whole. When operating the device, it is desirable to provide protection for transistors from linear mode and overcurrent. The transition of transistors from switching to amplifying mode leads to their rapid overheating and subsequent destruction. The transistors used in the regulator are capable of withstanding overloads and short circuits in the load for tens of microseconds, no longer. Therefore, in order to save the regulator even in emergency situations, it is advisable to use a protection device. For its connection, two outputs are provided - the upper shunt terminal R27 in the load circuit (with a limiting resistor R25) and the input of the blocking device (VT2) of the pulse shaper. The protection node must generate a signal that keeps the transistor VT2 open until the cause of the accident is eliminated, and control the current in the load power circuit, protecting powerful transistors from switching to linear mode and overheating. The protection host device is not covered in this article. In the simplest control devices that do not require protection or when the likelihood of an emergency is small, the transistor VT2, resistors R5 and R25 and the shunt R27 can be omitted. Powerful transistors are protected by the VD4 diode from voltage surges when the load circuit breaks. Its maximum reverse voltage must not be less than the supply voltage, and its forward current must not be less than the rated current of the motor. Domestic diodes DCH151-125 or imported 150EBU02 are suitable here. When the device is powered from a battery, it should be blocked with capacitors C6-C13 with a total capacity of 10 microfarads per kilowatt of load power in order to reduce the destructive effect of high-frequency current on the battery. The rated voltage of the capacitors is not less than the battery voltage. The generator, comparator, pulse shaper and fan M1 are powered by a voltage of 15 V from a unit consisting of a DA1 stabilizer and a current amplifier on a VT3 transistor. The transistor and stabilizer must be installed on heat sinks with an effective area of at least 20 cm1. If the device has powerful transistors installed on heat sinks that provide them with the necessary cooling, you can do without the MXNUMX fan.
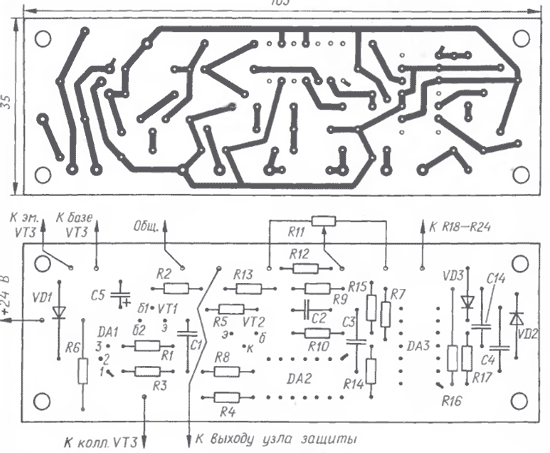
The low-current part of the device is located on the printed circuit board in Fig. 3. Powerful transistors VT4-VT9 are selected for a specific load. In this case, the number of transistors connected to the shaping amplifier DA3 must correspond to its output characteristics [2, 3]. As experience shows, when developing a SHI controller, it is necessary to provide for an overcurrent margin. This is due to the design of the transistors. Despite the declared value of the current, the cross section of the terminals of the transistors does not correspond to it. The voltage drop at the terminals of transistors with a cross section of 1,3 mm2, and, accordingly, the dissipated energy is wastefully large. The current density in the outputs of transistors should not exceed 15...20 A/mm2. The regulator uses IRF640 transistors for a current of 18 A and a voltage of 200 V. The device was also tested with transistors IRF3710 (100 V, 57 A), IRF3205 (55 V, 110 A), IRF3808 (75 V, 140 A) to control the electric motor power 3 kW and supply voltage 48 V. The control signal to the output transistors is recommended to be transmitted over a twisted pair of wires directly to the gate and source [4]. Do not pass the control current of the transistors through the common wire of the device because of the danger of switching interference from the load circuit to the control circuit. In practice, this manifests itself as increased heating of transistors and their unpredictable failure. Even better results are obtained by separating the power sources of a low-current node and a powerful one. The design of a powerful current regulator switch must be given the most attention. The quality of the device as a whole depends on its layout. It is recommended to place powerful transistors VT4-VT9 more compactly, solder large-section conductors (10 ... 20 mm2) to their terminals, and place resistors R18-R24 in close proximity to powerful transistors. Bends of conductors within a power unit are unacceptable, as they form a parasitic inductance. A device assembled from serviceable parts, as a rule, does not require adjustment. It is enough just to make sure that the master oscillator is stable by checking the pulse repetition rate (3 ... 4 kHz) at the emitter of transistor VT1, that the output power control limits are set correctly (select resistors R7, R13 if necessary) and that control pulses are present (with a voltage of at least 10 C) at a common point in the circuit of resistors R18-R24. The output transistors are mounted on a copper heat sink plate 160x60x4 mm in size, cooled by an M1 fan. Without the use of a fan, the heat sink area for each transistor is calculated based on its characteristics and power dissipation. As a cooling fan, you can use a personal computer cooler connected through a pre-selected resistor (not shown in the diagram in Fig. 1) to lower the voltage to 9 ... 12 V. The heat sink can be used as a combined output of the drain of transistors. The battery of capacitors C6-C13 should be mounted in close proximity to the battery, and when used on a vehicle, placed in a separate box to protect it from moisture. Diode VD4 can be placed in any convenient place. When working with a protective device, a ready-made shunt 75ShSM MZ (or 75ShS) is used. Its value is selected based on the load current of the regulator. In the case under consideration, a 100 A shunt was used due to the fact that the device was designed to control the ZDT-31 electric motor for a voltage of 24 V and a current of 80 A. To connect the load, copper wires with a cross section of 8 A per 1 mm2 should be used, suitable, for example , wire from the PVZ series. At the ends of the wires, cable lugs are mounted that correspond to their cross section. In conclusion, a few remarks in case of replacing powerful transistors VT4-VT9. Transistors of the IRF series have a significant gate capacitance - from 1200 pF (for IRF640) to 5310 pF (IRF3808), hence the requirements for resistors R18-R23 and the DA3 amplifier. With an increase in the number of powerful transistors, it may be necessary to replace the IR2110 shaping amplifier with a more powerful one, for example, the LM5110, or add a push-pull transistor power amplifier (a typical IR2110 connection allows such refinement [2]). The current consumed from the amplifier is determined by the total resistance of the R16R18-R24 circuit. The resistance of resistors R19-R24 is calculated as follows. First, the average charging current of the gate capacitance is determined:
where Upit is the power supply voltage of the amplifier DA3, V; C3 - transistor gate capacitance, F; t - transistor opening/closing time, s. Then the resistance of the resistor in the gate circuit is R3=Upit/I3,OM. The gate circuit resistors are best soldered directly to the transistor leads. When choosing the components of the SHI regulator, preference should be given to higher-frequency radio elements. Literature
Author: N. Tokmakov, Syktyvkar; Publication: radioradar.net
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Device for the fight against domestic rodents and insects ▪ A new value for the upper limit of the neutrino mass has been established ▪ In Africa, too, they can build a synchrotron ▪ Smart bed with anti-snoring mechanism
▪ section of the site Interesting facts. Selection of articles ▪ Giant article. Popular expression ▪ What are the specifics of Italy in the XNUMXth-XNUMXth centuries? Detailed answer ▪ article Bodyworker. Job description ▪ article Extractive inks. Simple recipes and tips ▪ article Blue sting for soldering. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Comments on the article: Kostya Do you have a protection circuit?
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: