
|
|
Mixing and branching cascades. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
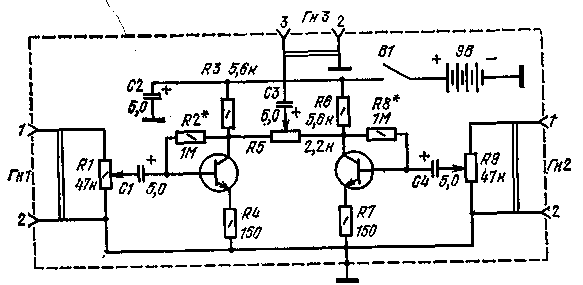
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Audio equipment It is customary to call mixer cascades designed to combine two or more electrical signals into one common signal. Sometimes cascades for this purpose are called summing, since they essentially have an independent addition of the voltages of several signals. Branching stages are called cascades designed to repeat the voltages of the same signal on several independent outputs. In amateur radio practice, such cascades are also called signal multipliers. The cascades mentioned above are widely used in sound recording and playback. Unregulated mixing stage for two inputs Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of a simple summing stage for two inputs, assembled on two bipolar transistors with a common collector load. The input signals are fed to the sockets Gn.1 and Gn2, then to the bases of transistors 77 and T2. The summation of the signals occurs in their common collector load on the resistor R5. The voltage transfer coefficient of each stage is about 0,7. To eliminate the influence of the input resistance of the subsequent ULF, with which this cascade will work, an additional emitter follower on the TK transistor has been introduced. The output total signal is taken from the emitter of the transistor T3 and fed through the capacitor C5 to the output socket GnZ. Power is supplied from a separate battery, but you can use a stabilized ULF power supply with which the cascade will work.
When repeating the design, transistors of the KTZG5G type can be used. The adjustment comes down to selecting, if necessary, the resistances of resistors R.1 and R9 in the base circuits of transistors T1 and T2 to set the collector current of each of them to 0,25 mA. As practice has shown, the input impedance of each input is 1-2 MΩ, the output is about 100 Ω. The coefficient of non-linear distortion is 0,1% at an input voltage of 1 V and 0,5% at an input voltage of 2 V. Mixing stage with two adjustable inputs and output Figure 2 shows a schematic diagram of a simple summing stage for two inputs, in which two transistors and variable resistors are used in the input and output circuits. The presence of variable resistors R1 and R9 allows you to adjust the voltage of the original signals at the inputs of the cascade to create certain effects and prevent overload at the inputs. The variable resistor R5, connected between the collectors of transistors T1 and T2, makes it possible to sum the signals in a variety of ratios. For example, in the right extreme position of its engine, the signal of the right one according to the input scheme is amplified more than the left one, and vice versa. In the middle position of the slider, both signals are amplified approximately the same (10-15 times). The input impedance of each stage is about 40 kOhm, the output resistance is about 4 kOhm. Supply voltage 9 V, current consumption - up to 2 mA.
When repeating, you can use transistors such as KT315V, KT315G. The adjustment comes down to selecting the resistances of resistors R2 and R8, at which the collector currents of transistors T1 and T2 will be approximately 1 mA each. A feature of this cascade is its sensitivity to overloads in the input circuits with fully inserted engines of variable resistors R1 and R9. In this case, the coefficient of non-linear distortion at the stage output reaches 0,5% at an input voltage of 100 mV. Therefore, it is recommended to use a cascade with incompletely inserted sliders of variable resistors R1 and R9. FET mixing stage Figure 3 shows a schematic diagram of a mixing stage designed for use in high-quality ULF. Its main advantage is a large input impedance of both inputs (1 MΩ each), high linearity of the amplitude characteristic. These advantages are due to the use of field-effect transistors T1 and T2 in the cascade. The inputs and output of the cascade are not adjustable. Input sockets Gn1 and Gn2, output - GnZ. The gain of each channel is approximately 3. The maximum input signal voltage at each input is 0.5 V.
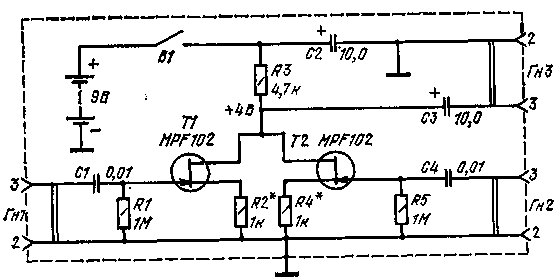
When repeating the design, field-effect transistors of the KP303E or KP303V type can be used. To further improve the quality of the cascade, it is recommended to increase the supply voltage to 15-20 V. If necessary, the gain for one of the inputs can be increased to 10 by reducing the resistance in the source circuit of the transistor of the corresponding cascade (R2 and R4) to 100-300 Ohm . The cascade was originally described in an American amateur radio magazine. Cascade for mixing two stereo signals All the cascades described above are designed to obtain a common signal from two voltages coming from different sources, for example, simultaneously from the output of an electrophone and a microphone or two microphones, a tape recorder and a telephone, etc. The total signal can then be amplified and reproduced by any monophonic ULF with loudspeaker. Here we consider a special cascade that combines both channels. What for? Most often, this is necessary to play a stereo program through a mono electro-acoustic installation, when a stereo player is available, and the amplifier and loudspeaker are mono. And if the ULF input of a monophonic installation is connected to the output of only one of the two channels of the player, then the sound will be inferior. For high-quality playback of stereo programs through mono installations, it is necessary to combine the signals of both channels at the VLF input.
This problem can be solved by any of the cascades described above, but it is still better to do this with the help of a special cascade that has very small non-linear distortions and operates at an increased supply voltage. Figure 4 shows a schematic diagram of a cascade for mixing two stereo channels into one mono channel. As can be seen from Fig.4, the cascade has much in common with the cascade in Fig.1. The difference is in the input circuits of transistors T1 and T2, as well as in the presence of a 1 V zener diode D18. These changes help to reduce the effect of interference due to supply voltage ripple and reduce the possibility of overload at the inputs. The zener diode D1 is replaced by two series-connected zener diodes of the D814B type. Branching stage with three outputs Figure 5 shows a schematic diagram of a branching stage with three outputs, designed for independent connection of up to three consumers to one signal source. In this case, the signal source output is connected to the Gn1 socket, and the consumer inputs are connected to the Gn2-Gn.4 sockets. In practice, radio amateurs rarely use such branching cascades, connecting several consumers to the signal source output at once, for example, when recording from one electric player to the inputs of three tape recorders at the same time. Here, the low input impedance of the load impairs the operation of the preamplifier of the electric player, and in addition, the tape recorders influence each other. When using a cascade according to the scheme of Fig. 5, such mutual influence is not observed. It is made on four field-effect transistors. The cascade on the transistor T1 is connected according to the amplifier circuit with a common source. Transistors T2-T4 are used in decoupling source followers. The gain given by the cascade for each channel is 10-15.
When repeating the design, you can use transistors such as KP102E-KP102L or KP103E-KP103K. If necessary, by disconnecting the capacitor C2, the gain can be reduced several times. Power supply from a battery or a stabilized source with a voltage of 10-20 V. Current consumption 10-12 mA. Literature
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ Clothes are killing the planet ▪ Octospot - action camera for diving enthusiasts ▪ Siemens A65: state employee with polyphony
▪ section of the site Electrical safety, fire safety. Article selection ▪ article Like the sun in a small drop of water. Popular expression ▪ article Which year in Europe was characterized by the absence of summer? Detailed answer ▪ article Hygienic, general and local therapeutic baths. Health care ▪ article Load switch for a sound card. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article Mug of milk. Focus Secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: